 |
|
|
1366 - Tax (ducal
levy) records confirm operations of Den Hoorn (the 'Horn')
brewery in university town (University of Leuven founded 1425)
of Leuven, Belgium; 1708
- Sebastien Artois awarded title of Master Brewer;
June 15, 1717 -
Artois acquired brewery; renamed Brasseries Artois;
1926 - produced
barley beer as annual special Christmas beer, named Stella
(Latin for star); 1987
- second largest brewer in Belgium; merged with Brasseries
Piedboeuf, largest brewer in Belgium, formed Interbrew;
2004 - merged with
Cmpanhia de Bebidas das Amricas (AmBev), created InBev, world's
largest brewer, by volume.
1385 - Giovanni di
Piero Antinori joined the Florentine Winemakers Guild;
1898 - incorporated
as "Fattoria dei Marchesi Lodovico e Piero Antinori";
1900 - Piero
Antinori bought several vineyards in Chianti Classico region,
including 47 hectares at Tignanello;
1924 - Niccolo Antinori (son) made
Chianti containing Bordeaux grape varieties;
1965 - Marquis
Piero Antinori (25th generation) became Managing Director
(President in 1988); 1966
- Piero Antinoro took over; investigated early harvesting of
white grapes, different types of barrique, stainless steel vats,
malolactic fermentation of red wines;
1971 - launched Tignanello (20% Bordeaux
blend), barrique-aged wine from eponymous vineyard aged that
contained Cabernet Sauvignon, Cabernet Franc (ineligible for
Chianti Classico appellation); 1975
- blend contained no white grapes;
1978 - launched 80% Cabernet Solaia, from
neighbouring vineyard; January 1986
- part of investment group (Whitbread, Bollinger) which acquired
Atlas Peak winery in California for $11 million;
1987 - acquired 325
hectares around Badia a Passignano, expanded into Piedmont, set
up joint venture in Btaapti, Hungary;
2007 - revenues of $214 million; 27th
generation.
1445 - Monks in Hoegaarden (province of Flemish Brabant in Belgium,
part of Netherlands at the time) first brewed wheat beer (used
coriander, Curacao orange peel); became known as Belgian-style
wheat beer; 1709 -
12 breweries; 1726
- 36 breweries, over 110 malting houses; end 19th century - 36
breweries in village of only 2,000 inhabitants; 1957
- Tomsin, last wheat beer brewery in Hoegaarden, closed;
1965 - Pierre Celis
(had worked at the Tomsin wheat beer brewery), town milkman,
revived brand; began one Brewing Copper in the dairy where he
worked; named brewery ‘De Kluis’, (‘The Cloister’) in
acknowledgement of first brewery established by monks; 1985
- produced over 75,000 hectolitres/year, brewery destroyed by
fire (rebuilt with help, share in business by Artois brewery);
1987 - acquired by Interbrew
(now Anheuser-Busch InBev); distributed worldwide;
November 9, 1993 -
Interbrew, S.A. registered "Hoegaarden" trademark first used
February 3, 1992 (beer).
June 1, 1495
- First written record of Scotch Whiskey appeared in Exchequer
Rolls of Scotland, Friar John Cor as distiller.
1516 - German
beer purity law (Reinheitsgebot); mandated that beer could
contain only four ingredients: barley, yeast, hops, water;
1987 - struck down by European Union for restricting
trade.
1568
- Antonio Cinzano recognized as property owner of oldest
vermouth-producing house; 1757
- Cinzano family admitted to official body of University of
Master Distillery; March 10, 1914
- Francesco Cinzano & Co. registered "Cinzano" trademark first
used December 1890 (vermouth); 1925
- red and blue logo introduced with new marketing strategy.
1608
- King James I granted Sir Thomas Phillips royal licence to
distil˜uisce beatha (gaelic for 'water of life', or whiskey), in
'the territory of the Rowte' in Co. Antrim (first official
recorded evidence of whiskey-making in area that became
Bushmills); 1743 -
first recorded reference to Old Bushmills Distillery ("in the
hands of smugglers", according to Victorian whisky journalist
Alfred Barnard); 1784
- Old Bushmills Distillery officially registered as company, pot
still became trademark; used 100% malted barley for superior
whiskey; June 4, 1912
- Old Bushmills Distillery Co., Ltd. registered "Old Bushmills"
trademark, first used August 13, 1850, in U.S. (Irish malt
whiskey); 1923 -
distillery acquired by Samuel Wilson Boyd;
2009 - Ireland's oldest working
distillery.strategy.
1691 -
Joannes Nolet began distilling fine spirits in alembic copper
pot still, Distilleerketel #1 (kettle) in Schiedam, Netherlands
(north of Rotterdam); 1902 - opened Nolet
Distillery in Baltimore, MD (lost in 1919 due to Prohibition's
Volstead Act); 1983 - returned to U. S. market;
1990 - introduced Ketel One vodka; 2007
- 10th generation of management.
July 3, 1693
- Governor of the Cape, Simon van der Stel, granted land,
fifteen kilometers south of Stellenbosch, to Henning Hüsing;
named the farm Meerlust to describe sense of pleasure he
obtained from sea breezes that blew inland from False Bay;
January 1757 - acquired by Johannes Albertus Myburgh;
2008 - Hannes Myburgh, eighth generation
owner.
August 4, 1693
- Dom Perignon, Benedictine monk,
invented Champagne.
1695 - Petrus
De Kuyper, his wife Anna Custer, maker of wooden casks for
transporting Dutch gin and beer, established distillery;
1752 - Jan De Kuyper (third son) took over distillery at
Schiedam (leading centre for production of Dutch gin);
1769 - Johannes and Pieter De Kuyper (grandsons) bought
distillery in Rotterdam; February
24, 1914 - John de Kuyper & Son registered "De
Kuyper" trademark fist used 1695 (gin); 1920s - started
distilling liqueur; 1930s - produced almost 20
varieties of liqueurs; 1934 - formed distribution
agreement with National Distillers Products Corp of New York to
sell products in USA, established joint production facility in
New Jersey; 1986 - Jim Beam Brands Co acquired
right to manufacture, market De Kuyper products in USA under
perpetual agreement; 1995 - Queen Beatrix of the
Netherlands bestowed title "Royal", company name changed from
Johannes de Kuyper & Zoon to De Kuyper Royal Distillers; world's
largest and leading producer of liqueur; 11th generation of
family management.
February 20, 1703
- Mount Gay Estate, Barbados, began distilling rum; Mount Gay
Distilleries Ltd. of Barbados; 18th century - William Sandiford
bought, consolidated 280 acre parcel of land, renamed Mount
Gilboa; 1747 -
Mount Gilboa acquired by John Sober; operated the from England
as absentee landlord; 1787
- hired Sir John Gay Alleyne, to manage estate;
1810 - Cumberbatch
Sober (son) renamed plantation Mount Gay (in honour of Sir John
Gay Alleyne); ran property until 1860;
1908 - acquired by Barbadian planter
Aubrey Ward; established Mount Gay Distilleries Limited;
December 27, 1938 -
Baccone, Speed & Jenney, Inc. registered in U. S. "Original
Mount Gay Distillery Mount Gay" trademark first used in November
1936 (rum); 1989 -
majority interest acquired by Remy Cointreau Group; oldest rum
in world.
1706 - Thomas
Twining (31) began selling tea from premises on the Strand in
London (had acquired Tom's Coffee House); one of the first
companies to introduce tea drinking to the public; sold more dry
tea than wet tea; Twinings Gunpowder Green Tea was expensive,
sold for today's equivalent of more than 160 ponds for 100
grams; learned tea trade from Thomas D'Aeth, an East India
Company merchant; 1749 - exporting to America;
1784 - Richard Twining, grandson, persuaded William
Pitt the Younger to pass the Commutation Act, reduced taxes on
tea 119% to 12.5%, effectively ended tea smuggling trade, made
it more widely available to public- retained imports of tea came
to 4,962,000 lbs vs. 16,307,000 lbs. in 1785 as smuggled tea was
imported openly; June 1, 1909
- R. Twining & Co. LD registered "Twinings" trademark first used
1710 (tea, coffee, cocoa, chocolate).
June 13, 1708
- Sebastian Artois awarded title of Master Brewer of Den Horen
(¨the Horn¨); 1717 - acquired Debn Horen, renamed
it Artois Brewery; 1926 - Stella (¨the star¨) beer
introduced; 1987 - Stella Artois merged with
Jean-Theodore Piedboeuf Brewery (brewed Jupiler beer), renamed
Interbrew; 2004 - merged with AmBev, biggest
brewer in world, by volume, renamed InBev.
1730 -
Patrick Murphy (from Greatforth, Ireland) founded house
of Patrick Murphy in Jerez De La Frontera, in province
of Cádiz in autonomous community of Andalusia in
southwestern Spain; 1740
- Jean-Charles Haurie Nebout arrived;
1745 -
began to help in management of Murphy's vineyards;
1762 -
named heir to Murphy's estate (inherited all his
properties, including vineyards in finest areas of
Macharnudo and Carrascal);
1772 - eventually permitted to take part
in all three branches of trade (grower, storekeeper,
shipper); founded new company Juan Haurie y Sobrinos
(Juan Haurie and Nephews, with five nephews; included
wine business, several farms, shops; principal interest
remained in wine, steadily acquired new vineyards);
1794 -
died, capital remained in business, kept undivided as
central trust fund for benefit of five nephews equally);
one nephew was Pierre de Domecq Loustau Lembeye, son of
Haurie's sister Dona Maria; Catherine Lembeye (sister)
had married Jean Domecq;
1816 - their son, Pierre Domecq Lembeye,
enterprising young French aristocrat, member of British
firm Ruskin, Telford & Domecq (1809-1864, importer of
sherry to England, exclusive agent of grand uncle, Juan
Haurie y Sobrinos) arrived in Andalusia with mission to
represent Ireland in prestigious house in London wine
trade; November 1818
- acquired rights to company in exchange for payment of
all outstanding debts; 1822
- founded Casa Pedro Domecq;
1839 - Jean-Pierre Domecq
Lembeye (brother) took over;
1869 - died, Pedro Domecq
Loustau (nephew) took over;
1874 - put Fundador ("Founder"),
first aged brandy in Jerez, on sale;
1894 -
died, Juan Pedro Aladro Domecq headed company;
1914 -
died, widow sold palace and all her shares in the winery
to brothers Domecq Núñez de Villavicencio for life
annuity; 1941
- Pedrro Domecq Rivero reorganized company, formed
collective corporation;
1955 - Jose Ignacio Domecq (patriarch of
last Domecq in the cellar, internationally recognized by
experts as "The Nose" due to his special gift for
tasting, rating wines) initiated distribution of
brandies Domecq in Mexico, Argentina, Colombia,
Venezuela, Brazil; 1980
- shareholders incorporated Group Andalusia
Mora-Figueroa Domecq; 1994
- Group Domecq acquired by British multinational Allied
Lyons; renamed Allied Domecq, one of first worldwide
groups in field of wines and spirits.
March 22, 1733
- Joseph Priestly invented carbonated water (seltzer).
1734 -
Jacques Fourneaux, merchant of champagne wines, established
company; came to be known as Fourneaux-Forest; 1912
- Pierre-Charles Taittinger ran business involved in
distribution, export of champagne with one of his
brothers-in-law; 1932 - Pierre Taittinger took
over Fourneaux-Forest; 1945 - François, third son
of Pierre Taittinger, and two brothers, Jean and Claude, oversaw
period of remarkable growth for champagne house.
1742 - Samuel
Whitbread established first brewery at the Goat Brewhouse;
1750 - moved operations to eastern rim of Georgian
London, established first purpose-built mass-production brewery
in Britain; 1796 - first brewer to exceed annual
production of 200,000 barrels; 1868 - introduced
bottling, became national brand; 1948 - went
public; 1995 - Whitbread Hotel Company acquired
rights to Marriott brand; 2000 - sold beer
company; 2001 - sold pubs, bars business;
2006 - sold 239 Pub Restaurants to M&B; agreed to sell
50% shareholding in Pizza Hut UK Ltd.; 2007 - sold
TGI Friday's business; leading hospitality company, number one
brands in hotels, restaurants, coffee shops.
1743 - Claude
Moët, wine trader descended from old family resident in
Champagne region since 14th century, founded his house in
Epernay, shipped wines to Paris; 19th century -
grandson, Jean-Rémy Moët expanded expanded business, opened
house to foreign markets; succeeded by his son and his
son-in-law, Pierre-Gabriel Chandon de Briailles; company renamed
Moët & Chandon.
1749 -
Giacomo Justerini arrived in London from Bologna; formed
partnership with George Johnson as wine merchants; 1760
- Justerini returned to Italy, King George III bestowed first of
eight Royal Warrants (8 successive monarchs) on company;
1831 - acquired by Alfred Brooks, renamed Justerini &
Brooks, wine merchants and blenders; one of first London spirits
merchants to buy stocks of mature malt whisky, create its own
blend, named Club; June 1779 - J&B whisky range
began with advertisement in Morning Post and Daily Advertiser;
1962 - merged with W. A. Gilbey Ltd., gin maker.
1749 -
William Younger established William Younger Brewery in Leith,
Edinburgh; 1856 - William McEwan established
Fountain Brewery in village of Fountainbridge, Edinburgh;
February 27, 1890 - John Barras, Jr. launched Newcastle
Breweries; 1931 - William Younger merged with
William McEwan, formed Scottish Brewers Ltd.; 1960
- Scottish Brewers merged with Newcastle Breweries, formed
Scottish & Newcastle Breweries Ltd.
1749 - First
known documentation of rum production at Appleton Estate;
1845 - Appleton
Estate acquired from Francis Dickinson family by William Hill;
acquired A. McDowell Nathan, one of Jamaica`s most successful
merchants; 1916 -
acquired by J. Wray and Nephew Ltd. (division of Lindo Brothers
& Co); all Appleton Estate rums produced from single 11,000-acre
estate in Nassau Valley; April 11,
1995 - Rums International, Inc. registered
"Appleton Estate Since 1749 Jamaican Rum" first used in April
1986 (rum); second oldest producer of rum.
May 27, 1755
- Hans Christopher Christiansen installed first municipal water
pumping plant in America at Bethlehem, PA; city supplied from a
70 foot high tank that was filled with water pumped from a
spring through wooden pipes.
1759 - Arthur
Guinness signed 9000-year lease on disused brewery at St James's
Gate in Dublin for initial £100, annual rent
of £45; decided soon after to brew variation of porter
stout popular in London); 1799 -
concentrate solely on production of porter;
1803 - Arthur Guinness II took over ownership,
management of Brewery; 1834 - Glass Tax
repealed, GUINNESS® bottled in glass rather than stoneware;
1850 - Sir Benjamin Lee Guinness (grandson) took over
Brewery; 1862 - introduced GUINNESS® beer label
(buff oval label with harp and Arthur Guinness’s signature);
1868 - Edward Cecil (great grandson) took over; size
of the Brewery doubled; 1876 - Harp registered as
trademark; 1886 - first major brewery
incorporated as public company on London Stock Exchange; largest
brewery in world; 1906 - 3,240
employees ( one
in 30 Dubliners depend on GUINNESS®
brewery for their livelihood); June 4, 1907
- Arthur Guinness Son & Co. Limd registered Guinness "Guinness's
Extra Stout James's Gate Dublin Bottled By Arth Guinness
Son & Co. Limited" trademark first used March 29, 1862 (stout);
1914 - produced almost 3
million barrels; 1931 - S.S. Guinness steamship
launched, first custom-built to transport GUINNESS® beer;
January 15, 1935 - registered "Guinness" trademark
first used January 1, 1764 (beer);
1963
- last wooden keg racked at Brewery at St. James’s Gate;
metal kegs used
for storing, shipping;
1976 - over 7 million glasses of GUINNESS® drunk daily;
2001 - almost 2 billion pints of GUINNESS® a year
sold worldwide, over 1 million pints of GUINNESS® a day sold in
Great Britain alone.
1772 - Philippe Clicquot-Muiron
established Veuve Clicquot, small area of vineyards near Bouzy
and Ambonnay (Montagne de Reims area of France);
1801 - Francois
(son) took over; Nicole-Barbe Clicquot (daughter-in-law, widowed
at 27, thus "Veuve" Clicquot) built business; oversaw marketing
and distribution, new practices in the cellars; conceived system
of remuage (bottles placed into wooden racks, neck first, at
angle of 45 degrees; turned and tilted each day so that bottle
pointed further downwards; gradually bought all sediment into
neck behind cork, removed during disgorgement; decanting before
serving no longer required, leaving in glass for sediment to
settle no longer necessary); 1828
- Eduoard Werle, wealthy employee who paid off firm's debts,
made a partner (assumed full control in 1841);
1884 - Alfred Werle
(son) took over; 1984
- Veuve Clicquot taken over by Joseph Henriot, head of Champagne
Henriot, owner of 11% of Veuve Clicquot stock (most significant
minor shareholder); assumed role of chairman of company (from
Alain de Vogue, CEO since 1973, distant relation of Edouard
Werle); 1986 -
acquired by Louis Vuitton for $750 million;
June 1987 - Moet Hennessy merged with
Louis Vuitton in $4 billion deal; formed LVMH Group (world's
largest luxury goods company).alone.
April 27, 1773
- The British Parliament passed Tea Act, designed to save
East India Company, grant it monopoly on
American tea trade.
1777
- William Bass set up brewery in Burton-on-Trent; business
thrived, developed into one of UK's leading brewers;
1876 - Bass red
triangle became first trademark registered in UK;
1961 - acquired
number of well-known regional brewing companies (Mitchells &
Butlers in Midlands); 1967
- merged with Charringtons in London; made Bass one of largest
brewers, pub owners in UK; 1988
- acquired Holiday Inns International;
1990 - acqired North American Holiday
Inn business; 1994
- launched Crowne Plaza, move into upscale hotel market;
1997 - launched new
hotel brand, Staybridge Suites by Holiday Inn, entry into
profitable North American upscale extended stay market; fastest
brand in segment to reach 50 units in Americas;
1998 - acquired
InterContinental hotel company;
2000 - acquired Southern Pacific Hotels
Corporation (SPHC) in Australia, leading hotel company in Asia
Pacific; sold Bass Brewers to major Belgian brewer for £2.3
billion; name changed to Six Continents PLC;
April 15, 2003 -
completed split of company into InterContinental Hotels Group
PLC (hotels, soft drinks businesses) and Mitchells & Butlers plc
(retail business); April 2005
- IHG launched Staybridge Suites UK;
2006 - signd operating joint venture
with All Nippon Airways (ANA); IHG ANA Hotels Group Japan
largest international hotel operator in Japan (world's second
largest hotel market).
April 1779 - Bortolo Nardini bought Osteria sul
ponte, inn located at eastern entrance to Palladian bridge
spanning river Brenta in Italy's Veneto region; inn became
"Grapperia Nardini" (Italian grape pomace acquavite);
1860 - Bartolo
Nardini (grandson) introduced steam distillation (vs. direct
flame); 1915 -
grappa very popuar with troops in WW I; oldest steam distillery
in Italy; only traditional Italian distillate;
1960s - introduced
vaccuum distillation (distaillation at lower temperatures);
October 30, 2001 -
Ditta Bortolo Nardini s.p.a. registered "Nardini" tarddemark
first used in April 1779 (grappa);
2010 - managed by Giuseppe, Cristina, Angelo,
Antonio, Leonardo Nardini; leading brand of high quality grappa,
with about 25% of total market share, production of 4 million
bottles exported in most important markets worldwide.
1780 - John Jameson
founded Bow Street Distillery in Dublin, Ireland; family motto:
"without fear", appears on every bottle;
1820 - John Jameson & Sons second
largest distiller in Ireland; 1890
- Ireland had about 90% of global export whiskey market, Jameson
had about 10% share of Ireland's annual whiskey output;
1966 - John Jameson
& Sons Ltd, John Power and Sons, Cork Distilleries Company
merged, formed United Distillers of Ireland; soon changed name
to Irish Distillers Limited; 1975
- Jameson distilled outside Ireland for first time in 200 years;
1988 - acquired by
Pernod Ricard Group; 1995
- annual global sales of Jameson exceeded 10 million bottles;
entered Top 100 World Spirit brands by value;
1996 - worldwide
sales of Jameson reached million case mark,
2006 - Jameson sold 2 million cases
worldwide.
 John Jameson
- Jameson Irish Whiskey
(http://www.jamesonwhiskey.com.au/getfile/a2686f4d-b7e0-4c9a-ad4a-d6b116c9a3b6/john-jameson-picture.aspx)
John Jameson
- Jameson Irish Whiskey
(http://www.jamesonwhiskey.com.au/getfile/a2686f4d-b7e0-4c9a-ad4a-d6b116c9a3b6/john-jameson-picture.aspx)
1783 - Jacob
Schweppe invnted efficient
system for manufacture of carbonated mineral water;
October 6, 1790 - showed his process for making
artificial mineral water.
May 9, 1785 -
British inventor Joseph Bramah patented beer-pump handle.
July 16, 1785
- Florens-Louis Heidsieck established wine making business in
Reims, France; 1828 - business taken over by
nephew, Christian Heidsieck, cousin Henri Guilaume Piper;
renamed Piper-Heidsieck.
1786 - John
Molson founded Molson Brewery, Canada's most successful brewer;
1788 - Brewery produced 13,932 gallons of beer;
1800 - first used glass bottles; 1816 -
first partnership agreement with sons (John Jr., William,
Thomas); signaled beginning of continuing family involvement in
company; 1836 - approximately 60,000 gallons of
beer produced; 1846 - 100,000 gallons produced;
1859 - first Molson ads; 1886 -
175-fold increase in beer volume since founding year; same
profit as that sold in first year, after deduction of taxes (26
cents per gallon); 1909 - yearly production
milestone of 2,000,000 gallons; 1911 - name
changed to Molson's Brewery Ltd., private, limited joint-stock
company; 1926 - ceased to be its own maltster;
1936 - 268,405 barrels produced; February 15,
1945 - went public; 1949 - first million
barrel year (25 million gallons); 1954 -
introduced "Molson Golden" beer; 1961 - $106.2
million in sales; 1962 - name changed to Molson
Breweries Limited; 1973 - name changed to The
Molson Companies limited; 1985 - $1.063 billion in
sales; July 28, 1986 - North America's
oldest continuing brewery; 1989 - merged with
Carling O'Keefe, formed Canada's largest brewer, fifth
largest brewer in North America; 1997 - with
Foster's Brewing Group purchased Miller Brewing Company's 20%
stake in Molson Breweries = partnership of The Molson Companies
Limited (50%) and Foster's Brewing Group (50%); 1998
- purchased Foster's Brewing Group 50% stake; TMCL - 100% owner
of Molson Breweries; 1999 - name changed to Molson
Inc.; January 2001 - sold Montreal Canadians to
Georges N. Gillett Jr., retained a 19. 9% share NHL hockey team;
February 2002 - acquired Kaiser, second leading
brewer in Brazil, became 13th largest brewing company in world.
1787
- John Courage started Courage & Co Ltd at the Anchor Brewhouse
in Horsleydown, Bermondsey, UK;
1797 - renamed Courage & Donaldson;
1888 - registered
as 'Courage'; 1955
- merged with Barclay, Perkins & Co Ltd, renamed Courage,
Barclay & Co Ltd; 1960
- merged with Simonds' Brewery, renamed Courage, Barclay,
Simonds & Co Ltd; October 1970
- name changed to Courage Ltd; 1972
- acquired by Imperial Tobacco Group Ltd;
1986 - Imperial Tobacco acquired by
Hanson Trust; Courage acquired by Elders IXL;
1990 - renamed
Foster's Brewing Group; 1991
- Courage section of Foster's merged breweries of Grand
Metropolitan; 1995
- acquired from Foster's by Scottish & Newcastle, renamed
Scottish Courage; January 2007
- rights for production, marketing, sales of Courage brands
acquired by Wells & Young's Brewing Company; joint venture
renamed Courage Brands Ltd.world.
November 8, 1789
- Elijah Craig, of Bourbon, KY, aged corn whiskey in new charred
oak barrels, turned moonshine into Bourbon whiskey.
1793
- Thomas Coates joined Fox & Williamson, established distilling
business in Black Friars Distillery in Plymouth, UK (oldest
working distillery in UK); developed recipe for Plymouth Gin,
began its production; name soon changed to Coates & Co;
1823 - Gin Act of
1823, mandated paying of separate licenses for distillation.
rectification; Coates & Company focused solely on gin
rectification; 1850
- supplied over 1000 barrels of 'navy strength' 57% abv gin/year
to Royal Navy; 1880s
- legal judgment - only UK gin to have geographic designation
(like appellation controllee - Plymouth Gin could only be made
in Plymouth.); 1896
- first ever recipe for Dry Martini specified Plymouth Gin
(Stuart's Fancy Drinks and How to Mix Them);
1900s - become
world's largest volume brand of gin (1000 cases/week went to New
York alone); 1930s
- star of cocktail era (only gin still around today named in
numerous recipes in renowned Savoy Cocktail Book, bible of
mixology; March 24, 1953
- Coates & Co. (Plymouth) Limited registered "Coates and Co's
Plymouth Gin Victoria Regina" trademark first used in 1882
(gin); 1958 -
distillery acquired by Schenely Industries;
1990s - acquired by private group of
investors, restored brand to original 41.2% strength (83 degrees
proof), grew brand through clever marketing, word of mouth,
distribution deal with Vin & Spirit (Sweden);
2005 - acquired by
V & S Group (Vin & Sprit, owners of Absolut vodka);
2008 - acquired by
Pernod Ricard.
1795 - King
Carlos IV transferred land deed to second José Cuervo, José
María Guadalupe Cuervo, granted him first concession to
commercially produce mezcal wine, tequila (Don Jose Antonio de
Cuervo received land grant in 1758 to cultivate Agave plants in
Jalisco, Mexico); 1812 - founded Fabrica La Rojena
to produce Jose Cuervo Tequila, each barrel 'branded' with a
crow (Cuervo in Spanish); oldest spirits distillery in Latin
America; 1873 - exported to America; 1880
- bottles introduced for tequila distribution; April 10,
1934 - Ana Gonzalez Rubio (VDA. De Cuervo Trading as
Jose Cuervo) registered "Jose Cuervo La Rojena Tequila"
trademark first used January 1909 (brandy).
August 24, 1795
- Reverend Samuel Henshall received world's first patent for
corkscrew (in England)(; called the "piratical screwmaker";
decribed as "a new Mode of applying the Screw, and a Mode which
every Person who sees it will be surprised that he himself did
not find out"; manufactured by Matthew Boulton, famous
Birmingham entrepreneur.
1801 - James
Chivas became apprentice in William Edward's grocery store
(foods, beverages, wines, spirits) in Aberdeen, Scotland;
1841 - took over business (at Edward's death) in
partnership with Charles Stewart; began to bottle blends of
Scotch whiskies (first brand, Royal Glen Dee); 1843
- granted Royal Warrant as "Purveyor of Groceries to Her Majesty
Queen Victoria"; 1857 - partnership with Charles
Stewart dissolved;
established Chivas Brothers to blend whiskies (with brother,
John); 1891 - Chivas Regal, flagship brand,
introduced (malt scotch from Strathisla distillery); 1909
- entered American market; 1923 - named "Purveyor
of Scotch Whisky to His Majesty King George V"; June 11,
1935 - Chivas Brothers registered "Chivas Regal"
trademark first used in 1891 (whiskey); 1936 -
registered as Chivas Brothers Ltd.; 1949 -
acquired by Seagram Distillers Plc; December 19, 2001
- acquired by Pernod Ricard Group for 5.7 billion pounds.
April 5, 1806 - Isaac Quintard of
Stanfield, CT, received a patent for "Cider and Bark Mills".
October 12, 1810
- Oktoberfest festival began in West Germany with horse
race in honor of marriage of Crown Prince Ludwig of Bavaria to
Princess Therese von Sachsen-Hildburghausen.
1813 -
Joseph Noilly developed first formula for dry French vermouth;
1855 - son Louis Noilly joined son-in-law Claudius
Prat to form company that became Noilly Prat in
Marseillan, aunny port in south of France on Mediterranean
coast.
1818
- Peter Heering produced Cherry Liqueur, ruby-red liqueur, in
Denmark (soaked lightly crushed Danish cherries, blended spices
in neutral grain spirits, cask-matured mixture for up to five
years, added sugar during aging process);
June 12, 1962 - Peter Frederik Suhm
Heering registered "Verry Cheering Cherry Heering" trademark
(cherry liqueurs).
 Peter Heering
- Cherry Heering
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5d/
Peter_Frederik_Suhm_Heering.jpg/220px-Peter_Frederik_Suhm_Heering.jpg)
Peter Heering
- Cherry Heering
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5d/
Peter_Frederik_Suhm_Heering.jpg/220px-Peter_Frederik_Suhm_Heering.jpg)
April 23, 1819
- Samuel Fahnestock, of Lancaster, PA, received a patent for an
"Apparatus for Making Mineral Waters; soda fountain.
1819 - German
chemist Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge (25) analyzed Arabian
mocha beans given by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe; isolated
world's first sample of pure caffeine ( found in 63 species of
plants).
1819
- William Boylan, pharmacist, created elixir in Paterson, NJ
apothecary (derivative of birch trees); named Boylan's Birch;
1900 - joined with
Jonathan Sturr, local politician, started Boylan & Sturr
Bottling Company; 1901
- partner's interest acquired by Boylan, continued to formulate,
bottle flavored carbonated soft-drinks;
1930s - exited soda business, sold
formulas, sole route to Frank Fiorina (driver);
1940 - closed
bottling operation (tough competition); manufactured,
distributed Boylan's Draught Birch Beer to taverns in Passaic
County, NJ; 1978 -
Ronald and Mark Fiorina (grandsons) took over;
1980s - expanded to
manufacturing of full line of fountain syrups; grew sales to
over $1 million; 1992
- profit margins shrank, re-focused on “flagship brand”,
Boylan's Birch Beer; 1995
- distributed own products; expanded line of available flavors;
September 1995 -
introduced Black Cherry, Ginger Ale (known as “Bottleworks”
line); June 1997 -
launched Boylan Bottleworks Orange, Grape, and Creme;
1998 - released two
root beers (Boylan Bottleworks Root Beer, Diet Root Beer);
2004 - launched
"The Natural Kind" label (all-natural requirements).
1820 - John
Walker (15) established small grocery store in Kilmarnock, west
of Scotland; applied principles of tea blending to malt
whiskies, produced Walker's Kilmarnock Whisky; 1865
- Alexander Walker (son) produced first blend (malt and grain
mixed), Walker’s Old Highland; 1870 - introduced
square bottle (label applied at angle of 24 degrees); 1908
- Walker's Kilmarnock Whiskies renamed Johnnie Walker Whisky;
striding man logo introduced; June 21, 1910 - John Walker &
Sons, Limited registered "Johnnie Walker" trademark in U.S.,
first used in January 1880 (blend of straight scotch whiskies);
1933 - King George V
granted Royal Warrant to company (official purveyor of whisky to
the Royal Household).
1820
- Alexander Keith (25), Scottish immigrant, acquired brewery in
Halifax, Nova Scotia from Charles Boggs (had worked there since
1817 as brewmaster, business manager); operated it as Nova
Scotia Brewery; created original secret recipe for his own India
Pale Ale; 1853 -
Donald Keith (son) joined business; name changed to Alex. Keith
& Son; late 1800s - one of Canada's largest breweries;
1928 - acquired
from Keith's granddaughter by Oland Brewery (founded 1867);
oldest working brewery in North America.
 Alexander Keith
- Nova Scotia Brewery
(http://www.glenmargaret.com/ferecent/keith.jpg)
Alexander Keith
- Nova Scotia Brewery
(http://www.glenmargaret.com/ferecent/keith.jpg)
1821
- Girolamo Luxardo, from Genova, founded distillery in Zara, port
city on Dalmatian coast, to produce Maraschino ("rosolio
maraschino", liqueur produced in Dalmatia since medieval times,
often made in convents, perfected by his wife);
1829 - obtained
exclusive "privilege" from Emperor of Austria;
1913 - Michelangelo
Luxardo (third generation) built extremely modern distillery,
one of largest in Austro-Hungarian Empire;
post WW II - iorgio Luxardo (fourth
generation) rebuilt distillery in Veneto region of Italy (Zara
incorporated into Kingdom of Italy, after WW I, as 85% of its
population were Italians); 2009
- sixth generation manufactures Maraschino, Sambuca, Amaretto,
Grappa, Limoncello, Passione Nera, gourmet division (liqueur
concentrates for bakers, ice cream manufacturers, fruit syrups,
delicious marasca cherry jam.
1822 - John Taylor
established distillery; 1863
- James Burrough, pharmacist, acquired gin & liqueur distilling
firm of John Taylor & Son of Cale St., Chelsea; created
Beefeaters Gin (nine botanicals, precise combination became
close guarded trade secret); used image of a Yeoman Warders (of
the Tower of London, serve as a bodyguard to the King or Queen
of Great Britain on formal occasions) on the product, named it
after their unofficial name - Beefeater (became icon of global
spirits industry; 1963
- largest exporter of Gin from the UK;
1987 - James Burrough Ltd. PLC acquired
by Whitbread; 1991
- acquired by Allied Domecq; only premium international dry gin
distilled in London.jam).
1824 - George
Smith founded Glenlivet distillery in Speyside, Scotland to
legitimize whiskey he was already making; 1880 -
John Gordon Smith (son) took legal action to protect family
brand, prevent other distillers from branding 'Glenlivet' name
on their casks; 1884 - legal settlement determined
only Smith's original single malt could be named "The Glenlivet";
December 29, 1908 -
G. & J. G. Smith registered "The "Glenlivet" Trademark Geo. & J.
G. Smith Guaranteed Solely the Famous Highland Malt Whiskey
Produced at the Glenlivet Distillery & Bottled in Scotland"
trademark in U.S. first used June 27, 1907 (pure malt scotch
whiskey); number one single malt whiskey in U. S.
1826 - John
Horniman launched tea-packing business in Newport, Isle of
Wight, England; 1852
- sons moved the business to London warehouse just north of City
on Wormwood Street (Shepherdess Walk); first to sell tea in
pre-packed, pre-weighed, sealed in packets (vs. loose tea open
to possibility of adulteration by worthless additives (hedge
clippings, dust to increase weight); prospered, advertised
widely, Horniman's tea became household name; taken over by
Frederick John Horniman (son); 1917
- controlling interest in W. H. and F. J. Horniman & Co. Ltd.
acquired by Lyons.
1827 -
Jacobus, Gottlieb, Philipp Mumm, Friedrich Giesler, established
P.A. Mumm et Cie. in Reims, France (initials stood for their
father, Peter Arnold Mumm); 1853 - taken over by
George Hermann (descendant of Mumm brothers); 1875
- introduced Cordon Rouge, red ribbon draped around neck of
bottles of champagne; 1881 - first house to break
into US market.
1828/1829
- Missionary Samuel Reverend Ruggles planted first coffee on
Kona coast of Hawaii; arabica trees taken from cuttings planted
on Oahu few years earlier; 1840 - first written
mention of coffee in Kona; most of coffee grown in North, South
Kona cultivated on land owned by Kamehameha Schools Bishop
Estate (KSBE, 1884) - leases tracts to more than 600 farmers;
more than 1,200 acres of KSBE-owned land are now in Kona coffee
production.
1829 -
David G. Yuengling established
Eagle Brewery on Centre Street in Pottsville, PA; 1873
- name changed to Yuengling Brewery.
February 6, 1829
- Count Athanese Hennequin de Villermont, former Admiral in War
of 1812, Paul Renaudin, Jacques Joseph Placide Bollinger (both
associated with Muller-Ruinart) established Bollinger Renaudin &
Cie., champagne growers and producers (Champagne Bollinger) in
village of Ay in Champagne, France;
1870 - first shipment exported to U. S.;
1884 - gained royal
warrant from Queen Victoria (renewed in 1901, 1911);
1888 - Georges and
Joseph Bollinger (sons) took over business;
1918 - Jacques Bollinger (25, Georges's
son) took charge; 1941
- Madame Elizabeth 'Lily' Law de Lauriston Boubers, widow,
became head of company; 1950
- awarded Royal Warrant from George VI and Queen Mother (renewed
in 1955); 1961 -
created wine recently disgorged ('R.D.');
1964 - acquired Mentzendorff (U.K.
importer (since 1851), to assure correct distribution of
Bollinger’s Champagnes in most important market;
1971 - Claude
d"Hautefeuille, nephew, took over;
1978 - Christian Bizot, son of Lily's youngest
sister, named head of House (employee since 1952); increased
exports to 83% of production; 1987
- restructured, formed Jacques Bollinger Cie., family-owed
holding company (all shares held by family);
December 1993 -
Ghislain de Montgolfier (great grandson of Jacques Joseph
Bollinger) took over as seventh president (on board of directors
since 1985); September 2007
- Jerome Philipon named managing director (first outside family
to run business); one of few remaining Grande Marque houses
owned, controlled, managed by same family since its founding.
April 3, 1829
- James Carrington, of Wallingford, CT, received a patent for
the "Manufacture of Coffee Mills".
1830 -
Charles Tanqueray (20), heir to three generations of
Bedfordshire clergy, abandoned family profession, established
small distillery in Bloomsbury district of London; 1862
- martini created; initially called "Martinez", named for
traveler bound for Martinez, CA (mixed 4 parts red, sweet
vermouth with one part gin, garnished with a cherry); 1868
- Charles Waugh Tanqueray (son) assumed control; 1870
- gin and tonic created; British invented tonic water, made with
quinine (good tasting way to fight malaria in tropics;
discovered it mixed well with gin.
1830 - George
Wyndham, agriculturalist, pastoralist, wine grower, purchased
"Annandale", farm of 2,000 acres in Sydney, Australia, renamed
it "Dalwood" after portion of his father's Dinton Estate in
England (built his home, "Dalwood House"); planted first
commercial plantings of Shiraz, at Wyndham Estate in Hunter
Valley along banks of Hunter River, in New South Wales;
1831 - settled
100,000-acre property, "Bukkulla", near Inverell, established
vineyard from vines brought from Dalwood;
1837 - released first vintage of Dalwood
Wines to rave reviews; 1860
- total vineyard holdings produced 11,000 gallons of wine;
Dalwood's vine plantings expanded, became second largest
vineyard in colony; exported Dalwood wines to England, India;
1867 - Dalwood
vineyards to more than 65 acres, principally cabernet, shiraz,
white hermitage; received Bronze, Silver medals in Paris
International Exhibition; 1892
- only Bukkulla owned by Wyndhams;
1901 - Dalwood acquired by J.F.M. Wilkinson of
Coolalta; 1970 -
Dalwood Wines renamed Wyndham Estate; "industry pioneer"
responsible for launching Australian wines onto world stage.
 George Wyndham - Wyndham Estate
(http://www.dalwood.org.au/img/george.jpg)
George Wyndham - Wyndham Estate
(http://www.dalwood.org.au/img/george.jpg)
October 27, 1832
- James Worts, partner William Gooderham (brother-in-law)
established business in Toronto, ON, sold five barrels of flour
to local baker at 25 shillings barrel;
1841 - established dairy farm adjacent
to distillery; 1845
- sold 53,000 gallons of whiskey;
1861 - built largest, most modern distillery in
Canada (grain elevators had capacity of 80,000 bushels,
distilling operation could take in 1,500 bushels each day,
produce 7,500 gallons of whisky, other spirits); biggest
distillery in Canada; George William Gooderham (son) took over;
1900 - George
William Gooderham (grandson) took over;
1923 - acquired by Harry C. Hatch,
associates for $1.5 million; 1927
- merged with Hiram Walker Company, formed Hiram Walker-Gooderharn
& Worts Limited.
1837 - John
Dewar became partner in Alex MacDonald's (uncle) wine business
in Perth, Scotland; renamed MacDonald and Dewar; 1846
- established his own business, among first to sell Scotch in
glass bottles with his name on them; 1871 - John
Alexander Dewar (son) joined business; 1879 - made
partner; 1886 - brother Tommy made partner;
1891 - Andrew Carnegie ordered keg of Dewar's scotch to
be sent to President Benjamin Harrison; 1899 -
introduced Dewar's White Label;
December
3, 1907 - John Dewar & Sons, Ltd. registered
"Dewar's" trademark in U.S., first used January 1, 1850
(whiskey); 1911 - created
largest mechanical sign (68 feet) in Europe on Thames Embankment
in London; 1925 - Dewar's Buchanan's, Johnnie
Walker merged with Distillers Company Ltd. 1927 -
introduced re-sealable spring cap (vs. cork); 1955
- Queen Elizabeth granted Royal Warrant; 1986 -
White Label #1 blended scotch whiskey in U.S.
 John Dewar
- DEWAR's
(http://www.whisky-pages.com/images/john-dewar.jpg)
John Dewar
- DEWAR's
(http://www.whisky-pages.com/images/john-dewar.jpg)
1837
- Joseph and Edward Tetley, salt merchants, established Joseph Tetley & Co. in
Huddersfield in Yorkshire, England; bought raw tea, blended,
packaged it, sold in London, center of tea trade; brothers
parted company; 1871
- Joseph Tetley, Jr., became partner; blended teas from around
world, packaged them, developed blend of orange pekoe and pekoe
cut black tea (became mainstay in United States, Britain);
1888 - signed
distribution agreement with The Wright & Graham Company
(Franklin Street, TriBeCa section of Manhattan, New York); sold
tins of Tetley brand Indian and Ceylon loose tea from nearby
White Street site (mostly to department stores such as R.H.
Macy). At the time these black teas stood out in the United
States, a market that had previously been dominated by green tea
and Formosan (Taiwanese) teas; 1913
- acquired Wright & Graham, incorporated Tetley Tea
Incorporated; established manufacturing facilities on Greenwich
Street; 1930 - tea
bags accounted for just 5% of Tetley Tea sales in United States;
1936 - Joseph
Tetley, Jr., died, William Tetley-Jones (son-in-law) took charge
of parent company; 1937
- died, Tetley Ironside Tetley-Jones (son), fresh out of
Cambridge University, took over; cast firm's lot with tea bags
in United Kingdom; 1939
- tea industry fell under auspices of the Ministry of Food
(returned to fair trade status in July 1951);
November 23, 1943 -
Joseph Tetley & Co., Inc. registered "Tetley" trademark first
used July 10, 1889 (tea); 1949
- introduced "Tetley Teabags" in United Kingdom;
1957 - Tetley USA
acquired by Beech-Nut Life Savers, the U.S. maker of baby food,
candy, chewing gum; sister Tetley companies split (Tetley U.K.
joined Beech-Nut's international division);
1962 - acquired Martinson Coffee;
1972 - Tetley USA,
Tetley UK (part of Beech-Nut beverage operations) acquired by J.
Lyons & Company Limited; 1977
- Lyons acquired by Allied Breweries, renamed Allied-Lyons PLC
(became Tetley USA's new corporate parent);
1982 - acquired U.S. and U.K. businesses
of Coca-Cola's Tenco division (instant coffee business sold to
Chock Full O'Nuts Corp. for $7 million in 1989);
1995 - Lyons, now
Allied Domecq, sold worldwide beverage business to a management
buyout team; formed The Tetley Group;
February 2000 - sold U. S. coffees
assets (to Mother Parker's Tea and Coffee Company, Rowland
Coffee Roasters, Inc.); focused on growing the tea business;
acquired by Tata Tea Limited (Calcutta, India) for $432 million;
2002 - Tetley USA
sold private label business, focused on branded retail products
tailored for American consumer (preferred single-cup bags rather
than larger ones for the pot.
 Joseph Tetley, Jr.
- Tetley Tea
(http://thm-a01.yimg.com/nimage/3926716b7660f3f0)
Joseph Tetley, Jr.
- Tetley Tea
(http://thm-a01.yimg.com/nimage/3926716b7660f3f0)
January 26, 1838
- Tennessee passed first Prohibition law in history of the
United States; made it a misdemeanor to sell alcoholic beverages
in taverns and stores.
1840
- Thomas Carling founded brewery across from military camp in
London, ON; 1845 - John and William Carling (sons) took over
brewery; 1849 -
renamed W. & J. Carling Co.; 1875
- Thomas H. Carling (John's son), two members of Dalton family
(connected with brewery management) made partners; renamed
Carling and Company; 1880
- entered U. S. market. acquired "Rogers & Hughes Forest
Brewery" in Cleveland, OH; 1882
- reorganized as Carling Brewing and Malting Company Ltd. of
London; 1898 - sold
American rights for Carling to Cleveland & Sandusky Brewing
Company (until 1911); 1927
- renamed The Carling Breweries Limited;
1930 - acquired by Canadian Breweries
Limited (created by Edward P. Taylor's merging of 20 smaller
breweries; grew to be world's largest brewing company);
1933 - James A
Bohannon (Peerless Motor Car Company) exchanged Peerless stock
for rights to formulas for Carling brews, their identifying
labels, trademarks; new company named Brewing Corporation of
America; introduced Carling Black Label; Brewing Corporation of
America acquired by Canadian Breweries Limited;
November 27, 1934 -
Carling Breweries Limited registered "Carling's" trademark in U.
S. first used September 19, 1933 (ales);
1946 - Black Label brand discontinued
(reintroduced in 1950); first to use woman on television to
attract male beer-drinker (identifiable character of Mabel);
1960 - fourth
largest brewery in America, sales of 4,822,075 barrels of beer;
1976 - American
division, sold by Carling of Canada, merged with National
Brewing Company of Baltimore; formed "Carling-National
Breweries"; 1979 -
acquired by G. Heileman Brewing Company of LaCrosse, WI;
1991 - G. Heileman
filed for Chapter 11-bankruptcy protection;
1994 - acquired by The Stroh Brewery of
Detroit.stores.
 Thomas Carling - Carling Black Label
Thomas Carling - Carling Black Label
(http://thepantryonline.co.uk/images/i-bet-he-drinks-carling-black-label-GE6KD7GN.jpg)
1843 -
Johann-Joseph Krug, formerly of
Champagne Jacquesson & Fils,
founded the Krug champagne house.
1844 - German
immigrant Jacob Best and his four sons setting up a brew shop on
Chestnut Hill in Milwaukee; 1862 - Captain
Frederick Pabst married son Philip Best's daughter; 1864
- Pabst bought half-interest in brewing company (volume of 5,000
barrels a year); 1873 - company produced 100,000
barrels annually; Pabst was president.
1845 - John Bird
Fuller (brewer's son) joined by Henry Smith (Romford Brewery of
Ind & Smith), John Turner (Smith's brother-in-law, head brewer);
formed Fuller Smith & Turner in Griffin Brewery in gardens of
Bedford House on Chiswick Mall;
1910 - acquired Beehive Brewery and pubs in
Brentford; 1929 -
partnership dissolved, Limited Company formed;
1993 - Anthony
Fuller founding chairman of Independent Family Brewers of
Britain (informal group of 27 family-owned/controlled brewery
CEOs, own over 4,200 pubs throughout England and Wales, employ
around 46,000 people); 2005
- acquired George Gale & Co. of Horndean, Hampshire, brewers
(HSB, Butser, Prize Old Ale) and 111 pubs; descendents of first
partners still heavily involved in day-to-day running of company
(363 quality pubs, bars and hotels); oldest brewery operating in
London, one of oldest brewery sites in United Kingdom ( brewery
dates back to the mid-1700s.
1846 - Harvey
Perley Hood bought milk route in Charlestown, MA; 1856
- bought farm in Derry, NH, started wholesale milk business;
1880 - Charles Harvey Hood (son) joined company, form
partnership, HP Hood & Son; 1890 - incorporated as
HP Hood & Sons (owned four wagons, nine horses, operated three
railroad cars daily); 1900 - first ice cream
produced in Hood Creamery retail stores; May 21, 1957
- registered "Hood" trademark first used in 1900 (fluid milk,
fluid cream, aerated cream, egg nog, yogurt, cheese, fresh ice
cream, milk sherbert, and water ice, and frozen confections in
stick, sandwich, or in bar form...); 1971 - use of
milk bottles discontinued; name changed to HP Hood Inc.;
1972 - first dairy to produce frozen yogurt in U.S.,
Frogurt (based on Bloomingdale's request for low-fat frozen
dessert); 1975 - Hood Ice Cream ranked #1 in New
England (according to Nielsen); 1980 - acquired by
Agway, agricultural supply company, to help members of Northeast
dairy cooperatives stabilize milk markets; 1991 -
produced first non-dairy product (Hood Non-Dairy Country
Creamer); 1993 - nation's leading producer of extended-shelf
life (UHT) dairy products; 1995 - acquired by John
A. Kaneb Family (third owner in 149 years); 2003 -
renamed HP Hood LLC; one of largest branded dairy operators in
United States; sales approximately $2.3 billion; approximately
5,000 employees.
 Harvey Perley Hood -
founded H. P. Hood in 1846
(http://www.rootsweb.com/~usgenweb/nh/rockingham/biopics/HoodHarveyPerley.jpg)
Harvey Perley Hood -
founded H. P. Hood in 1846
(http://www.rootsweb.com/~usgenweb/nh/rockingham/biopics/HoodHarveyPerley.jpg)
1846
- Francesco Peroni established Birra Peroni S.p.A. in Vigevano,
Italy; 2003 -
majority stake acquired by SABMiller.employees.
1846 - Dario
Telles de Menzes, Portuguese man, settled in Maranguape (state
of Cear), Brazil, set up prosperous still called Ypioca, liquor
produced directly from juice of first crush of sugar cane,
national spirit of Brazil; second generation, led by captain
Dario Borges Telles, introduced cast iron stills, processing
still entirely manual; 1929 - Paulo Campos Telles,
took over, introduced bottling liters with precision dropper,
aging in balsamic barrels (allowed stocking for periods of over
two years); 1968 - fourth generation, under
Everardo Ferreira Telles, assumed control; originated new
additional establishments, diversified range of products; one of
most solid beverage companies in country; produced 2.5 million
liters/year; 2001 - five modern industrial units
produced 40 million liters/year; employed 1.200 directly, more
than 20.000 indirectly; only Cachaça from Cear.
 Dario Telles de Menzes
- founder Ypioca
(http://tbn1.google.com/images?q=tbn:r3LBPmzhDBAPvM:http://www.ypioca.com.br/port/historia/primeira.jpg)
Dario Telles de Menzes
- founder Ypioca
(http://tbn1.google.com/images?q=tbn:r3LBPmzhDBAPvM:http://www.ypioca.com.br/port/historia/primeira.jpg)
1847
- J.C. Jacobsen founded Carlsberg (named for son Carl) outside
Copenhagen, Denmark; November 10,
1847 - produced first brew;
1868 - first export to Edinburgh,
Scotland; 1904 -
introduced Carlsberg pilsner's logo designed by Thorvald
Bindesboll; 1882 -
Carl Jacobsen (son) opened brewery under name Ny (New)
Carlsberg; father changed name of his brewery to Gamle (Gl.,
old) Carlsberg; 1906
- Ny Carlsberg, Gl. Carlsberg merged, formed Carlsberg Breweries
(Carl Jacobsen, son, as Director);
1939 - 55% of all beer imported to U.K. from
Carlsberg; 1970 -
merged with rival Danish brewery Tuborg, formed United Breweries
A/S; 1992 - merged
with English brewery Tetley (became sole owner in 1997);
2001 - formed
Carlsberg Breweries A/S (60% owned by Carlsberg A/S, 40% by
Orkla ASA); 2004 -
Carlsberg A/S acquired Orkla's share of Carlsberg Breweries.
1847
- John Kinder Labatt bought Simcoe Street brewery in London, ON
in partnership with Samuel Eccles;
1853 - became brewery's sole proprietor;
1945 - went public;
June 4, 1957 -
registered "Labatt's" trademark first used in 1895 (ales and
beers); 1995 -
acquired by Belgium-based Interbrew (world's third largest
brewer); 2004 -
merged with Brazilian-based AmBev (world's fifth largest
brewer), formed InBev S.A.
1847
- Stone Hill Winery founded
(Hermann, MO, along Missouri River);
1873 - won gold medal in Vienna World's
Fair; 1876 - won
gold medal in Philadelphia World's Fair; 1900
- second largest winery in the United States; shipped 1,250,000
gallons of wine per year; 1965
- acquired by Jim and Betty Held; restored picturesque
buildings, vaulted underground cellars;
2008 - produced 260,000 gallons of wine,
used state-of-the-art equipment , latest technology;
2009 - Missouri's oldest,
most awarded winery.
1848 - August Krug started August Krug
Brewery, hired Joseph Schlitz as an accountant;
1856 - took over
management of brewery after Krug's death;
1858 - married Krug's widow, changed
name to Joseph Schlitz Brewing Co.;
1976 - ranked as the No. 2 brewery in
America; June 10, 1982
- acquired by Stroh Brewery Company of Detroit, MI.
 Joseph
Schlitz
(http://s3.amazonaws.com/findagrave/photos/2001/222/schlitzfamilybio.jpg)
Joseph
Schlitz
(http://s3.amazonaws.com/findagrave/photos/2001/222/schlitzfamilybio.jpg)
May 1850 - illiam H. Bovee (27) hired James Folger to build The Pioneer
Steam Coffee and Spice Mills on Powell Street in San Francisco;
inaugurated production of coffee ready for the pot: roasted,
ground, packaged in small tins, identified by Pioneer labels;
1855 - Ira Marden made partner, Folger bookkeeper;
1859 - Bovee sold his interest, Marden & Folger
formed; 1865 - bankrupt; acquired Marden
interest; formed partnership with Otto Schoemann;
J. A. Folger & Co.
organized; 1877 -
Schoemann interest
acquired by employees, W. H. Lamb, August Schilling; name
changed to Folger, Schilling & Co; September 1881
-
Schilling
withdrew, renamed J. A. Folger & Co.; 1885 - Lamb
interest acquired by Folger, became sole proprietor;
1889 - James A. Folger, II (26) became president;
principal product was bulk-roasted coffee, delivered to grocery
stores in sacks and drums, stored in bins to be scooped out for
customer; February 1890 - business incorporated; March 7,
1922 - registered "Folgers Golden Gate" trademark first
used in 1878 (coffee, tea, spices, mustard, and food-flavoring
extracts); 1963 - acquired by Procter & Gamble
Company; 1968 - introduced Folgers Crystals
instant coffee; June 4, 2008 - acquisition by J.M.
Smucker Company from Procter & Gamble for $3.3 billion
announced; biggest U.S. producer of coffee.
January 31,
1851 - Gail Borden announced invention of
evaporated milk (devastated to see children die aboard his
steamer on return trip from England, apparently as a result of
scanty milk from shipboard cows).
May 6, 1851 - Dr. John Gorrie,
of New Orleans, LA, received
first patent for an "Ice Machine" (a "new and useful Machine for
the Artificial Production of Ice and for general Refrigeratory
Purposes").
June 2, 1851
- Maine enacted first U.S. alcohol prohibition law.
1852 -
Frenchman Etienne Theé founded Almaden Vineyards;
succeeded by Charles LeFranc (son-in-law); made first commercial
planting of fine European wine grapes in Santa Clara County;
continued by Henry LeFranc (son), Paul Masson (Henry's
son-in-law); 1892 - Masson's first
champagneintroduced at Almaden (eventually became known as
"Champagne King of California"; 1901 - Masson
start his own winery in Saratoga, CA; 1940s
-Almaden introduced "blush" wine (White Grenache Rosé), first
popular pink wine in United States; 1951 - merged
with Madrone Vineyards, owned by Lucky Lager; control regained
by Lefranc Corporations, Almaden’s original owner; 1967
- acquired by National Distributors; 1987 -
acquired by Heublein; 1980s - introduced
bag-in-the-box packaging; 1994 - acquired by
Canandaigua Wine Company; February 28, 2008 -
acquired by The Wine Group LLC from Constellation Brands.
1852 - August
Andreas Ziemann established coppersmith workshop
in Stuttgart, Germany;
1885 - developed
new type of wort-cooling system;
1901 - produced fermentation, storage vessels
made of aluminum; 1955
- built, installed first stainless steel fermentation vessels;
1965 - commissioned
first brewhouse automation system; 1988 - acquired Helmut Bauer
GmbH in Bürgstadt am Main; 1996
- planned, built world’s largest brewery in Zacatecas, Mexico;
2006 - acquired majority of Ningbo Lehui Food
Machinery (China); 2009
- largest manufacturer of brewing plants, brewing vessels in
world, most comprehensive and innovative know-how in brewing
technology, brewing techniques; only provider to develop,
manufacture vessels for entire production block of brewery,
brewhouse, tank farms in its own factories.
1854
- Pierre Pellier left France for Santa Clara Valley with grape
cuttings ("Black Burgundy" - Pinot Noir, French Colombar,
Chasselas, Fontainebleau, Pinot Noir, Madeline, others) and
prune cuttings from orchards of Agen;
1856 - with Louis Pellier (older brother) conducted
nursery business in San Jose; 1863
- acquired 148.8 acre ranch in Evergreen, CA (part of the
Chaboya land Grant) from Louis for $1,000; planted grape
cuttings; introduced Pinot Noir; Louis Pellier grafted French
prune cuttings onto rootstock of wild plums, produced Santa
Clara Valley prunes (offshoot of La Petite d'Agen, native of
Southwest France); founded the valley’s wine industry;
1881 - Henrietta (daughter) married
neighboring vintner Pierre Huste Mirassou (came to America in
1878, died in 1889); 1929 - peak of
prune planting, California had 171,330 acres (267.7 square
miles) of prune orchards; 1961 -
Edmund Mirassou (fourth genertation) brought first vines to
Monterey County, pioneered grape growing on California's sunny
Central Coast; June 28, 1977 -
Mirassou Sales Co. (dba Mirassou Vineyards Partnership)
registered "Mirassou: trademark first used September 1, 1940
(wines); 2004 - acquired by Gallo;
2010 - sixth generation of family
management; America's oldest winemaking family.
 Pierre & Henrietta Pellier
- Mirassou
(http://www.mirassou.com/images/Interior-FirstGeneration-PierrePellier.jpg)
Pierre & Henrietta Pellier
- Mirassou
(http://www.mirassou.com/images/Interior-FirstGeneration-PierrePellier.jpg)
 Pierre & Henrietta Mirassou
- Mirassou
(http://www.mirassou.com/images/Interior-SecondGeneration-PierreMirassou.jpg)
Pierre & Henrietta Mirassou
- Mirassou
(http://www.mirassou.com/images/Interior-SecondGeneration-PierreMirassou.jpg)
1853 - Thomas
Hardy established winery on banks of River Torrens in Adelaide,
Australia; grew to become one of world's great wine companies;
mid 1970s - five generations of Hardy family had
guided, shaped Thomas Hardy & Sons; April 2003 -
BRL Hardy Ltd. Pacific Wine Partners (50/50 joint venture of
Constellation and BRL Hardy) acquired by Constellation Brands;
renamed Hardy Wine Co.; 25% of domestic Australian market,
exports to more than 60 countries.
1855
-
Frederick John Miller bought small brewery, Plank Road Brewery,
in Milwaukee, WI for $2,300; 1888 - reorganized as
Frederick Miller Brewing Company;
1903 - named most popular beer, High Life
(Champagne of Bottled Beer);
May 1933
- renamed
"Miller Brewing Company"; 1968 - country's eighth
largest brewer; 1969 - acquired by Philip
Morris Corporation; July 2002 - acquired by South
African Breweries, renamed SABMiller plc.
1856 -
Lawyer Louis
Bouloumie founded Vittel spa
in Vosges
Mountains of eastern France
(1854 - bought the
Gérémoy Spring);
1882 - Société Générale des Eaux Minérales de
Vittel formed; June 1898 - first million bottles
sold; January 1951 - 100 million bottles produced;
May 1968 - introduced first PVC bottle (polyvinyl
chloride or plastic) aimed at mainstream consumer market;
1969 - Nestle acquired 30% stake in company (third
largest mineral water company in French market); October
1990 - billionth bottle produced; Nestle bought up
almost all of Vittel's remaining share capital; 2002
- Nestle consolidated bottled-water brands worldwide into single
subsidiary, Nestle Waters.
 Louis Bouloumie
- founder Société Générale des Eaux
Minérales de Vittel
(http://kiem.culture-routes.lu/uploaded_files/infos/pr/11/27/27_1.jpg)
Louis Bouloumie
- founder Société Générale des Eaux
Minérales de Vittel
(http://kiem.culture-routes.lu/uploaded_files/infos/pr/11/27/27_1.jpg)
August 19, 1856 - Gail Borden
received patent for "Improvement in Concentration of Milk";
condensed milk; could be kept pure (not spoil) and storable
without benefit of refrigeration, distributed over great
distances; 1857 - began condensing operations in
Burrville, CT; February 1858 -
founded New York
Condensed Milk Company
with financing from
Jeremiah Milbank;
1860 - incorporated in New Jersey;
1899 - Borden's
Condensed Milk Company
incorporated in New
Jersey;
August
7, 1906 - registered "Borden's" trademark first used in
January 1866 (condensed milk, cream and evaporated cream, and
buttermilk);
October
1919 - name changed to Borden Company; 1938
- began ad campaign featuring Elsie the Cow logo; 1995
- acquired by
Kohlberg Kravis Roberts &
Company.
1857 - Count Agoston Haraszthy (45),
first Sheriff of San Diego County, founder of a city in
Wisconsin (Sauk City), ferryboat owner and member of the
Hungarian Royal Guard, founded Buena Vista Winery in Sonoma, CA;
planted some of the state's first European varietals (Tokay,
Zinfandel, and Shiras grape varieties);
1906 - earthquake destroyed its
underground cellars; 1940
- Frank Bartholomew, former head of AP, acquired 500 acres of
Sonoma land without knowing an abandoned winery came with the
property; with help of Andre Tchelistcheff, considered America's
most influential post-Prohibition winemaker, restored Buena
Vista's vineyards, caves and winery to its original grandeur;
1981 - acquired by
Moller-Racke family of Germany;
2001 - acquired by Allied-Domecq; California's
oldest premium winery.
 Count Agoston Haraszthy
- founder Buena Vista Winery
(http://www.sfhistoryencyclopedia.com/art-2005/Haraszthy-1in.jpg)
Count Agoston Haraszthy
- founder Buena Vista Winery
(http://www.sfhistoryencyclopedia.com/art-2005/Haraszthy-1in.jpg)
1857 - William Hespeler, merchant,
George Randall, contractor, built Granite Mills in Waterloo, ON;
Waterloo Distillery - small subsidiary;
1863 - William Roos (Randall's
brother-in-law) joined company;
1864 - Joseph Emm Seagram hired;
1869 - Seagram
acquired Hespeler's share of company; renamed "George Randall
and Company"; 1878
- Seagram bought out Randall; 1881
- name changed to "Seagram and Roos";
1883 - bought out Roos, used names
"Joseph Seagram Flour Mill and Distillery Company", "Joseph E.
Seagram, Miller, Distiller"; produced 3,000 barrels of whisky
per year; 1911 -
incorporated, distillery's name changed to Joseph E. Seagram and
Sons Ltd. (Edward, Thomas, Joseph, Norman);
1928 - acquired by Distillers
Corporation Ltd. (founded May 1924 by Samuel Bronfman), formed
Distillers Corporation-Seagrams Ltd.winery.
1857 - Castle
Breweries, first brewery in India, set up in Ooty; four more
breweries followed; March 15, 1915 - Thomas
Leishman, Scotsman, purchased 5 breweries to form United
Breweries Ltd.; 1955 - Kingfisher Lager Beer
introduced.
January 5, 1858
- Ezra J. Warner, of Waterbury, CT, received patent for a "Can
Opener" (a new and Useful Improvement in Instruments for Cutting
Open Sealed Tin cans and Boxes"); design of a can opener
(intended for grocers' use).
1859
- Adolphus Busch opened a wholesaler commission house in St.
Louis, sold brewing supplies; 1860 - Eberhard
Anheuser acquired Bavarian Brewery (ranked 29th of 40
breweries in St. Louis), renamed "E. Anheuser & Co."; 1861
- Busch married Lilly Anheuser,
Eberhard's daughter;
1864
- Adolphus Busch started working at E. Anheuser & Co as
salesman; 1875 - co-partnership incorporated under
name of E. Anheuser and Company Brewing Association;
1876
- Charles W. ("Carl") Conrad, St. Louis wine merchant,
contracted with Anheuser-Busch to brew "Budweiser" with imported
(Saazer) hops and (Bohemian) barley, mash prepared by infusion
(Budweis is name of small Bohemian city; introduced because of
its Germanic sound, potential appeal to American and German
migrants); 1870s - first U.S. brewery to adopt
pasteurization; 1872 - first use of A&E eagle on
packaging; July 16, 1878 - Charles W.
("Carl") Conrad
registered "Budweiser" trademark (canceled October 21, 2005);
April 29, 1879 - company renamed
Anheuser-Busch Brewing Association;
January 16, 1883
- C. Conrad & Co., bottler and distributor for Budweiser®,
declared bankruptcy during "Panic of 1883"; April 24, 1883
- Anheuser-Busch acquired rights to bottle and sell
Budweiser;
March 2, 1886 - C. Conrad & Co. (Mainz, Germany)
registered "Budweiser" trademark first used in January 1876
(lager bier only genuine as decreed by the courts original as
decreed by the courts); 1891 - Anheuser-Busch
Brewing Association acquired brand/trademark, ownership of
'Budweiser' name; July 23, 1907 - Anheuser-Busch
Brewing Association registered "Budweiser" trademark first used
in January 1876 (beer); January 15, 1918 -
registered "Michelob" trademark first used April 15, 1896
(draft-beer); August 26, 1958 - registered "Bud"
trademark first used in June 1939 (beer); July 13, 2008
- agreed to be acquired by Belgian rival InBev for $52
billion; created global brewing giant with ownership of some of
world’s best-known brands (Stella Artois, Bass, Hoegaarden).
1859 - Charles Arbuckle, Duncan McDonald, William Roseburg organized
McDonald & Arbuckle, wholesale grocery business in Pittsburgh,
PA; 1860 - John Arbuckle (brother) joined company;
renamed McDonald & Arbuckles; 1865 - one roaster,
sold roasted coffee in airtight, original, one pound packages
(vs. loose coffee in roasted state);
January 21, 1868 - John Arbuckle, of Allegheny City, PA,
received a patent for an "Improvement in Roasted Coffee"
("roasting coffee and then coating it with a glutinous or
gelatinous matter, for the purpose of retaining the aroma of the
coffee, and also act as a clarifying-agent when the ground
coffee has been boiled in water"); process of glazing coffee to
seal in freshness of coffee bean; 1873 - launched
Ariosa coffee package, first successful national brand of
packaged coffee; 1881 - 85 roasters running in
Pittsburgh and New York; March 31, 1891 - Henry E.
Smyser, of Philadelphia, PA, received a patent for a "Package
Making and Filling Machine"; received a patent for an "Automatic
Weighing Machine" ("intended to automatically measure and
deliver weighed quantities of granulated, pulverized, or sililar
material"); March 1, 1892 - Smyser received a
patent for a "Feed-Machanism for Weighing-Machines"; assigned to
Arbuckle Brothers; 1896 - Arbuckle entered sugar
refining business (based on Smyser patents); 1898
- Brooklyn sugar refinery produced 5,000 barrels per day of
package sugar; February 3, 1903 - John Arbuckle,
of Brooklyn, NY, received a patent for an "Apparatus for
Roasting Coffee" ("each bean shall be separately roasted by
being surrounded on all sides by the hot air of fire-gases and
while out of contact with other beans"); assigned to Arbuckle
Brothers; 1913 - introduced Yuban coffee (guest
coffee for guests at Christmastime, short for 'Yuletime
Banquet'); April 7, 1914 - Arbuckle Brothers
registered "Yuban" trademark first used November 1, 1913
(coffee); 1944 - General Foods acquired Yuban.
 John Arbuckle
- Arbuckle Coffee
(http://books.google.com/books?id=Y5tXt7aoLNoC&pg=PA523&img=1&zoom=3&hl=en&sig=ACfU3U3me26bsR5wu7U-3aLnkAeTzykrQw&w=575)
John Arbuckle
- Arbuckle Coffee
(http://books.google.com/books?id=Y5tXt7aoLNoC&pg=PA523&img=1&zoom=3&hl=en&sig=ACfU3U3me26bsR5wu7U-3aLnkAeTzykrQw&w=575)
1859 - Luigi
Moretti (37) founded "Beer and Ice Factory" in Udine, in
region of Friuli; already had well-established business in
wholesale trade of cereals, wine, liquors, foodstuffs, beer
bought in nearby Austria.
1859 - Louis
Henri Denis Jadot, originally from Belgium, founded Maison Louis
Jadot (family had bought Clos des Bursules, Beauned Premier Cru,
in 1826); 1900 -
Louis Jean Baptiste (son) took over; acquired many vineyards;
1939 - Louis
Auguste Jadot took over: with help of Rudy Kopf (founder of
Kobrand Corporation, Jadot's U.S. importer) developed export
markets in England and U.S.; 1962
- Andre Gagey took over (joined company in 1954);
1985 - acquired by
Rudy Kopf family; 1992
- Pierre-Henri Gagey (son) became president (joined company in
1984).
 Louis Henri Denis
Jadot - Maison Louis
Jaddot
Louis Henri Denis
Jadot - Maison Louis
Jaddot
(http://www.lovejadot.com/images/founder.jpg)
April 6, 1859
- Legislature of state of Massachusetts created first Inspector
of Milk position in U.S.
1860 -
Gaspare Campari founded Gruppo Campari in Milan;
October 22, 1929 -
Davide Campari registered "Campari" trademark first used in
March 1888 (liquor to be drunk with simple or carbonated water
and generally used as an aperient); 1932
- created Campari Soda,
pre-mixed cocktail in cone-shaped bottle designed by Italian
futurist designer, Fortunato Depero.
 Gaspare Campari
- Gruppo Campari
(http://www.italie.nl/culinair/wijn/images/lombardia_gaspare-campari.jpg)
Gaspare Campari
- Gruppo Campari
(http://www.italie.nl/culinair/wijn/images/lombardia_gaspare-campari.jpg)
1860 - German immigrant August Schell, Jacob
Bernhardt, former brewmaster at Benzberg Brewery (in St. Paul,
MN) established Minnesota Brewing Company in New Ulm, MN next to
spring in Cottonwood River Valley;
1866 - Schell acquired Bernhardt's share for
$12,000; 1878 -
Adolph and Otto Schell (sons) took over;
1880 - Otto Schell, George Marti
(brother-in-law) took over; 1902
- brewery incorporated, Otto Schell as president;
1911 - George Marti
took over; Prohibition - brewery produced "near beer," assorted
soft drinks, candy; 1936
- Alfred Marti (son) took over;
1969 - Warren Marti (grandson) took over;
1985 - Ted Marti
(great grandson) took over; introduced line of "specialty"
beers; brewery made 38 different beers, 16 of which were
contracted lines sold under different names;
2002 - acquired 109
year-old Grain Belt beer; became largest brewery (in terms of
gallonage) in Minnesota, oldest brewery in Minnesota;
second-oldest family owned brewery in US.
 August Schell
- Schell's Brewing
Co.
(http://www.schellsbrewery.com/images/image01.jpg)
August Schell
- Schell's Brewing
Co.
(http://www.schellsbrewery.com/images/image01.jpg)
1860s -
Piotr Arsenieyevich Smirnov founded Smirnov vodka distillery;
first in world to use charcoal filtering process; 1886
- made 'Official Purveyor' of vodka to imperial Russian court;
1910 - Vladimir Smirnov, third son, assumed
control; 1917 - distillery confiscated by
Bolsheviks during October Revolution; Vladimir Smirnov sentenced
to death, escaped Russia; 1920 - restarted family
business in Constantinople; 1924 - moved company
to Lwów, Poland; name changed to Smirnoff; 1925 -
second distillery opened in Paris; 1934 - acquired
during Great Depression by Russian emigree Rudoplh Kunett; moved
company to United States; 1938 - acquired by G.F.
Heublein & Bro.; 1955 - name changed to Heublein,
Inc.
March 27, 1860
- M. L. Byrn of New York City received a patent for a
"Corkscrew" ("a new and useful improvement in corkscrews"); a
"covered gimlet screw with a 'T' handle".
1861 -
Charles Krug (27), Prussian immigrant, founded Charles Krug
Winery; first in Napa Valley; major local winery figure of his
era; 1893 - acquired by James Moffitt; 1943
- acquired by Cesare (60) and Rosa Mondavi, Italian immigrants,
for $75,000; 1959 - Rosa named president at Cesare
death; Robert (son) - General Manager, Peter (son) - Vice
President; 1965 - Robert moved south to Oakville,
Peter became President; 1966 - Robert founded
Robert Mondavi Winery.
1861 - Edward
Frauenheim, German immigrant, partners formed Frauenheim, Miller
& Company on 17th Street in Pittsburgh, PA; named first beer
Iron City in honor of Pittsburgh's leading industry;
1880s - name
changed to Frauenheim and Vilsack (interests of Frauenheim's
original partners acquired by Leopold Vilsack); annual capacity
of 50,000 barrels, (one of largest outside of East Coast);
1899 - merged with
20 regional breweries, formed Pittsburgh Brewing Company; total
capacity more than one million barrels per year;
1918 - total
production of 855,795 31-gallon barrels;
1933 - formed new subsidiary, Iron City
Brewing Company; November 24, 1953
- registered "Iron City" trademark first used December 2, 1889
(beer); mid-1950s -
best-selling beer in Pittsburgh area;
1962 - introduced easy-opening "snap
top" can; 1963 -
introduced twist-off re-sealable bottle top;
1964 - annual sales
of $17 million; 1976
- launched first low calorie beer, Mark V;
1984 - revenues topped $44.7 million;
1985 - acquired by
Australian financier Alan Bond's Bond Corporation Holdings Ltd.
for $28.5 million; January 1988
- reorganized as unit of new $1.2 billion Bond acquisition of G.
Heileman of Wisconsin; 1991
- acquired by Michael Carlow for $28.5 million (40; with his
father Frank, had recently taken control of the troubled
Pittsburgh-based candy maker D.L. Clark Company);
February 1995 -
Carlow declared bankruptcy;
September 12, 1995 - Keystone Brewers, headed by
32-year old former trash hauling company owner Joseph Piccirilli,
financier James M. Gehrig, paid $12.4 million, assumed $17
million in debt; August 2004
- first large U.S. firm to use new aluminum bottle (cold
longer); eleventh-largest brewer in United States;
2005 - filed for
Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection;
2007 - acquired, brought out of bankruptcy by
Unified Growth Partners; renamed Iron City Brewing Company.
June 22, 2009 -
brewing moved to Latrobe, PA.
1862 - Jerry P.
Thomas, first assistant to principal bartender at A.J. McCabe's
El Dorado, gambling saloon in San Francisco, published "How To
Mix Drinks or The Bon Vivant's Companion", first known published
cocktail recipe book; invented cocktails.
1862 - Andrew
Heublein founded company as restaurant, hotel business;
1875 - company
incorporated; 1890
- Gilbert F. Heublein (son) took over;
1915 - incorporated in Connecticut as
G.F. Heublein & Bro.; 1937
- John Gilbert Martin (great-grandson) became president;
1939 - acquired
Smirnoff Vodka from Russian emigree Rudoplh Kunett (had acquired
it in 1934 from Vladimir Smirnov) for $14,000;
1955 - changed name
to Heublein, Inc.; August 14, 1956
- registered "Heublein" trademark first used in April 1955
(prepared alcoholic cocktails, brandy, and liqueurs);
1982 - acquired by
RJR Nabisco; 1987 -
acquired by GrandMet for $1.3 billion.
 Andrew Heublein
(at right) - Heublein Inc.
(http://farmingtonvalley.net/photos/talcott/images/181/640x480.aspx)
Andrew Heublein
(at right) - Heublein Inc.
(http://farmingtonvalley.net/photos/talcott/images/181/640x480.aspx)
1862 - Jacob
Schram bought 200 acres near St. Helena, in Napa Valley;
established Schramsberg Winery;
1876 - produced 12,000 gallons;
1889 - Schramsberg
and Inglenook only CA wines listed on menu at Palace Hotel;
1940 - acquired by
John Gargano (California Champagne Company);
1951 - acquired by
Douglas Pringle; 1965
- acquired by Jack and Jamie Davies.
February 4, 1862
- Don Facundo Bacardi Masso bought small, tin-roofed,
dirt-floored distillery for 3,500 pesos on Matadero Street in
eastern city of Santiago de Cuba; created world's first
light-bodied rum; devised charcoal filter system, began aging
rum in oak barrels; 1910-
Emilio (oldest son) expanded to Spain (Cuba's first
multi-national); 1915
- expanded to U. S.; 1919
- renamed Compania Ron Bacardi, S. A.;
March 6, 1934 - registered "Bacardi"
trademark first used in 1862 (rum);
1949 - Jose M. "Pepin" Bosch (son-in-law
of Emilio's brother-in-law's son), former Cuban Finance
Minister, became 4th president;
October 1960 - Fidel Castro nationalized company
assets (loss of $76 million, 90% of company's sales volume);
began again in Puerto Rico; 1992
- Manuel Jorge Cutillas (Emilio's great-great-grandson)
reorganized, created holding company, Bacardi Limited
(previously five separate operating companies; expanded brands;
acquired Martini & Ross group of companies = transformed from
rum to spirits company; 1998
- acquired DEWAR's Blended Scotch Whiskey, BOMBAY SAPPHIRE gin
brands; world's largest private spirits company;
2005 - Faundo L.
Bacardi (5th generation) became Chairman of the Board;
2008 - annual sales
of 20 million cases in more than 150 countries (excluding Cuba).
 Don Facundo Bacardi Masso
- founder Bacardi
(http://www.s9.com/images/portraits/1522_Bacardi-Facundo-Don.jpg)
Don Facundo Bacardi Masso
- founder Bacardi
(http://www.s9.com/images/portraits/1522_Bacardi-Facundo-Don.jpg)
April 20, 1862 -
Louis Pasteur and Claude Bernard completed first test of
pasteurization (heated foods sufficiently to kill germs without
significantly altering chemical composition); applied by brewers
- heated finished beer to above 160ºF to kill harmful bacteria;
germ-free beer did not require constant refrigeration for
lengthy shipment or storage; came to be used for milk, other
products; January 28, 1873
- Louis Pasteur received a patent for "Brewing Beer and Ale";
improvement in process of brewing beer and ale;
July 22, 1873 -
received a patent for a yeast process.
1863 - Caleb Chase began in business as coffee
roaster in Boston; 1878 - joined with James
Sanborn, formed Chase & Sanborn Coffee; shifted from bulk to
packaged coffee; first ground coffee to be distributed to both
coasts; first to pack, ship roasted coffee in sealed cans;
1882 - sold 100.000 ponds of coffee/month; 1929
- merged with Fleischmann Company, Royal Baking Powder Company,
became Standard Brands Incorporated; July 13, 1954
- Standard Brands Incorporated registered "Chase & Sanborn"
trademark first used February 1, 1888 (coffee); May 1983
- filed for Chapter 11 federal bankruptcy protection;
September 1984 - acquired by Hills Bros.; 1985
- acquired by Nestle Holdings; December 1999 -
acquired by Sara Lee.
1864 - Gerard Adriaan Heineken bought
money-losing Hooiberg (Haystack) brewery in heart of Amsterdam
(dates to 1592); 1884 - registered green
Heineken label as a trademark; December 1933 -
made Leo van Munching Sr. sole distributor in U. S. market.
1865
- Theodore Hamm inherited Keller's Excelsior Brewery (started in
1860) from his friend, business associate, A. F. Keller (died
after arriving in California for the Gold Rush); brewery
constructed over artesian wells on east side of Saint Paul, MN
in section above Phalen Creek valley, known as Swede Hollow;
1886 - William
(son) joined company, 75 employees, 40,000 barrels, T. Hamm
Brewing Co. second largest in state;
September 1894 - moved to new building;
1896 -
incorporated; 1903
- William (son), William Jr. (grandson) inherited business;
November 7, 1950 -
Hamm Brewing Co. registered "Hamm's" trademark first used
November 10, 1894 (beer); 1968 - acquired by Heublein Brewing
Company; acquired by Olympia Brewing Company;
1980 - merged with
Pabst; 1984 -
acquired by Stroh's; 1999
- acquired by Miller Brewing; acquired by by South African
Breweries.
1865
- Scottish businessman Lauchlin Rose entered juice business;
1867 - patented
process of preserving lime juice without using rum;
August 20, 1867 -
British Parliament enacted Merchant Shipping Act; mandated that
lime or lemon Juice and other anti-scorbutics be provided and
kept on board certain ships; sweetened juice from Rose's West
Indian limes became shipboard staple;
May 30, 1899 - L. Rose & Company Limited
registered "Rose's Sweetened Lime Juice" trademark first used in
July 1867 (lime juice); 1901
- introduced in United States; 1957
- L. Rose & Company acquired by Schweppes;
1982 - merged with Mott's (acquired by
Cadbury Schweppes); 2003
- introduced Rose's Cocktail Infusions; used in more mixed
drinks than any other non-alcoholic ingredient;
2008 - beverage
operations divested, acquired by Dr Pepper Snapple Group, Inc.
December
26, 1865 - James H. Nason, of Franklin, MA, received
patent for a "Coffee Percolator" ("construction of apparatus for
preparing the extract or infusion from coffee").
1866
- James Vernor, former
employee of Higby and Sterns' Drug Store, opened pharmacy in
Detroit; opened barrel of 4-year-old ginger ale extract; aging
had mellowed taste to perfection; created Vernor’s Ginger Ale; sold
bottling franchises with strictly adherence to recipe;
1896 - closed
drugstore, concentrated on ginger ale business; James Vernor Jr.
entered business; August 15, 1911
- James Vernor registered "Vernor's" trademark first used
January 1, 1880 (ginger-ale and ginger-ale extract);
1966 - acquired by
investor group; 1971
- acquired by American Consumer Products;
1979 - acquired by United Brands;
1985 - closed
flagship Detroit bottling plant, granted local bottling rights
to Pepsi-Cola; 1987
- acquired by by A&W Beverages;
1993 - acquired by by Dr Pepper/Cadbury
Schweppes;
America’s oldest continuously produced soft drink.
 James Vernor
- Vernor's Ginger Ale
(http://image1.findagrave.com/photos/2009/223/13440272_125012212463.jpg)
James Vernor
- Vernor's Ginger Ale
(http://image1.findagrave.com/photos/2009/223/13440272_125012212463.jpg)
May 1867 -
Jacob Leinenkugel, John Miller built Spring Brewery (water from
spring on brewery grounds), 24 by 50 foot building in Chippewa
Falls, WI (home of world's largest lumbering mill); 400 barrels
brewed, kegged in first year delivered in one horse-cart;
1884 - Miller
interest acquired by Leinenkugel; renamed Jacob Leinenkugel
Brewing Company; 1890
- production increased to 200 barrels/day;
1898 - incorporated;
1907 - Matthias
(Matt) Leinenkugel (son) became president;
1950s - acquired Bosch Brewing Company
(Houghton, MI), expanded distribution to Minnesota, Upper
Peninsula of Michigan, Chicago;
1955 - first brewery in U.S. to be 100% equipped
with closed, glass-lined fermentation tanks;
1988 - acquired by
Miller Brewing (second largest brewer in world); remained
family-run; 2008 -
brews 7 year-round, 4 seasonal brews distributed in 38 states;
seventh oldest brewery in United States.
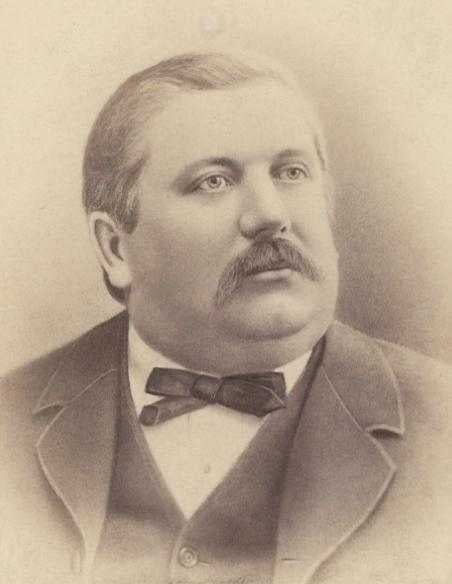 Jacob Leinenkugel
(http://wqow.images.worldnow.com/images/10390367_BG1.JPG)
Jacob Leinenkugel
(http://wqow.images.worldnow.com/images/10390367_BG1.JPG)
August 8, 1868
- Baron James de Rothschild acquired Chateau Lafite (for sale as
part of Ignace-Joseph Vanlerberghe succession) in village of
Pauillac, France; October 22, 1868
- passed away, became joint property of Alphonse, Gustave and
Edmond deRothschild (sons); 74 hectares of vineyards;
1855 - "golden age"
of Medoc; 1946 -
Baron Elie de Rothschild entrusted with recovery of Estate;
1962 - acquired
Chateau Duhart-Milon, owned by Casteja family for more than
century; 1974 -
Baron Eric (nephew) took over management of Lafite;
1984 - acquired
Chateau Rieussec (Sauternes and Chateau Paradis Casseuil, Entre
Deux Mers); 1988 -
acquired Vina Los Vascos (founded around 1736) from Chilean
family Echenique-Eyzaguirre; acquired Chteau l'Evangile (owned
by Ducasse family for over century);
1992 - acquired Quinta do Carmo (owned
by Portuguese royal family since time of King Don Juan IV).
 Baron James de Rothschild
- Chateau Lafite
(http://www.lafite.com/var/ezflow_site/storage/images/history/1868/493-1-fre-FR/1868.jpg)
Baron James de Rothschild
- Chateau Lafite
(http://www.lafite.com/var/ezflow_site/storage/images/history/1868/493-1-fre-FR/1868.jpg)
1869 - Dr. Thomas Bramwell Welch,
physician and dentist, and Charles Welch (son) successfully
pasteurized Concord grape juice to produce "unfermented
sacramental wine" for fellow parishioners at his church in
Vineland, NJ; marked beginning of processed fruit juice
industry;
April 25, 1916 -
Welch Grape Juice Company registered "Welch's" trademark first
used in 1892 (grape-juice); 1952 - acquired by The
National Grape Cooperative Association, Inc. (grower-owned
agricultural cooperative of 1,400 grape growers with farms
throughout Michigan, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Washington,
Ontario, Canada).
1869
- Arthur Brooke founded Brooke, Bond & Co. (added Bond to firm's
name to make it sound more upper class); one of first British
tea merchants to market uniform blend of tea, sell directly to
retailers (bulk at wholesale rates) instead of to middlemen;
1912 - Gerald
Brooke (son) became chairman of company; made company's red
delivery vans so popular that British toy stores sold
miniatures; extended sources of supply, built 30,000-acre
plantation empire in India, Ceylon, Africa;
1984 - acquired by Unilever.
 Arthur Brooke
- Brooke, Bond & Co.
(http://www.bbc.co.uk/manchester/content/images/2005/03/01/
arthur_brooke_150_150x180.jpg)
Arthur Brooke
- Brooke, Bond & Co.
(http://www.bbc.co.uk/manchester/content/images/2005/03/01/
arthur_brooke_150_150x180.jpg)
1870s
-
Bohemian
Frantissek (Francis) Korbel ("goblet, drinking cup" in Czech),
Joseph and Anton Korbel, formerly of F. Korbel & Bros.,
successful manufacturing business producing materials for
building industry in San Francisco, CA,
purchased sawmill, property near Guerneville in Russian River
Valley of Sonoma County, in partnership with another
entrepreneur; brought in another brother, Winsel, from Bohemia,
to run business; brothers bought out partner 1882
- ran small winemaking operation, produced some 20,000 to 30,000
gallons of wine from vineyard yields; 1884 -
closed dairy, converted all ranch lands to vineyards, devoted
all of energy to winemaking; mid-1890s - shipped
first champagnes; 1900 - internationally known,
award-winning label; 1954 - acquired by Adolf
Heck, third-generation winemaker (former president of Italian
Swiss Colony Wine Company); 1956 - reintroduced
Korbel Brut, lighter and drier than any American champagne on
market; introduced Korbel Natural', Korbel Blanc de Blancs (100%
Chardonnay), Korbel Blanc de Noirs (100% Pinot Noir), all
created using champagne yeasts; October 13, 1970 -
Adolf L. Heck and Allan J, Hemphill, both of Guerneville, CA of
received two patents for an "Apparatus for Riddling Bottled
Wines"; automatic riddling machine allowed each bottle of Korbel
champagne to undergo exact turns at precise times to ensure
consistent taste and quality in every bottle (riddling done by
hand, costly and time-consuming method that left champagne's
quality vulnerable to variability of human hands);
November 9, 1971 - received a second patent for
"Riddling Bottled Wines"; 1982 - Gary Heck (son)
appointed president; 1984 - named chairman of board; 2000
- shipped record 1.678 million cases of champagne.
1870 - John
Ross, owner of Broadford Hotel on island of Skye, made liqueur
concoction (base of 100% aged Scotch Whiskies, blended with
finest herbs, honey), supposedly descended from gift for
services from Bonnie Prince Charlie to MacKinnon of Skye;
September 20, 1893
- James Ross (son), of The Drambuie Liqueur Company Limited,
registered "Drambuie" trademark in Great Britain (liqueur);
May 9, 1933 -
Drambuie Liqueur Coy Limited (Edinburgh, Scotland) registered "Drambuie"
trademark in U. S. first used August 1871 (distilled alcoholic
liqueur); Drambuie - "the dram that satisfies" ('An Dram
Buidheach' - Gaelic).
January 25, 1870
- Gustavus D. Dows, of Boston, MA, received a patent for an
"Improvement in Soda-Fountains"; vessel in which carbon dioxide
was injected, formed soda-water beverage, delivered drink
using internal pressure; modern form of soda fountain;
1858 - made first ornamented soda fountain in the U.S.
from white Italian marble with spread eagles perched on the
syrup cocks; 1862 - invented a double stream draft
arm and cock, for a large or small stream; 1863 -
made and sold soda fountains for $225.
July 12, 1870
- William W. Lyman of Meriden, CT, received a patent for a "Can
Opener" ("relates to an improved instrument for opening metal
cans and boxes"); household can opener with rotating cutter that
pivoted around hole punched in center of can;
1925 - The Star Can
Company of San Francisco introduced jagged wheel for rotating
the can by; December 1931
- Philips invented electric can opener;
April 2, 1935 - Dewitt F. Sampson
(Elmhurst, IL) and John M. Hethersall (Brooklyn, NY) received a
patent for a "Container Opener" (object was "to provide a
container opener which at one stroke or turning movement
provides a substantial pouring opening in a wall of a
container"); can opener also known as a "churchkey".
1871
- Thomas J. Lipton opened for business in Glasgow, Scotland;
1880 - twenty
stores; 1890 - 300
stores; visited Ceylon, bought five bankrupt plantations
(eventually acquired about a dozen others), unveiled slogan
"Direct from the Tea Gardens to the Teapot"; advertisements
claimed "It's brisk" (taster's jargon for any tea that is not
stale or flat-tasting); 1898
- knighted by Queen Victoria; went public as Thomas J. Lipton,
Ltd.;
1899 - entered tea
business, celebrated arrival of first twenty thousand tea chests
in Glasgow; priced tea at one shilling seven pence per pound
(vs. usual price of 3 shillings per pound); tea
trade's largest worldwide success throughout 20th century;
replaced China tea decisively in West (British colonial-built
industries took root in new tea lands of India, Ceylon
elsewhere); China trade dwindled into insignificance;
January 25, 1949 -
registered "Lipton" trademark first used in 1893 (tea and
packaged soup).
1872 - Ernest
Reuben Lilienthal,
salesman in New
York for Freiberg & Workum whiskey vendors of Ohio,
moved to San
Francisco, established Lilienthal & Co., wholesale liquor
operation; sold Freiberg & Workum products, especially Cyrus
Noble Bourbon; 1895 - largest wholesaler in west;
1896 - liquor business spun off from company’s
other enterprises, incorporated as Crown Distilleries Company;
1916 - combined with grocery operations of Haas
Brothers;
February
13, 1934 - Benjamin P. Lilienthal registered "Cyrus
Noble" sour-mash bourbon trademark first used in 1871
(whiskey).
1872 - Danish
financier Carl F. Tietgen founded Danish Sugar; acquired Phoenix
sugar refinery at Langebro bridge in Copenhagen;
1881 - founded
Danish Distillers; 1934
- founded Dansk Handels- og Industri-Compagni (A/S Danisco) as
conglomerate; 1989
- Danish Sugar, Danish Distillers, Dansk Handels- og
Industri-Compagni merged, formed A/S Danisco; acquired
Andelsselskabet Sukkerfabrikken Nykobing, became only sugar
producer in Denmark; 2001
- name changed to Danisco; 2007
- sold Flavours Division to Firmenich, became four divisions:
Genencor, Cultures, Texturants, Sweeteners and Sugar.
 Carl F. Tietgen
- Danisco
(http://www2.kb.dk/elib/mss/dmg/teknik/TIETGEN-1.jpg)
Carl F. Tietgen
- Danisco
(http://www2.kb.dk/elib/mss/dmg/teknik/TIETGEN-1.jpg)
April 9, 1872 -
Samuel R. Percy, of New York, NY, received a patent for
"Improvement in Drying and Concentrating Liquid Substances by
Atomizing"; dried milk.
1873 -
James and William Horlick, brothers from Gloucestershire,
founded J & W Horlicks in Chicago; June 5, 1883 -
William Horlick (Racine, WI) received a patent for "Granulated
Food for Infants and Process for Preparing the Same" (malted
milk drink mixing powder with hot water); July 8, 1886
- Horlick's of Wisconsin offered first malted milk to public; 1969 - acquired by Beecham
Group.
1874 - John
Thomann established Thomann Winery in St. Helena, CA (Henry
Thomann, uncle, had established vineyard in Sacramento, CA in
1852 on land bought from General John A. Sutter [may have been
first vineyard planted in California for purpose of winemaking];
produced first wine in 1856; John Thomann (nephew) joined
business in 1858; made peach and grape brandy [one of first in
State] in 1859; rented wine business from his uncle in 1860;
moved business to Napa County in 1874);
1906 - acquired by Caroline and Emil
Leuenberger (Caroline Sutter [daughter of San Francisco
businessman and sea captain, John A. Sutter] had purchased 80
acres on lower slopes of Howell Mountain [near St. Helena, CA]
in 1890, named Sutter Home [in honor of her father]; Caroline
and Emil Leuenberger established Sutter Home Wine and Distillery
Company on Folsom St, in San Francisco in 1895; winery produced
200,000 gallons in 1900; lost everything in 1906); renamed
Sutter Home; sold Howell Mountain Winery;
1909 - no wine produced (decline since
Panic of 1907); 1919-
Prohibition began, winery went dormant;
1947 - acquired by John and Mario
Trinchero; early 1950s
- produced 52 different wines; 1958
- Bob Trinchero (son of Mario) joined business;
1960 - John
Trinchero interest acquired by Mario and Bob Trinchero;
1968 - produced
Amador Countu Zinfandel - first real success;
1972 - introduced
white zinfandel; 1986 - acquired Victorian mansion on property
(reunited with vineyard); March 4,
1986 - Sutter Home Winery, Inc. registered
"Sutter Home" trademark first used in 1900 (first used in
business in 1972; wine); 1987
- Sutter Home White Zinfandel best-selling premium wine in
United States; 1998
- produced about 4 million cases of zinfandel; sixth largest
winery in U.S.; 1999
- renamed Trinchero Family Estates.
1875 -
Frederick and Jacob Beringer purchased 215 acre parcel of land
for $14,500 in Napa Valley; called winery Los Hermanos, or "The
Brothers"; 1876 - first crush (approximately
40,000 gallons or 18,000 cases; 1887 - Beringer
wines won first awards at Mechanics Institute Exposition in San
Francisco; 1934 - first winery to offer public
tours, began area's tourist wine business; 1956 -
wine tasting offered; 1990 - Beringer 1986
Cabernet Sauvignon named #1 Wine of the Year by Wine Spectator;
1996 - Beringer 1994 Chardonnay named #1 Wine of
the Year by Wine Spectator (first time for a white); oldest
continuously operating winery in Napa Valley; October 1,
2000 - Beringer
Wine Estates Holdings, Inc. acquired by Foster's Brewing Group
Limited for $1.2 billion.
 Frederick Beringer
(http://www.napanow.com/
graphics/fberinger.jpg)
Frederick Beringer
(http://www.napanow.com/
graphics/fberinger.jpg)
 Jacob Beringer
- Beringer Winery
(http://www.napanow.com/graphics/jberinger.jpg)
Jacob Beringer
- Beringer Winery
(http://www.napanow.com/graphics/jberinger.jpg)
1875
- John Fraser formed partnership with David Chalmers Neave,
printer at Singapore Straits Printing Company; acquired
Keasberry's Mission Press, renamed it Fraser and Neave;
1883 - founded
Singapore and Straits Aerated Water Company to produce
carbonated soft drinks; 1898
- incorporated as Fraser and Neave (F&N), Ltd.;
1931 - formed
Malayan Breweries Limited in joint venture with Heineken
Breweries; 1932 -
launched Tiger Beer; 1936
- acquired distribution franchise for Coca-Cola in Singapore and
Malaysia; 1941 -
acquired Anchor Brewery and brand;
July 27, 1999 - F & N Group initiated new
strategic direction: food and beverage, properties,
publishing/printing (acquired 20.1% interest in Times Publishing
Limited in December 1999, 87.5 % interest in June 2000.
1875
- Robert Barr, family in cork cutting business since 1830,
started producing, selling aerated waters (soft drinks) at
Burnfoot Lane in Falkirk, Scotland;
1887 - Robert F. Barr (son) established
R.F. Barr's Glasgow, independently run, Barr aerated waters
business, in Great Eastern Road, Glasgow;
1892 - Andrew G. Barr (son) took over
Glasgow business as sole proprietor, name changed to A.G. Barr &
Co.; 1901 -
launched original recipe IRON BREW; quickly became No1 soft
drinks business in Scotland; re-launched IRN-BRU onto UK
national stage, beyond; 1903
- William Snodgrass Barr (brother, 24) took over management
control of A.G. Barr & Co. Glasgow; engaged many sporting heroes
of day to endorse brand; 1959
- A.G. Barr & Co. Ltd. acquired Robert Barr Ltd. Falkirk;
1964
- brand name changed to phonetic respelling as IRN-BRU;
1965
- went public; 1967 - acquired Stotherts Ltd. Atherton,
brought soft drinks cans into Barr product portfolio;
1978 - received
O.B.E. (order of the British Empire) for services to soft drinks
industry; 1979 -
replaced Plastishield glass bottles with PET (Polyethylene
Terephthalate) packaging; 2000-2009
- invested in own brands (IRN-BRU, Tizer, D'N'B, St Clements),
expanded via in-house new product development, franchise
distribution agreements (Orangina, Rubicon, Rockstar), brand
acquisitions (Strathmore Spring water, Vitsmart, Rubicon, TAUT);
introduced IRN-BRU into number of international soft drinks
markets (Russia, Spain, Australia);
February 2009 - IRN-BRU became official
soft drink sponsor of Rugby League until 2010, broadcast sponsor
of Sky Sports' Super League coverage for 2009 (over 10 million
viewers through 60 live games broadcast during season).
 Robert Barr
- A. G. Barr plc
Robert Barr
- A. G. Barr plc
(http://www.agbarr.co.uk/images/Robert-Barr-100x120.jpg)
1876
- Bass brewery registered red triangle logo trademark, first
(reg. no. 1) in United Kingdom.
1876
- Charles E. Hires, Philadelphia pharmacist, introduced Hires
Root Beer at 1876 U.S. Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia;
herbal tea made of roots, berries, herbs; originally called
Hires Root Tea; called it "root beer" at suggestion of friend
who thought that, given popularity of beer, more workers would
buy it; 1878
- sold 864 bottles of extract in first year (1991 - almost two
million); 1879 -
lost patent for name "Root Beer";
1893 - offered bottled root beer;
January 16, 1894
- Charles E. Hires Company registered "Hires" trademark first
used in 1878 (root beer).
 Charles E. Hires
- Hires Root Beer
(http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcR__DVa7T3TIJCocsAzM0LlcA2nCz_lFASdM7MO6SNRhOl6GfYQ&t=1)
Charles E. Hires
- Hires Root Beer
(http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcR__DVa7T3TIJCocsAzM0LlcA2nCz_lFASdM7MO6SNRhOl6GfYQ&t=1)
1876 - Giuseppe and Pietro Simi ( traveled
from Tuscany, Italy, to California during the Gold Rush) founded
Simi Winery; 1881 - moved winemaking operations to
Healdsburg (northern Sonoma County); 1890 -
completed construction of first stone cellar.
March 25,
1876 - Carl von Linde, professor at Technical
University of Munich, Germany, received Bavarian patent for
refrigeration machine; August 1877
- received German Reichspatent; assigned part of patent rights
to Gabriel Sedlmayr of Munich Spaten Brewery, to locomotive
builder Georg Krauss, to Heinrich von Buz, director of
Maschinenfabrik Augsburg, in exchange for funds needed to
develop, build, test new refrigeration machine; reliable,
economic refrigeration system used in breweries because of
shortage of natural ice during in warm winters for fermentation,
cooling of cellars; Rotterdam Heineken Brewery ordered ice
machine for ice production; 1878 - Carlsberg
Brewery in Copenhagen ordered large refrigeration unit.
June 1876 - Seibei Nakagawa, recently returned to Hokkaido,
northernmost island in Japanese archipelago, from
studying
art of beer
making in Germany, chosen as brewmaster to oversee construction
of beer factory; September 1876 - Kaitakushi
Brewery completed; 1877 - Sapporo Lager created,
prominently displayed Pioneers' symbol, North Star; 1886
- renamed Sapporo Brewery Factory acquired by Okura Trading
Company (Kihachiro Okura); December 1887 -
acquired by group of entrepreneurs, led by Eiichi Shibusawa and
Soichiro Asano; established Sapporo Beer Company; September
1887 - group of local entrepreneurs established Japan
Beer Brewery Company in Mita,
Meguro, Tokyo; February
1890 - began selling Yebisu Beer; 1906 -
Kyohei Magoshi, head of Japan Beer Brewery Company, merged
Sapporo, Japan, Osaka breweries, formed DaiNippon Beer Company
Ltd. (70% of the Japanese beer market); local brands, common
ownership; September 1949 - DaiNippon Beer
Company Ltd. divided into two companies: Nippon Breweries, Ltd.
and Asahi Breweries, Ltd. (upon application of Law for
Elimination of Excessive Concentration of Economic Power);
1956 - Sapporo Beer revived in its birthplace,
Hokkaido; 1857 - distributed throughout Japan once
again; January 1964 - Nippon Breweries, Ltd.
changed name to Sapporo Breweries, Ltd.; December 1971
- Yebisu Beer, mainstay brand of the DaiNippon Beer Company
Ltd., relaunched after 28-year hiatus.
February 14, 1878 -
Austin & Reuben Hills sold coffee, tea extracts, dairy
products in San Francisco market stall; 1882 -
opened retail store on Harrison St. called Arabian Coffee and
Spice Mills; July 1900 - introduced ground coffee
in
vacuum packed cans (process
patented in 1898 by Norton Brothers of Chicago); bearded figure
in turban, flowing robe logo first appeared; 1906
- company trademark selected, "the taster", inspired by coffee's
Ethiopian origin; 1914 - Red Can brand of coffee
introduced; January 9, 1923 - registered "Hills
Bros" trademark first used March 1, 1878 (coffee); 1930
- expanded to Chicago, became region's best selling coffee;
1964 - expanded to New York area; 1976
- acquired by Jorge Wolney Atalla of Brazil; 1982
- acquired by private investment group; 1985 -
acquired by Nestle; 1999 - acquired by Sara Lee
Corporation; 2005 - acquired by Massimo Zanetti
Beverage USA subsidiary of Segafredo Zanetti Coffee Group.
1879
- Lars Olsson Smith introduced a new kind of vodka called
"Absolut Rent Branvin" (Absolute Pure Vodka); used revolutionary
new distillation method called rectification (still used today);
April 17, 1979 -
Absolut Vodka first exported to U. S. (sold only 10,000
nine-liter cases in first year);
1985 - leading imported vodka in the US.
April 8, 1879
- Echo Farms Dairy Co. of New York sold milk in glass
bottles, first time in U.S.
June 17, 1879 -
Charles G. Hutchinson, of Chicago,
IL, received a patent
for an
"Improvement in Bottle-Stoppers"; seal with rubber stopper
pulled out of bottle by wire attached to bottle; drinker pulled
wire to open bottle; release of pressure caused a 'pop' sound
(derivation of "soda pop"); widely used in early bottling of
sodas; replaced by "Bottle-Sealing Device" for which William
Painter, of Baltimore, MD, received a patent on February 2, 1892
and founded Crown Cork and Seal Company.
June 21,
1879 - Carl von Linde founded Gesellschaft für Linde’s
Eismaschinen Aktiengesellschaft ("Linde's Ice Machine Company",
in Wiesbaden) to commercially refine, market refrigeration
machines; end of 1880s - equipped 445 breweries
with 747 refrigeration machines; ensured year-round
refrigeration; enabled breweries to brew bottom-fermented beer
in summer and winter (beer remained fresh longer, customers
preferred the taste vs. "English" top-fermented brown beers or
ales), considerably increase output, profitability; 1929
- sold 6,599 large refrigeration machines: 2,057 to breweries,
1,865 for food refrigeration, 727 to ice factories, 14 to mines
for sinking shafts in frozen subsoil, 3 for cooling furs - in 17
countries, regions (from Argentina, Central America to China,
Japan, Russia).
 Carl von Linde
- refrigeration machinery
(http://www.chemheritage.org/Discover/Online-Resources/Chemistry-in-History/Themes/Early-Chemistry-and-Gases/asset_upload_file942_36858_thumbnail.jpg)
Carl von Linde
- refrigeration machinery
(http://www.chemheritage.org/Discover/Online-Resources/Chemistry-in-History/Themes/Early-Chemistry-and-Gases/asset_upload_file942_36858_thumbnail.jpg)
1881
- Dr. Satori Kato of Japan presented first instant coffee during
Pan-American World Fair.
1881 -
Genoa-born Andrea Sbarbaro, founder of San Francisco's first
savings and loan association, organized Italian Swiss
Agricultural Colony (Swiss board member) in Sonoma Valley as a
collectivist colony modeled after the cooperative theories of
John Ruskin and Robert Owen; gained reputation for fine dry
wines; December 19, 1939 - registered " Italian
Swiss Colony" trademark first used in 1881 (wines); 1942
- acquired by National Distillers Products Corp.; April
1953 - acquired by Petri Wine Co. for reported $16
million (nation's third largest producer of domestic wines).
February 19,
1881 - Kansas became first state to prohibit all
alcoholic beverages.
April 5, 1881
- Edwin J. Houston and Elihu Thomson, of Philadelphia, PA,
received a patent for a "Centrifugal Creamer"; centrifugal
separator; vessel spins inside case that receives the lighter
components separated "by the action of centrifugal force," while
heavier components drain through an opening in the same tubular
shaft by which the vessel is rotated; various uses - separating
milk and cream, clearing muddy water for paper making.
1882 - Alfred
Loving Tubbs bought 254 acres just north of Calistoga, at foot
of Mount Saint Helena; co-founded Napa Valley Wine Company;
1886 - 50,000 cases produced; 1896 -
Chateau Montelena was seventh largest winery in Napa Valley;
1958 - acquired by Yort Wing Frank, Chinese
electrical engineer, and his wife, Jeanie, as retirement home;
1968 - acquired by Lee and Helen Paschich;
1972 - began producing wines again, under James Barrett;
1976 - Chateau Montelena Chardonnay 1973 won first
place in Judgment of Paris wine competition over four white
burgundies and six California Chardonnays (bottle of that
vintage in Smithsonian National Museum of American History).
1882 - J. G. Bieberbach (immigrated to
New York City from Germany at request of Shafer Brewing
Company, first company in nation to brew Pilsner
beer), established J. G. Bieberbach Company at 113 Summer
Street in Worcester, MA; bottled seltzers, ginger ale, imported
mineral water, wholesaler of alcoholic beverages;
1916 - acquired
by D. M. Crowley & Co., wholesale and retail liquor business
(founded in 1901 Dennis M. Crowley, great grandfather of the
present owners of Polar Beverages); 1918
- acquired Leicester Polar Spring Company (included rights to
use of spring in Spencer, MA, abundant source of pure spring
water); renamed Bieber Polar Ginger Ale Company;
1920s -focused on
ginger ale, spring water business; added flavored soft drinks
to plant's production (Pale Dry Ginger Ale, Cola, Orange Soda,
Root Beer); 1950 -
third generation of Crowleys took over (Ralph, Edward, James and
Denis -brothers); 1966
- Polar Ginger Ale renamed Polar Corp.; 1988
- sales of $16 million (sold Polar beverages, private-label soft
drinks); 1992 -
fourth generation took over, Ralph Crowley, Jr., named President
and CEO; acquired rights to manufacture, distribute National
brands (7 Up, A&W, Sunkist, Seagram's, Royal Crown, Diet Rite); December
1996 - acquired long-time competitor Adirondack
Beverages (Adirondack, Waist Watchers, Clear & Natural, private
label brands); 2000
- “super regional” organization (over twenty acquisitions, five
divisions with proprietary brands;
September 2001 - formed Northeast Retailer
Brands, LLC (alliance with another long time competitor, Cott
Corporation); 2004
- acquired Snapple of Boston (Vitamin Water, Snapple Iced
Teas); 2009 -
country’s largest independent soft-drink bottler; fourth-
generation, family-owned business.
1883 - C. H.
Wente, first-generation immigrant from Germany, purchased 48
acres in Livermore Valley, planted vineyards; learned
about winemaking from Charles Krug; 1918 - Ernest
and Herman Wente (sons) joined business; Ernest managed
vineyards, Herman acted as winemaker; company passed on to
Ernest's only son Karl; 1935 - introduced
California's first varietal wine label, Sauvignon Blanc;
1977 - Eric (Karl's son) took helm; 2006 -
managed by fourth, fifth generations of Wente family (2,000
acres of vineyards in Livermore Valley, San Francisco Bay, 700
in Arroyo Seco, Monterey); California's oldest continuously
family-owned and operated winery.
 C. H. Wente
- Wente Vineyards
(http://cache.daylife.com/imageserve/0cm2bR7aQP0gq/340x.jpg)
C. H. Wente
- Wente Vineyards
(http://cache.daylife.com/imageserve/0cm2bR7aQP0gq/340x.jpg)
1883
- Jams Concannon planted first vines in Livermore Valley, CA;
established Concannon Vineyards, one of California's oldest
wineries; first Irish vintner; 1961
- produced world's first Petite Sirah; discovered America's
first female winemaker, Hungarian ballerina named Katherine
Vajda.
 James Concannon
- Concannon Vineyards
(http://www.concannonvineyard.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/04/james.jpg)
James Concannon
- Concannon Vineyards
(http://www.concannonvineyard.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/04/james.jpg)
November 25, 1884 -
John Meyenberg, of St Louis, MO, received two patents, for an
"Apparatus for Preserving Milk" and for a "Process of Preserving
Milk"; evaporated milk.
February,
1885 - founded Helvetia Milk Condensing Company in
Highland, IL to can milk without using sugar as a preservative
(Helvetia - Latin for Switzerland); June 14, 1885
- "Highland Evaporated Cream" made its debut as world's finest
unsweetened evaporated milk; year-end profit of $1,400, 12
employees; 1886 - much milk that canned in first
six months spoiled on merchants' shelves; 1887 -
spoilage traced to bacteria, eliminated; 1894 -
Pet name first used for "Our Pet Evaporated Milk," label for
company's new "baby" sized six-ounce can, sold for a nickel;
1895 -more than half the company's sales were in the
West; September 10, 1912 - registered "Pet"
trademark first used April 26, 1894 (evaporated milk);
1918 - ten production sites; 1923 -
company renamed Pet Milk Company; 1934 - first
company to add vitamin D to dairy products via the process of
irradiation; 1950 - more cans of Pet Milk
purchased than at any time in company's 65-year history (baby
boom); one of the single largest selling items on supermarket
shelves; 1966 - name changed to Pet Incorporated.
December 16,
1884 - William H. Fruen, of Minneapolis, MN,
received first U.S. patent for an "Automatic Liquid-Drawing
Device"; measured quantity of liquid released from a reservoir
when coin inserted in slot.
1885
- Pharmacist Charles Alderton invented Dr. Pepper at Morrison's
Old Corner Drug Store in Waco, TX (named for Dr. Charles Pepper,
friend of Morrison); 1891 - Alderton and
Robert S. Lazenby form Artesian Mfg. & Bottling Company (later
renamed Dr Pepper Company - period after Dr. removed in 1950's)
= oldest major manufacturer of soft drink concentrates and
syrups in the United States; March
27, 1906 - registered "Dr. Pepper" trademark first used
in 1890 (aerated tonic beverages and syrups for the same).
1885
- Bernard Ehlers, Sacramento grocer, acquired dying vineyard
from Reverend Alfred Todhunter (bought it in 1882) for $7,000 in
gold coin; 1886 - completed planting vineyards,
constructed stone winery building (remains focal point of
Estate); 1923 - acquired by local resident Alfred
Domingos; when prohibition ended, Domingos brothers established
Old Bale Mill Winery (named
for English physician Edward Turner Bale who had married General
Mariano Vallejo's niece, was awarded 17,000 acre land grant in
1841), ran successfully until 1958; 1987 -
Parisians Jean and Sylviane Leducq acquired 7 acres of vineyard
that were part of original land tract prior to 1882; May
2001 - acquired original stone winery, estate home built
by Bernard Ehlers; reunited Ehlers Estate.
1885
- Joaquim Salles, others
owned pig slaughterhouse in Água Branca section of Sao Paulo,
Brazil; 1888 - German beer Louis Bücher joined
Salles, set up Antarctica Paulista, first beer factory in
country; March 13, 1889 - Antarctica beer first
advertised; February 12, 1891 - brewery founded as
Company Antarctica Paulista S/A (61 shareholders); 1893
- shareholders, principal creditors Zerrener, Von Bullow & Cia.,
broker and exporter of coffee, assumed control (currency
devaluation put company on verge of bankruptcy); Antonio
Zerrener, Adam Ditrik von Bülow majority shareholders;
1997 - Companhia Antarctica Paulista Industria
Brasileira de Bebidas e Conexos (IBBC) merged with Companhia
Cervejaria Brahm; formed Companhia de Bebidas das Américas
(American Beverage Company - AmBev), incorporated September 14,
1998; largest private company of consumer goods in Brazil, Latin
America’s largest brewer; fifth largest brewer in world;
September 6, 2004 - merged with Interbrew; formed InBev,
world's largest brewer, by volume.
July 8,1885 - Group of investors
(Scottish merchant Thomas Blake Glover, Nippon Yusen Kaisha
secretary W. H. Talbot, E. Abbott, second Mitsubishi president,
brother of founder Yonosuke Iwasaki, First National Bank of
Japan founder Eiichi Shibusawa) reopened Spring Valley Brewery
in Yokohama, Japan (established in 1869 by Norwegian-American
William Copeland, closed in 1884); renamed Japan Brewery
Company, Ltd.; 1888 - combined with Meiji-ya to
market Kirin Beer for first time (Kirin - creature from Chinese
mythology, symbol of well-being and good fortune).

Thomas Blake Glover, Yonosuke
Iwasaki (seated 2nd from left, 2nd from
right) - founders Kirin Holdings
(http://www.mitsubishi.com/e/history/ series/thomas/images/glover.jpg)
May 8, 1886
- Atlanta pharmacist, Dr. John Stith Pemberton's sweetened
"Pemberton's French Wine Coca" (with sugar syrup instead of
wine) first offered to customers as soda fountain beverage by
Willis Venable at Jacobs' Pharmacy for $.05 per glass (sold
about 9 glasses per day); formula combined lime, cinnamon, coca
leaves, seeds of Brazilian shrub; originally used as nerve,
brain tonic, medical elixir (headache remedy); became flavor
syrup for "Coca-Cola" (1855 -
Pemberton founded J. S. Pemberton and Company in Columbus, GA;
sold chemical elements for elixirs; 1869 -
moved laboratories to Atlanta; formed J. S. Pemberton Medicine
Company, in partnership with Ed Holland, to manufacture
Pemberton's French Wine of Coca, Pemberton's Indian Queen Hair
Dye, Pemberton's Globe of Flower Cough Syrup [received patent on
March 1, 1870]; 1884 - changed to stock
company; name changed to Pemberton Chemical Company [in
partnership with David Doe, Frank Robinson, Holland];
November 1885 - Atlanta voted to become a dry city
(effective July, 1886); January 1, 1886 -
Pemberton, Frank Robinson, David Doe, Edward Holland formed
Pemberton Chemical Company);
May 29, 1886 - Coca-Cola advertised for
first time in Atlanta Daily;
January 14, 1888 - A. O. Murphey, E. H.
Bloodworth, J. C. Mayfield formed partnership with Pemberton,
called Pemberton Medicine Company;
October 1888 - obtained charter for
company; January 15, 1889
- incorporated Coca-Cola
Corporation; manufactured three previous products and
Pemberton's Orange and Lemon Elixir; Pemberton's bookkeeper,
Frank M. Robinson, named the mixture Coca-Cola®, and wrote it
out in his distinct script; Asa Candler formed Walker, Candler &
Company with Charley Pemberton (son), Woolfolk Walker
(Pemberton's former sales manager);
April 14, 1888 - Charley Pemberton's 1/3
interest, co-signed by Dr. J. S. Pemberton (farther), acquired
by Walker, Candler & Company (Walker, Joe Jacobs of Jacobs
Pharmacy, Candler) for $550; April
17, 1888 - acquired 50% of Walker/Margaret
Dozier (Walker's wife) interest for $750;
August 1888 - three varieties of
Coca-Cola on market; August 30,
1888 - Candler acquired remaining Walker/Dozier
interest for $1000; April 22, 1891
- acquired rights from Joe Jacobs, sole remaining member of
Woolfolk, Candler & Company; 1891
- Candler, sole proprietor (under questionable circumstances);
had acquired recipe, equipment, machinery to manufacture drink
for about $2,300; January 29, 1892
- The Coca-Cola Company incorporated (despite Coca-Cola
Corporation incorporation in 1888);
January 31, 1893 - registered
"Coca-Cola" trademark first used June 28, 1887 (nutrient or
tonic beverages); contained cocaine as ingredient until 1904
(drug banned by Congress); 1894
- Mayfield reincorporated Pemberton Medicine Company as Wine
Coca Company, attempted to continue selling Coca-Cola (under
name of Pemberton's French Wine Coca, but with formula modified
to resemble Coke); March 12, 1894
- Joseph A. Biedenharn (Biedenharn Candy Company, Vicksburg, MS)
first sold Coca-Cola in 9.3 oz. Hutchinson bottles with patented
Hutchinson bottle-stoppers; sent case to Asa Candler who took no
interest (focused on fountain sales);
1895 - sold in every state;
July 21,1899 -
exclusive rights to bottle, sell Coca-Cola in practically entire
United States (exclusive of soda fountain business) acquired by
Benjamin F. Thomas (38), Joseph B. Whitehead (lawyers from
Chattanooga, TN); 600-word contract specified syrup supply at
$1/gallon plus assumption of advertising expense; joined John T.
Lupton; first bottling plant under new contract opened in
Chattanooga (second plant opened in Atlanta in 1900); large
scale bottling began; began to develop what became worldwide
Coca-Cola bottling system; sold bottling rights to individuals
within defined geographic areas to establish regional Coca-Cola
bottling operations; 1908
- Coca Cola Corporation's charter expired;
1909 -nearly 400 bottling plants, most
family-owned, operated; 1910
- Candler burned early records of company;
1914 - Dozier contested 1888 sale of her
stock; claimed her signature had been forged; claimed that Dr.
Pemberton's signature also forged; Woolfolk Walker disappeared
in 1888; Charley Pemberton died from apparent suicide in 1894);
1916 - contour
bottle, introduced, designed by Root Glass Company (Terre Haute,
IN), approved by bottlers; awarded trademark status in 1960;
1919 - The
Coca-Cola Company acquired for $25 million by group of investors
headed by Ernest Woodruff, W. C. Bradley;
1920 - more than 1,000 bottling plants
(95% locally owned, operated);
August 14, 1945 - Coca Cola Company registered
"Coke" trademark first used December 10, 1941 (non-alcoholic
maltless beverages and the syrups for making such beverages);
April 12, 1960 -
Coca-Cola Company registered "Coca-Cola" trademark (carbonated
soft drink - "The Trademark Consists of the Distinctively Shaped
Contour or Confirmation, and Design of the Bottle" (first
commercial use on September 1, 1916);
November 19, 1963 - registered "Fresca"
trademark first used January 22, 1963 (Bottled Flavored Dietary
Soft Drink and Syrup for Making the Same);
December 3, 1963 - registered "Fresca"
trademark first used March 8, 1962 (Non-Alcoholic Maltless Soft
Drinks and the Syrups for Preparing Soft Drinks);
June 1, 1965 -
registered "HI-C" trademark first used December 31, 1954 (canned
fruit juice drinks-namely, Florida Punch, Orange Pineapple
drink, Pineapple Grapefruit drink, and apple Drink).
1886
- William M. and Ralph R. Foster, from New York, paid
£48,000 to build Melbourne's most modern brewery. November
1888 - first Foster's Lager prototype brewed, bottled in
heavy bottle with wired-down cork; February 1, 1889
- first public tasting; won first prize in city's Centennial
Exhibition's International Brewing Award against all comers;
November 13 1889 - sold business to local syndicate;
August 1903 - Society of Melbourne Brewers formed;
May, 8, 1907 - six Melbourne breweries formed
Carlton & United Breweries Proprietary Limited (CUB);
1958 - adopted modern,
highly transportable packaging of steel cans; 1970
- royal blue Foster's livery adopted; 1972 - All
Brand Importers started importing Foster's to US in over-sized
26-ounce can; 1976 - CUB sent one million cans of
Foster's to New York (largest single consignment of foreign beer
to ever enter the city); 1977 - 10 million liters
of Foster's sold in US.; 1987 - acquired UK brewer
Courage, became Courage's leading lager brand; 1995
- merger of Courage into Scottish & Newcastle Group created
largest brewer in UK; Fosters - #1 beer in London for more than
10 years; 1 in 5 British adults, almost 8 million, drink
Foster's every week; equivalent of 700 million pints of Foster's
drunk in Britain every year; 3rd largest-selling international
beer brand, over 100 million cans consumed worldwide every year,
world's third most widely distributed beer (in over 150
countries).
December 25, 1887 - First
Glenfiddich single malt whiskey (Gaelic
for ‘valley of the deer’ which surrounds river Fiddich in Spey
region of Scotland)
ran from William Grant stills;
1898 - became blender, bottler, wholesaler;
Charles Gordon (son-in-law) became first salesman (181 calls to
make first sale, 503 calls to make second sale); John Grant
(son) first exporter, sold the family whisky to Hudson Bay
Company of Canada; 2007 - Charles Gordon
(great-grandson) Chairman of the company.
1888
- Swiss brew master Joseph Villiger established brewery
Manufatura de Cerveja Brahma Villiger & Companhia in Rio de
Janeiro; September 6, 1888 - introduced Brahma
beer; 1904 - name changed to Companhia Cervejaria
Brahma; 1997 - merged with Companhia Antarctica
Paulista Industria Brasileira de Bebidas e Conexos; formed
Companhia de Bebidas das Américas (American Beverage Company -
AmBev), incorporated September 14, 1998; largest private company
of consumer goods in Brazil, Latin America’s largest brewer;
fifth largest brewer in world; September 6, 2004 -
merged with InterBrew; formed InBev, world's largest brewer, by
volume.
January 3, 1888
- Marvin C. Stone, of Washington, DC, received a patent for an
"Artificial Straw" ("a cheap, durable, and unobjectionable
substitute for the natural straws commonly used for the
administration of medicines, beverages, etc."); first wax
drinking straw to replace use of natural rye grass straws; first
straws were hand rolled; 1905 - invented a machine
to roll straws, necessary to keep up with the growing demand,
and new applications of spiral-wound tubing.
November 1889
- Osaka Beer Brewing Company established; October 1891
- Suita-mura Brewery (now Asahi Breweries’ Suita Brewery)
completed; May 1892 - Asahi Beer, created by Hiizu
Ikuta, manager, technical chief of Suita Brewery, launched;
February 1893 - reorganized as Osaka Breweries, Ltd.;
1900 - introduced Asahi Draft Beer, Japan’s first
bottled draft beer; March 1906 - Osaka, Sapporo
Brewery, Nippon Brewing Company merged, formed Dai Nippon
Brewery Co., Ltd. (separate division called Asahi);
September 1949 - Dai Nippon divided into two parts
(result of Excessive Economic Power Decentralization Law): Asahi
Beer, Ltd., Nippon Breweries, Ltd.; September 1958
- Asahi Beer in cans, Japan's first canned beer, introduced;
March 1982 - Tsutomu Murai, former executive vice
president of Sumitomo Bank (previously helped to rescue Mazda
Motor Corporation), took over Asahi operations (market share
down to 10% in 1981 from 36% in 1949); November 1982
- entered into agreement with Löwenbräu Company (West Germany)
to produce Lowenbrau Beer under license in Japan; February
1986 - Asahi draft beer introduced; March
1986 - Hirotaro Higuchi succeeded Murai as President;
March 1987 - introduced Asahi Super Dry, Japan's
first dry beer; became blockbuster hit; March 1988
- signed collaborative agreement with Bass Exports (UK) to
import, sell Bass Pale Ale; 1988 - beer = 80% of
sales; January 1989 - renamed Asahi Breweries,
Ltd.; July 1995 - concluded comprehensive,
multipurpose collaborative agreement with Miller Brewing Company
(U.S.); 1996 - Super Dry replaced Kirin
Lager as top-selling beer in Japan; record net sales, net
income; 1997 - 34.4% market share vs. 9.9% in
1985; 2001 - replaced Kirin as top Japanese brewer
(38.7% market share).
1890 - John
J. McLaughlin, pharmacist and chemist, whose brother founded
General Motors of Canada in 1916, opened small plant in Ontario
to manufacture soda water; intended to sell to pharmacies as
mixer for fruit drinks and flavored extracts; 1904
- J. J. McLaughlin Company introduced Canada Dry Pale Ginger
Ale; developed technique for mass bottling; January 18,
1907 - J. J. McLaughlin Limited registered "Canada Dry
Pale Ginger Ale" trademark in Canada; changed name to Canada Dry
Ginger Ale ('The Champagne of Ginger Ales"); appointed to the
Royal Household of Governor-General of Canada; 1919
- began shipping to New York City; 1921 - opened
first Canada Dry plant in United States on 38th Street in
Manhattan; May 16, 1922 -
J. J. McLaughlin Limited
registered "Canada Dry Pale Ginger
Ale" first used in 1890 in U. S. (pale ginger ale);
1923 - acquired by Canadian businessman P. D. (Parry
Dorland) Saylor; formed Canada Dry Ginger Ale, Inc.; 1930
- tonic water, club soda, Collins mix, fountain syrup produced
under Canada Dry name; 1936 - first international
license awarded to bottler in Lima, Peru; 1938 -
plants in 14 countries; 1953 - first major soft
drink company to put soft drinks in cans; 1964 -
first to introduce sugar-free drinks; 1986 -
acquired by Cadbury Schweppes plc for $230 million.
1890
- Don Enrique Ma. Barreto founded La Fabrica de Cerveza de San
Miguel, Southeast Asia's first brewery;
1893 - incorporated; escudo adopted as
new company's symbol; 1948
- established a brewery in Hong Kong, first local brewer in
crown colony.
1890 - Anton
Nichelini founded winery in Chiles Valley Wine Region in the
Eastern part of Napa Valley; 1934 - Bill Nichelini
(oldest son) acquired winery; 1959 - Jim Nichelini
(Bill's son) assumed control; 1990 - acquired by
partnership formed by three of Jim's cousins and his sister;
specialize in wine production of Chiles Valley grapes; oldest
"Family owned and operated " winery in Napa Valley.
1890 - Edward
Charles Edmond Barq, Gaston Barq (brother) founded Barq's
Brothers Bottling Company in French Quarter of New Orleans,
Louisiana; created Orangine, orange-flavored soda (won gold
medal at 1893 World's Columbian Exposition World's Fair in
Chicago, IL); 1898
- opened Biloxi Artesian Bottling Works (Biloxi, MS);
July 31, 1951 -
Barq's Incorporated registered "Barq's" trademark first used
November 5, 1915 (nonalcoholic, noncereal, maltless beverages
sold as soft drinks and syrups, extracts, compounds, and flavors
used in making same); 1995
- acquired by Coca-Cola.
1892 -
Joel Cheek
developed coffee blend for Maxwell House Hotel (Nashville, TN);
became known as Maxwell House Coffee; 1907 -
President Theodore Roosevelt commented that it was "good to the
last drop" (when served at The Hermitage, President Andrew
Jackson's former home in Tennessee); May 11, 1926
- General Foods
Corp. registered "Maxwell House Good to the Last Drop"
trademark first used January 1, 1915;
1928 - acquired by Postum Cereal Company.
1892 - Peter C. Larkin
founded Salada Tea Company Ltd. (name of Ceylon Tea Garden) in
Toronto, ON; December 3, 1892 - registered "Salada
Tea Company, Ltd. Golden Tea Pot Blend - Pure Ceylon Tea" in
Canada (tea); August 23, 1898 - registered
"Salada" trademark first used December 31, 1892 (tea) in U. S.;
1917 -
established U.S. headquarters, blending and packaging plant in
Boston, MA; 1957 -
merged with Shirriff Horsey Corporation Ltd. (flavoring
essences, called "buds", used to flavor dessert products, jelly
powders, jellies, puddings); renamed Salada-Shirriff-Horsey
Ltd.; October 1, 1958 - acquired Junket brand from
Chs. Hansen Laboratories; January 1962 - name
changed to Salada Foods, Inc.; 1969 - acquired by
Kellogg; June 1988 - acquired by
Unilever.
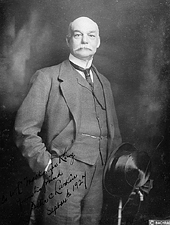 Peter C. Larkin -
Salada Tea
(http://data2.collectionscanada.ca/ap/c/c090250.gif)
Peter C. Larkin -
Salada Tea
(http://data2.collectionscanada.ca/ap/c/c090250.gif)
1893
- Horace Chase and Minnie Mizner Chase (wife), daughter of U.S.
Senator and Ambassador to Central America, founded Stags' Leap
Winery seven miles north of Napa, CA; named "Stags' Leap" after
Wappo Indian legend that, one version says, told of stag leaping
across crags of palisades (bordering east side of estate) to
escape hunters; 1913
- acquired by Mrs. Frances Grange;
1971 - acquired by Carl Doumani, underwent vast
restoration; 1997 -
acquired by Beringer Wine Estates (acquired by Foster's Brewing
Group, Ltd. in 2000).
January 31, 1893
- Coca Cola Company registered "Coca-Cola" trademark first used
June 28, 1887 (nutrient or tonic beverages).
July 11, 1893
- C.I. Hood & Co., Lowell, MA, registered "Hood's Sarsaparilla
CIH & Co. Compound Extract" trademark.
August 19, 1893
- Frank J. Wisner, owner of Cripple Creek Brewing in Colorado,
manufacturer of Myers Avenue Red root beer, invented root beer
float, or "Black Cow"; inspired to "float" a scoop of vanilla
ice cream on top of root beer from late night glimpse of snow on
top of blackened Cow Mountain (location of his gold claims)
illuminated by full moon.
1894 - Puritas
began marketing distilled bottled water from south slope of
California's San Bernardino Mountains, in California;
1903 - first
Arrowhead Brand Mountain Spring Water bottled in basement of
Arrowsprings hotel; 1905
- Arrowhead Springs Corporation began selling Spring Water in
Los Angeles; 1952 -
introduced fluoridated bottled water;
1987 - acquired by Nestle Waters North
America.
1894 - Percy
Morgan, British accountant, seven of state's leading wine
distributors and wineries, formed California Wine Association;
legal monopoly, controlled two-thirds of output of California
wine; 1900 -
majority of state's wineries had joined (Stag's Leap, Greystone
Cellars at St. Helena, Italian Swiss Colony, Cucamonga
Vineyards, Glen Ellen Vineyards, more);
at peak - largest wine-producing
cooperative in world: 52 wineries were members, controlled all
aspects of winemaking, from planting of grapes in field, to
production, bottling, shipment of wine;
1901 - majority interest acquired by
Isaias Hellman, president of Nevada Bank, and syndicate for $1
million; reportedly controlled 87% of wine made in California;
1907 - bought 47
acres in Richmond, CA, prime spot with access to
transcontinental railroad, port for ocean-going vessels; built
one of country's most massive wineries, luxury hotel, cabins for
workers, railroad that wound through property; sold many
varieties of wine under CALWA brand;
1919 - Prohibition passed, caught with
warehouse full of wine that it couldn't be sold; shut down
winery, left it to sit unoccupied on edge of San Pablo Bay;
1941 - site,
adjacent land acquired by U.S. Navy; constructed fuel depot,
turned hotel into barracks, mess hall (used until 1995).
 Percy Morgan
-
California Wine Association (http://www.losaltoshillshistory.org/Resources/Stonebrook-Ct-manor/Percy/Morgan.jpg)
Percy Morgan
-
California Wine Association (http://www.losaltoshillshistory.org/Resources/Stonebrook-Ct-manor/Percy/Morgan.jpg)
May 1, 1894 -
Theodore Harding Estabrooks founded T.H. Estabrooks Tea Company
in Saint John, New Brunswick; 1899 - blended
Indian, Sri Lankan teas (vs. Chinese, Japanese teas) ;
October 16, 1899 - registered "Red Rose" trademark in
Canada (tea, coffee, spices); 1929 - introduced
tea bags; 1932 - acquired by Brooke Bond & Company
of England; 1985 - acquired by Unilever NV; rights
to Red Rose brand in United States acquired by Redco Foods,
Inc.; February 1995 - Redco acquired by Teekanne
GmbH.
1895 - Angela
and Edoardo Seghesio purchased 56 acres in northern Alexander
Valley, CA; planted "Home Ranch" to what became family’s
lifeline – Zinfandel; 1902 - began Seghesio
Winery; 1910 - acquired additional acreage in
"Chianti, California"; planted 10 acres, North America’s oldest
planting of Sangiovese; 1919 - acqired Italian
Swiss Colony (4,000,000 gallon capacity winery, 1100 acres of
vineyards) for $127,500; 1920 - brought on
partners, his brother-in-law, Enrico Prati, Rossi Family
(previous owners); 1933 - sold his shares;
1958 - sons formed partnership in bulk wine business,
produced most of red wine made in Sonoma County; 1983
- first wines bottled under Seghesio label by Ted Seghesio,
fourth generation family winemaker; 1993 -
produced 130,000 cases; fifth generation took control of the
winery; eliminated all but home-grown wines; reduced production
to 30,000 cases; June 1, 2011
- Seghesio Family Vineyards acquired by Crimson Wine Group (five
brands, over 700 planted acres in five growing regions, over
250,000 cases within higher-end price segments, focus on
estate-grown wines).
1895
- Luigi Lavazza established Luigi Lavazza SpA cofee company in
Turin, Italy; August 2010
- acquired 6% interest in Green Mountain Coffee Roasters Inc. to
expand in U.S., develop new single-serve espresso machines and
capsules, Green Mountain may agree to sell Lavazza’s existing
machines in U.S. and Canada.
May 15, 1895 -
Frederick Mead incorporated The South African Breweries Limited
in London, UK with share capital of £350,000 and £300,000 of
debentures (had registered Natal Brewery Syndicate (South East
Africa) Limited in 1890, brewed first beer in July 1891; took
over operations of Natal Brewery Syndicate, had acquired Castle
Brewery in Johannesburg from Charles Glass in 1892); W.H.
Hackblock, former head of Morgan's Brewery in Norwich, UK,
chairman; 1897 -
went public; first industrial shares listed on Johannesburg
Stock Exchange; 1898
- launched Castle Lager from newly-commissioned lager brewery
(annual capacity 50 000 barrels);
1901 - annual profits rise to £100,000 and
assets exceed £1 million; 1910
- Rhodesian Breweries formed; 1912
- formed Union Hop Growers, joint venture with Ohlsson's
Brewery; developed new hybrids (first commercial use of South
African-grown hops in 1920); 1925
- acquired interest in Schweppes sparkling beverages;
1956 - acquired
Ohlsson's Cape Breweries, United Breweries (two of largest South
African brewing companies), gained 90% share of domestic market;
May 26, 1970 -
reincorporated in South Africa (after 75 years as English
company); 1977 -
took control of Amalgamated Beverage Industries Ltd. (Coca-Cola
bottler in South Africa); 1979
- acquired beer interests of Rembrandt Group (nearly 99% share
of South African market); merged wine, spirits operation into
independent 30%-owned subsidiary; acquired 49% of Appletiser
South Africa (Pty.) Ltd. (producer of fruit drinks); divested,
focused on beer, soft drinks, wine and spirits, hotels,
gaming; 2000 -
acquired majority stake in Narang Breweries (India);
2002 - 55% of $4.36
billion in revenues derived from non-South African operations;
acquired Miller Brewing Company for $3.48 billion in stock from
Philip Morris Companies Inc., number two U.S. beer maker;
renamed SABMiller plc; 2003
- acquired 60% of Birra Peroni S.p.A., Italy's number two
brewer; first major investment in Western Europe.
October 1, 1895
- Czech brewers (August Zátka, many others) founded Czech Share
Brewery in Ceske Budejovice, Czechoslavakia (1265 - Czech King,
Premysl Otakar II founded Ceské Budejovice, formerly Budiwoyz or
Budweis, granted town right to brew beer); produced first beer;
1922 - first artesian well bored; 1936
- changed name to Budvar – Ceský akciový pivovar Ceské
Budejovice; 1967 - Ministry of Agriculture of
Czech Republic established national enterprise Budejovický
Budvar (Budweiser Budvar, N. C.) as direct successor of Czech
Share Brewery; 380 trademarks registered in 101 countries in
world; most important are Budweiser, Budweiser Budvar, Bud,
"Budejovický Budvar", Czechvar (relate to place of origin, town
Ceské Budejovice (formerly Budiwoyz or Budweis).
1896 -
Giovanni Foppiano purchased working winery known as "Riverside
Farm" in Healdsburg, in Sonoma County; founded Foppiano Wine
Company; 1910 - Louis A. Foppiano (son) got loan
from his wife's family, bought winery; 1937 -
Louis J. Foppiano (grandson) rebuilt winery; one of first Sonoma
County wineries to bottle wine under its own winery label;
1940 - 1945 - second largest bottler of wine in
Sonoma County; founded Sonoma County Wine Growers Association
with 14 other wineries; 1994 - fifth generation
Foppianos began working at vineyard.
1896 - Vincenso
and Secundo Picchetti (brothers) entered commercial wine
business; built two story red brick winery building with redwood
storage tanks, oak casks for aging and storing wine; Picchetti
Brothers Winery registered as California Bonded Winery number
148 (Vincenso had migrated to Santa Clara Valley from Formarco,
Italy in 1872, worked as foreman with local vineyard owned by
Santa Clara College [now Santa Clara University], bought 1160
acres of land in 1880s); 1904
- Antone and John Picchetti (Vincenso's sons) took over;
1963 - commercial
wine production stopped; 1977
- remaining land sold to the Mid-Peninsula Open Space District;
1998 - Leslie
Pantling took possession of the winery, operated under lease
from Midpeninsula Regional Open Space;
2009 - produces approximately 9000 cases
of hand crafted wine/year.
1896 - Ernest Baruth (former co-owner of American Brewery), Otto Schinkel,
Jr. (26, former driver for American Brewery) bought San
Francisco brewery founded by Gottlieb Brekle; named it Anchor;
inherited tradition of brewing steam beer, nickname for beer
brewed along the West Coast under primitive conditions and
without ice;
of more than
two dozen breweries in San Francisco only Anchor survived;
1907 - German brewers Joseph Kraus and August Meyer,
and liquor store owner Henry Tietjen took over brewery after
Schinkel's death; April 7, 1933 -
Anchor Steam Beer brewed again after 13 years (Prohibition);
1934 - Joe Allen joined Joe Kraus in brewing
partnership; July 1959 - Anchor shut down, victim of competition
from mass-produced heavily marketed lighter beers; 1960
- acquired by Lawrence Steese, reopened; re-hired brewmaster Joe
Allen; September 24, 1965 - 51% of operation
acquired for few thousand dollars by Fritz Maytag,
great-grandson of founder of Maytag appliance company;
1969 - became Brewery's sole owner; began bottling
Anchor Steam Beer, first bottled Anchor Steam in modern times;
August 13, 1979 - first Steam Beer brewed at new
brewery on Mariposa Street; 1993 - first brewery
in world with its own in-house distillery; 1997 -
began making pot-distilled gin, Junípero;
2010 - acquired by Griffin Group (Keith
Greggor, Tony Foglio).
 Fritz Maytag -
Anchor Steam
(http://images.inc.com/slideshow/smallgiants/slide1.jpg)
Fritz Maytag -
Anchor Steam
(http://images.inc.com/slideshow/smallgiants/slide1.jpg)
1898 -
Caleb D. Bradham created a soft drink in his pharmacy in New
Bern, NC; mixed carbonated water, sugar, vanilla, oils, pepsin,
kola nut extract; customers called it "Brad’s Drink";
August 28, 1898 - changed name to Pepsi-Cola -
emphasized the pepsin and kola nut extract (supposed health
benefits: pepsin, an enzyme, for digestion; caffeine, an
alkaloid found in kola nuts, for energy); 1902 -
founded Pepsi-Cola Company in backroom of pharmacy; June
16, 1903 -
Caleb D. Bradham
registered "Pepsi-Cola"
trademark first used August 1, 1901 (flavoring-syrup for soda
water); March 2, 1923 - declared bankruptcy,
returned to pharmacy; May 7, 1923 -
Pepsi-Cola trademark, assets acquired at auction for $30,000 by
Craven Holding Corporation, group of Bradham's creditors;
1928 - acquired by Roy C. Megargel for $35,000; formed
National Pepsi-Cola Company in state of Virginia; June 8,
1931 - Pepsi-Cola Company declared bankruptcy;
1931 - Charles G. Guth, President of Loft Candy Company,
acquired sole rights to trademark, assets of defunct Pepsi-Cola
Company for $10,500 (Coca-Cola Company had refused to give
him jobber's discount on syrup served at over 138 candy stores
in greater New York area); August 10, 1931 -
formed Pepsi-Cola Company in state of Delaware; 1936
- new 12 ounce Pepsi bottle for 5 cents (same
price as six ounces of Coke)
created $2 million dollar operating profit, revitalized company;
became subsidiary of Loft; 1938 - Guth forced to
resign after losing suit over ownership of Company;
October 4, 1939 - Walter Mack, former executive of
Phoenix
Securities Corporation,
became president;
established board
of directors with real voting powers,
introduced cartoon comic strip called "Pepsi and Pete... the
Pepsi-Cola Cops", widely syndicated for eleven years, gave brand
visibility to Pepsi-Cola; standardized 12 ounce bottle for 341
franchised bottlers.

Caleb Bradham
- creator of Pepsi
(http://www.northcarolinahistory.org/images/uploaded/posts/thumb_44f4528d31fa7.jpg)
Donald M. Kendall
- Pepsico
(http://www.beverageforum.com/images/4Kendall.gif)
 D. Wayne Calloway
- Pepsico
(http://www.callawayfamily.org/images/davidwaynecalloway.gif)
D. Wayne Calloway
- Pepsico
(http://www.callawayfamily.org/images/davidwaynecalloway.gif)
1898 - Joe
Martinson began selling special roast from push cart on streets
of New York City (emigrated to the United States from Mitau,
Latvia, in late 1800s); 1908
- bought first small factory, began marketing premium blend to
hotels, restaurants; packaged ground coffee in cans, sold it to
stores; 1928 -
offered special blend in distinctive tins to grocery stores in
Brooklyn, Queens; 1930s
- bought small fleet of Rolls Royces, removed back seats,
painted Martinson logo on them, sent out salesmen, delivery guys
dressed as chauffeurs to deliver coffee to upscale hotels,
restaurants in Manhattan; July 17,
1956 - Jos. Martinson & Co., Inc. registered
"Martinson's Coffee" trademark first used March 1902 (coffee);
1962 - acquired by
Tetley USA ; February 2000
- acquired by Mother Parkers.
July 26, 1898
- William Painter, of Baltimore, MD, received a patent for a
"Bottling-Machine" ("adapted to the bottling of liquids with or
without gaseous pressure and with or without the charging of
each bottle with syrup or with other flavoring or reinforcing
liquids in appropriately varied and measured quantities"); Crown
Soda Machine; assigned to Crown Cork and Seal Company; first
machine that combined filling, capping of bottles at same time
for faster, more economical bottling; precursor of today’s
automated carbonated drink mixing, capping machines;
first meaningful
mechanized support for filling soft drinks bottles; quadrupled
output of average operator to 4 bottles per minute.
1899 -
Societa Anonima delle Terme di San Pellegrino founded; prepared
35,343 bottles of S. Pellegrino, shipped 5,562 abroad (borders of town of San Pellegrino
had been established
in 1395; named for San Pellegrino - martyr, bishop of Auxerre,
evangelizer of France; San Pellegrino
water had been analyzed for first time in 1782; San
Pellegrino spring became big tourist attraction in 1839).
September 6, 1899
- Pacific Coast Condensed Milk Company, founded by Elbridge A.
Stuart (former partner in Los Angeles wholesale grocery company
Craig, Stuart and Company) and a partner, acquired plant,
machinery of bankrupt Washington Condensed Milk Company in Kent,
WA; produced first cases of evaporated milk, called Carnation
Sterilized Cream ( saw
carnation on lid of box of Carnation cigars); September
18, 1900 - registered "Carnation Brand" trademark first
used November 1, 1899 (condensed milk); 1901 -
acquired partner's interest; 1906 - product name
changed to Carnation Evaporated Milk; began using advertising
slogan, "milk from contented cows"; 1916 -
company name
changed to Carnation Milk Products Company; 1919 -
more than 150,000 cows produced milk for Carnation's 20 plants
across the United States; 1985 - acquired by
Nestle for about $3 billion.
1900
- Paul Garrett established Garrett & Company in North Carolina
(declared chief wine-producing state of Union in 1840 by Federal
census); 1903
-moved headquarters to five-story winery in Norfolk, VA to
escape prohibition in North Carolina; claimed to have "the
largest clock on earth", wine capacity of four million gallons;
most successful of eastern winegrowers before Prohibition,
America's largest winemaker (five wineries in North Carolina);
1912 - prohibition
in Virginia forced move Penn Yan, in Finger Lakes of New York
state; Garrett's 'Virginia Dare' (name of first child born to
English settlers in America) red and white wines (based on the
native Scuppernong grape of the South) - most purchased wine in
U.S. during early 1900s, before Prohibition;
December 11, 1917 -
Garrett and Company registered "Virginia Dare" trademark first
used in 1891 (wines); 1919
- 17 processing locations, 10 million gallon combined capacity;
1934 - called
'Dean' of American winemen by Fortune magazine';
1940 - just two
licensed wineries in North Carolina.
 Paul Garrett
- Garrett & Co.
(http://www.escholarship.org/editions/data/13030/3q/ft967nb63q/
figures/ft967nb63q_00126.jpg)
Paul Garrett
- Garrett & Co.
(http://www.escholarship.org/editions/data/13030/3q/ft967nb63q/
figures/ft967nb63q_00126.jpg)
1900 - New Zealander Percival Dewe Boyd opened
Boyd Importing Tea Company in Portland, OR.;
August 28, 1951 -
Boyd Coffee Company registered "Boyds" trademark first used in
March 1903 (coffee, tea, a preparation of cocoa, chocolate,
sugar and milk for making a food beverage; food flavoring
extracts and food flavoring compounds; condiments...);
1958 - Rutherford
Percival Boyd (son) succeeded as President; first company to use
paper filters in restaurant coffee-makers;
December 29, 1964 -
registered "Flav-R-Flo" trademark first used July 3, 1963
(Coffee Making Equipment) for home use;
1972 - doubled the size of operations.
May 1900 -
George and Fernande de Latour purchased four acres in
Rutherford, CA; knew cure for phylloxera (vine-destroying
louse); imported resistant rootstock; 1919 - had
national contract to supply altar wine to churches across
country; 1923 - bought stone winery built in 1885
by former California Senator Seneca Ewer; 1933 -
winery production capability expanded three times, volume grew
to more than one million gallons; September 1938 -
André Tchelistcheff, of Institut National Agronomique in Paris,
became winemaker; 1969 - acquired by Hublein
Corporation; increased winery's production to about 450,000
cases annually; 1982 - Heublein acquired by RJR
Nabisco; 1987 - GrandMet acquired Heublein Inc.
from RJR Nabisco for $1.3 billion.
September 18, 1900
- Pacific Coast Condensed Milk Company registered "Carnation"
trademark first sued November 1, 1899 (condensed milk [and
preparations thereof-namely, coffee with milk, chocolate with
milk, and potatoes with milk]).
December 27, 1900
- Prohibitionist Carry Nation (six feet tall and 175 pounds,
hatchet-wielding) carried out her first public smashing of a
bar, at the Carey Hotel in Wichita, KS; sale of alcohol was
already illegal in Kansas (constitutional amendment in 1880) but
law was largely ignored, Nation (married to an alcoholic
husband) reasoned that it was the responsibility of law-abiding
citizens to destroy not only the alcohol but also the saloons
that sold it; largely forgotten when Prohibition adopted.
1903 - Ludwig Roselius and a team of researchers in Bremen, Germany, invented
decaffination process; discovered that brine-soaked beans (fell
into ocean) reacted differently to roasting; developed a
technique that removed 97 percent of the caffeine without
removing the flavor; 1905 - first sold in Germany
under the name "Kaffee HAG";
1906
- received a German patent for process in Germany; 1909
- came to the United States, marketed under the name
"Dekafa" or "Dekofa" by an American sales agent;
1914 - Roselius
founded his own company called Kaffee Hag Corporation in New
York, which marketed its decaffeinated coffee under the brand
name "Kaffee HAG" that was well proven from the European
business; 1923 - Sanka ("sans caffeine") first
marketed in the United States; 1928 - General
Foods Corporation taking over its distribution; 1932
- General Foods acquired Sanka Coffee Corporation; 1979
- General Foods acquired Roselius's original company, Kaffee
Hag, from Roselius's son.
August 11, 1903 -
Japanese chemist, Satori Kato, of Chicago, IL, received a patent
for a "Coffee Concentrate and Process of Making Same"
("production in a hard dry state of a coffee concentrate which
is not liable to become rancid and does not owe resistance to
rancidity nor its dry hard state to the presence therein of a
foreign matter or fiber, but which may consist entirely of the
aromatic and healthful constituents of the coffee-bean"); first
soluble instant coffee; assigned to Kato Coffee Company.
August 15, 1903
- German and British merchants of Hong Kong Anglo-Nordic Brewery
created Nordic Brewery Co., Ltd Tsingtao Branch in Qingdao,
China (Shandong province), with 400,000 Mexican Silver Dollars
raised through Deutsche Bank; annual production capability of
2,000 tons (light beer, dark beer);
1906 - Tsingtao Beer won its first gold
medal at Munich International Expo;
September 16, 1916 - acquired by Japan
Brewery Co., Ltd of Tokyo for 500,000 Silver Dollars; renamed
Japan Brewery Co., Ltd., Tsingtao Factory; produced light beer,
dark beer under brand names of Sapporo, Sun, Fushou, Kirin;
1939 - set up
malt-making workshop (only one of its kind in China);
1942 - expanded,
production capability increased to 4,663 tons;
1945 - taken over
by Qingdao City Government, renamed Tsingtao Brewery Company;
December 5, 1946 -
transferred to Bureau of Enemy Property Disposal, Shandong
Qingdao District of the Executive Yuan; name changed to Tsingtao
Beer Factory; 1972
- launched in U.S.;
January 19, 1982 - China National Cereals, Oils
and Foodstuffs Import and Export Corporation registered in U. S.
"Tsingtao" trademark first used in 1903 (beer);
1988 - sold 1.24
million cases in U.S; biggest Asian beer exported to U.S.;
July 15, 1993 -
merged with three breweries in Qingdao, renamed Tsingtao Brewery
Company Limited; went public;
October 21, 2002 - signed Agreement for
Strategic Alliance with Anheuser-Busch (bought 27% of company);
2008 - Domestic
Beer Sponsor of Beijing 2008 Olympic Games;
January 23, 2009 - sold 19.9% interest
to Asahi Breweries, Ltd for $667 million (Asahi second largest
shareholder behind Tsingtao Brewery Group; Anheuser-Busch InBev
will owned 7% minority share).
1904 -
Pharmacist and chemist John J. McLaughlin launched Canada Dry
"pale dry" Ginger Ale; 1923 - P D Saylor and
Associates acquired Canada Dry from McLaughlin family, formed
public corporation, Canada Dry Ginger Ale Inc.; 1986
- acquired by Cadbury Schweppes plc.
1904 - Swiss
chemist, Dr. George Wander, invented Ovomaltine (Ovo-maltine
name derived from two main ingredients: eggs and malt); first
malt based hot beverage powder in Europe; 1906 -
Albert Wander (son) launched in the UK as first convenient and
complete milk fortifier to provide hot nutritional drinks to
strengthen under-nourished children, breastfeeding women, the
weak, and the infirm; 1913 - first factory opened
in Hertforshire, name misspelled as Ovaltine; first Ovaltine ad
appeared; October 7, 1913 - Dr. A. Wander A-G.
Company (Berne, Switzerland) registered "Ovaltine" trademark
first used in 1906 (food drink); 1967 - Sandoz AG
acquired Wander Ltd.; 1996 - owned by Novartis AG
due to merger of Sandoz and Ciba Geigy; October 8, 2002
- Associated British Foods announced acquisition of Ovaltine
beverage line (largest producer of malt based hot beverages in
Continental Europe, Thailand and China) from Novartis AG for
over $270 million.
1904 - Louis
Kunde, German immigrant, Germany, acquired 1,000 acre Wildwood
Vineyards ranch (iron-rich, ancient red volcanic soils (first
planted in 1879 by pioneer John Drummond with imported cuttings
from Chateaux Margaux and Lafite Rothschild); crushed first
Estate harvest; 1920 - operated during
Prohibition, manufactured, purchased, sold "non-beverage wine"
or sacramental wines; 1922 - Arthur "Big Boy"
Kunde (son) took over; closed during WW II (sons drafted);
1955 - Bob and Fred (Arthur's sons) took over;
1977 - acquired 1,000 acre Kinneybrook Ranch.
 Louis Kunde
- Kunde Estate Winery
(http://www.kunde.com/static/images/content/beauty_aboutFamily.jpg)
Louis Kunde
- Kunde Estate Winery
(http://www.kunde.com/static/images/content/beauty_aboutFamily.jpg)
1904
- Samuele Sebastiani, immigrant from wine producing region of
Tuscany, Italy, acquired land, grew grapes in Sonoma, CA;
1944 - August and
Sylvia Sebastiani (son, daughter-in-law) purchased winery from
father's estate; increased winery's production hundredfold - put
premium varietal wines in popularly priced magnums, introduced
"Noveau" Gamay Beaujolais to America, created blush wine known
as Pinot Noir Blanc (called "Eye of the Swan");
1980 - Mary Ann
Sebastiani Cuneo (daughter, third generation) joined winery.
 Samuele Sebastiani
- Sebastiani Vineyards
(http://www.sebastiani.com/assets/client/Image/family/samuele_s.jpg)
Samuele Sebastiani
- Sebastiani Vineyards
(http://www.sebastiani.com/assets/client/Image/family/samuele_s.jpg)
July 29, 1905
- John Sumner, financed by friends, incorporated Ty.phoo Tea
Ltd; had previously bought 30 chests of tea, spent £200 on
advertising, packed tea under brand name (distinctive, trip off
the tongue, protected by trademark; founded Ty.phoo Tipps (in
part, Chinese word for doctor, double p originally printing
error but remained misspelled on packets of tea for years); gave
away jar of cream to each person that bought a pound packet;
first brand of tea sold pre-packaged, rather than loose, over
the counter; 1906 -
had special Ty.phoo branded teapots made to sell to customers;
March 1917 -
British Tea Controller granted permit to trade in leaf-edge tea;
1934 - employed its
own tea taster/blenders; 1940
- rationing of tea began, continued for 12 years;
1960 - brand
leader; annually packed more than 80 million pounds of tea,
exported to 40 countries worldwide;
January 24, 1968 - acquired by
Schweppes' old Food Division, formed new company called Ty.phoo
Schweppes; 1969 -
Cadbury's joined conglomeration, created Cadbury Schweppes
Ty.phoo; 1986 -
acquired in in management buyout, renamed Premier Brands;
1989 - acquired by
Hillsdown Holdings; 1999
- acquired by Hicks Muse Tate and Furst; first tea brand to
introduce green tea blend to UK market;
October 31, 2005 - acquired by Apeejay
Surrendra Group, one of India's largest tea producers.winery.
February 23, 1907 - Kirin
Brewery Company, Limited incorporated; acquired by Mitsubishi
family, affiliate of Mitsubishi keiretsu; first Kirin beer
factory established in Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama; 1949
- 25.3% market share; 1954 - number one brewer in
Japan (37.1% market share); 1976 - 63.8% market
share; 1984 - signed cross-licensing agreement
with Heineken N.V., Netherlands-based brewing company (Kirin
produced Heineken for Japanese market, Heineken produced Kirin
for Dutch market); 1987 - entered into a
cross-licensing agreement with Molson Companies Ltd.; 1993
- entered into joint venture, Budweiser Japan Co., for
distribution of Budweiser beer in Japan; 1996 -
Kirin, Budweiser established Kirin Brewery of America, LLC to
produce, distribute Kirin Lager, Kirin Ichiban, Kirin Light
brands in United States at Anheuser-Busch facility in Los
Angeles area (began production in April 1997); 2000
- Anheuser-Busch dissolved joint venture; replaced by licensing
agreement between the two companies (Kirin took over production,
distribution of Budweiser brand in Japan); 2001 -
Asahi Breweries replaced Kirin as top Japanese brewer (38.7%
market share vs. 35.8%); February 2002 - acquired
15% stake in San Miguel Corporation (90% market share in
Philippines) for $544 million.
1908 - Thomas
Sullivan, tea and coffee merchant in New York, invented tea
bags; packaged tea samples in tiny silk bags, many customers
brewed the tea in them; later made of thin paper.
June 20, 1908
- Melitta Bentz, housewife from Dresden, Germany, received a
German patent for
filter top device lined with disc shaped
blotting paper (way to brew perfect cup of coffee with
none of bitterness caused by over- brewing); had found that her
son's blotter paper used for school worked best; cut round piece
of blotting paper, put it in metal cup; December 15th,
1908 - started Melitta Bentz Company.; 1909
- sold 1200 coffee filters at the Leipziger fair in Germany;
1925 -
introduced red red and green filter package;
March 11, 1941 -
Wolfgang Horst Bentz, of Minden, Germany, received a patent for
a "Filtering Device for the Production of Beverages, such as Tea
or Coffee"' assigned to Melitta-Werke Bentz & Sohn;
April 3, 1956
- Horst Wolfgang Bentz doing business as Melitta-Werke Bentz
registered "Melitta" trademark (coffee [tea] [and coffee
substitutes]).

Melitta Bentz
- Melitta Bentz Company
(http://www.espresso-kaffee-blog.de/wp-content/uploads/2006/04/melitta%20bentz.jpg)
1909 -
Marko Vachkov organized Gamza Suhindol in village of
Suhindol in valley of Rositsa River (had returned from
business trip to France; named after gamza, local,
native grape variety; first nursery-garden of grafted
vines planted here in 1896, following phylloxera crisis
that destroyed nearly all of Europe's vineyards); first
grape-growers' and winemakers' co-operative on Balkan
Peninsula; 1920s-1930s
- Vachkov became one of region's most successful wine
producers; 1952
- nationalised by communist government (one of largest
producers in Bulgaria);
1992 - acquired from government by
descendants of winery's founder; first independent
winery in country after end of communism.
June 1909 - Group
of businessmen incorporated Shiner Brewing Association (Shiner,
TX; Herman Weiss first Brewmaster);
1914 - German immigrant brewer, Kosmas
Spoetzl, Oswald Petzold co-leased brewery;
April 1915 - acquired brewery; marketed
brew by loading Model T with kegs and ice, drove dirt roads
along region's cotton fields, offered thirsty laborers what
today is basically Shiner Blonde;
1950 - Cecelie Spoetzl (daughter) took over;
1983 - produced
60,000 barrels of beer; 1989
- acquired for its loyal customer base by Gambrinus Co. (run by
Carlos Alvarez, beer marketing executive, built U.S. market for
Grupo Modelo's Corona brands in early 1980s);
1994 - produced
100,000 barrels of beer; 2009
- produced 400,000 barrels, distributed to 39 states; oldest
independent brewery in Texas.
1912 - Stafford
Higgins founded Higgins & Burke Ltd., food wholesaling business,
in Toronto, ON; 1929
- Paul Higgins (son) joined wholesale grocery distribution
company; 1930 -
introduced tea product; 1932
- packaged tea under brand name - chose 'Mother Parker's' (homey
sound); wife created caricature; April 12, 1932
- registered "Mother Parker's" trademark in Canada;
1939 - Mother
Parker's coffee introduced;
February 2000 - acquired Martinson's Coffee;
Canada's oldest coffee company; largest family-owned purveyor of
coffee, tea in North America; one of largest private label
coffee, tea manufacturers in North America.
1915 - The Root
Glass Company (founded by Chapman Jay Root as Root Glass Works,
on May 27, 1901 at Third and Voorhees streets in Terre Haute,
IN, to manufacture glass bottles, other glass containers that
would withstand high internal pressures) organized team (T.
Clyde Edwards, Alexander Samuelson, Earl R. Dean) to design 6.5
ounce bottle for Coca-Cola bottle contest for bottle to
distinguish drink from imitations; Dean, mold shop supervisor,
designed bottle with parallel vertical grooves, tapered ends
(from illustration of cocoa tree pod from 1910 Encyclopedia
Britannica); November 16, 1915
- Alexander Samuelson (plant superintendent) of Terre Haute, IN
received a design patent or a "Design for a Bottle or Similar
Article"; assigned to Root Glass Company;
1916 - design team won contest for
design of Coca-Cola bottle at bottlers convention in Atlanta, GA
(beat 11 entries for originality, exclusiveness of design, ease
of handling, production cost, potential consumer recognition);
company received 5 cents royalty for every 144 bottles made (in
addition to cost of manufacture);
November 6,1923 - Chapman J. Root, of Terre
Haute, IN, received two successor design patents for "Design for
a Bottle"; 1930s -
largest glass plant in United States that manufactured
high-pressure glass containers;
1937 - bottle design rights acquired by
Coca-Cola; 1939 -
Root formed Associated Coca-Cola Bottling Plants Inc. to
consolidate bottling facilities; became nation's largest
independent Coke bottler; 1982
- Root family 57.5% interest acquired by Coca-Cola for $417.5
million.
 Earl R. Dean
- designed Coca-Cola bottle
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/e/e8/Earl_r_dean.jpg)
Earl R. Dean
- designed Coca-Cola bottle
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/e/e8/Earl_r_dean.jpg)
1917 - L. D.
Peeler, others acquired bankrupt Maysville Syrup Company
(Maysville, KY; had been 'Mint Cola' bottling franchisee of
Maysville Syrup since 1913; had produced about 160 cases of Mint
Cola a day from basement of general store); moved company to
North Carolina, renamed Carolina Beverage Corporation; purchased
recipe for cherry flavored soda derived from oil of almond from
St. Louis salesman (gave natural sweetness to the drink, made it
taste sweeter than other soft drinks with same amount of sugar;
blended flavor with 11 others, Mint Cola base;
1918 - created
Cheerwine (burgundy wine color, cheerful bubbles);
1981 - introduced
Diet Cheerwine; Mark Ritchie (great-grandson) oversaw expansion;
August 16, 1988 -
Carolina Beverage Corporation registered "Cheerwine" trademark
first used June 1, 1918 (soft drinks);
2003 - entered Norway market.
 Cheerwine
(http://www.blakescheerwineoldies.com/peeler.jpg)
Cheerwine
(http://www.blakescheerwineoldies.com/peeler.jpg)
May 1917 - Mrs.
Julius S. Walsh Jr. (St. Louis, MO, wife of President of
Terminal Railway Co. and Mississippi Valley Trust Co.) hosted
first cocktail party, for 50 guests, on record (source: St. Paul
Pioneer Press); Clover Leafs, Highballs, Gin Fizzes, Bronx
cocktails, Martinis, Manhattans served.
January 1, 1918 -
Gordon's Dry Gin Company, Limited registered "Tanqueray"
trademark first used in December 1892 (dry gin).
1920 - Charles L.
Grigg formed Howdy Corporation (named for Howdy orange drink) in
St. Louis, MO; February 5, 1929
- registered "Seven UP" trademark first used August 7, 1928
(carbonated, nonalcoholic, noncereal, maltless beverages sold as
soft drinks, extracts and flavors used in making same);
October 1929 -
introduced new soft drink named "Bib-Label Lithiated Lemon-Lime
Soda" (two weeks before stock market crashed); name changed to
"7 UP Lithiated Lemon Soda"; 1936
- name changed to 7 UP; company name changed to The Seven-Up
Company; 1978 -
acquired by Philip Morris; 1986
- merged with Dr Pepper; formed Dr Pepper/Seven Up Companies
Inc.; 1995 -
acquired by Cadbury Schweppes plc.
 Charles Leiper Grigg
- creator of 7- UP
(http://www.character.co.jp/7UP/images/Grigg_Photo.jpg)
Charles Leiper Grigg
- creator of 7- UP
(http://www.character.co.jp/7UP/images/Grigg_Photo.jpg)
January
16, 1920 - Prohibition began as the 18th Amendment to
the U.S. Constitution took effect; prohibited the "manufacture,
sale, or transportation of intoxicating liquors for beverage
purposes," achieves the necessary two-thirds majority of state
ratification, and thus becomes the law of the land; movement for
the prohibition of alcohol began in the early 19th century, when
Americans concerned about the adverse effects of drinking began
forming temperance societies; late 19th century -
these groups had become a powerful political force, campaigned
on the state level, called for total national abstinence;
December 1917 - 18th Amendment, also known as the
Prohibition Amendment, was passed by Congress, sent to the
states for ratification; October 28, 1919 -
Congress passed the Volstead Act, or National Prohibition Act,
over President Woodrow Wilson's veto - provided for the
enforcement of prohibition, included creation of a special unit
of the Treasury Department; failed to prevent the large-scale
distribution of alcoholic beverages, organized crime flourished
in America; February 20, 1933 - the 21st Amendment
to the Constitution was passed and ratified (December 5, 1933);
repealed prohibition.
1921 - Harold
Clapp, of Rochester, NY, launched $300 million baby food
business; oldest name in baby food; original formula called for
beef broth, vegetables and cereal; 1953 - acquired
from American Home Products Company by Duffy-Mott.
May 16, 1922
- J. J. McLaughlin Limited, Toronto, ON, registered "Canada Dry
Pale Ginger Ale" trademark first used in 1890 (ginger ale).
March 20, 1923
- Partners of wine & spirit merchants Berry Bros. launched Cutty
Sark Scots Whisky; September 5, 1933 - registered
"Cutty Sark" trademark first used January 1923
([spirits-namely,] whiskey [and other potable distilled
liquors]).
November 6, 1923
- Societe Anonyme Fabriques de Produits de Chimie Organique de
Laire registered "Sanka" trademark first used March 19, 1910
(tea and coffee extracts, both dry and liquid, and tea and
coffee substitutes).
1926 -
William Black opened first nut shop at Broadway and 43rd St. in
New York City; 1931 - converted chain of 18 nut
shops into Chock Full O' Nuts Coffee Shops (coffee and a
sandwich for $.05); first counter service coffee shop in New
York; 1953 - intorduced Chock Full O' Nuts Coffee
blend in grocery stores, named after original street-side nut
shop; 1954 - Page Morton Black (wife and
professional cabaret singer) sang Chock Full O' Nuts jingle;
1955 - number one coffee in New York City ($.35 per
cup); 1961 - introduced instant coffee; 1999
- acquired by Sara Lee Corporation; December 2005
- acquired by Massimo Zanetti Beverage USA.
May 11, 1926
- Cheek-Neal Coffee Co., Nashville, TN, registered "Maxwell
House Good to the Last Drop" trademark fist used January 1, 1915
([tea and] coffee).
1927
- Edwin E. Perkins of Hastings, Nebraska developed concentrated liquid drink mix called Fruit Smack;
removed liquid, repackaged remaining
powder in envelopes; changed product's
name to Kool-Ade (soon became Kool-Aid); came in six
flavors, sold door-to-door in four-ounce glass bottles (high
shipping costs, breakage); February
7, 1928 - registered 'Kool-Ade" trademark first
used August 18, 1927 (prepared powder containing flavor, fruit
acid, and color put up in a number of flavors for making
nonalcoholic beverage in the home);
1953 - acquired by General Foods Corporation.
November 27, 1928 -
William S. Scull Company (Camden, NJ) registered "Bosco"
trademark first used June 26, 1928 (chocolate malt syrup; Joab
Scull had started coffee business in Camden, NJ in 1831; William
S. Scull became head of company in 1858; William C. Scull
succeeded in 1916; produced coffee, tea and peanut products
under the Boscul brand [first used October 6, 1913]);
1950s - acquired by
Corn Products Company; 1985
- acquired by Bosco Products, Inc., independent company based in
Towaco, NJ.
January 6, 1929 - Sheffield Farms of New York
began using wax paper cartons instead of glass bottles for milk
delivery.
July 1, 1931
- Ice vending machines introduced in LA: 25 lbs, 15 cents.
1933
- Ernest (24), Julio (23) Gallo founded winery in California's
Central Valley (Modesto) with $5,900 in start-up capital ($5,000
loan from Ernest's mother-in-law), rented warehouse, bought
crushing, fermentation equipment on credit; contracted grapes
from local growers; promised payment when grapes sold.
1933 -
Francesco Illy founded Illycaffè SpA group in Trieste, Italy;
privately-held, third-generation family-owned premium coffee
company; 2005 - annual sales of 227 million euros
(+8% vs. 2004), overseas sales exceeded sales in Italy for first
time; 2007 - controls 10 companies worldwide,
dedicated to international distribution; employs over 600
people.
February 20, 1933
- House of Representatives completed congressional action to
repeal Prohibition; December 5, 1933 - Prohibition
came to an end in the United States as Utah became the 36th
state to ratify the 21st Amendment to the Constitution of the
United States of America, repealing the 18th Amendment.
1934 - A W
Leo, Tom Yates and Ralph Harrison developed first Hawaiian Punch
recipe; 1937 - Leo's Hawaiian Punch sold as
concentrated tropical fruit topping for ice cream; name Leo
dropped several years later; 1955 Hawaiian Punch became national
brand; December 28, 1954 - Pacific Citrus Products
Company registered "Hawaiian Punch" trademark first used May 3,
1933 (concentrated fruit punch in the nature of a non-alcoholic
maltless soft drink); 1961 - acquired by RJ
Reynolds Company, transferred to Del Monte subsidiary;
1990 - acquired by Procter & Gamble; 1999
-
all rights
to Hawaiian Punch acquired by Cadbury Schweppes plc for $203
million.
December 1, 1934 -
Ferdinand Petiot, French bartender
at King Cole Bar at
the St Regis Hotel
in Manhattan, created"
Red Snapper" drink
(Serge
Obolensky, aristocratic Russian, asked Petiot for vodka cocktail
he had in Paris - mix of vodka, tomato juice, spiced up with
salt, pepper, lemon, Worcestershire Sauce;
'bloody' considered too harsh in 1930s); Tabasco sauce added to
drink, renamed "Bloody Mary";
1960 -
became popular to serve cocktail with celery (guest at
Ambassador East Hotel in Chicago
requested it.
January 24, 1935 -
Gottfried Kreuger Brewing Company
sold beer in cans for first time, "Finest Beer" and "Cream Ale",
in Richmond, VA.
1936 - Stuart
Peabody, director of advertising for Borden, introduced 'Elsie'
as image for Borden's Milk in one of four cows in cartoon strip
in medical journal ads (doctors ordered reprints;
1938 - Borden
sponsored Rush Hughes, radio network news commentator on station
KXOK in St. Louis, MO; read prepared commercial which made
reference to letter: ''Dear Mama, I'm so excited I can hardly
chew. We girls are sending our milk to Borden's now! Love,
Elsie"; listeners sent fan mail to Elsie; became spokescow for
Borden; 1939 -
introduced 'live' at the "The Dairy World of Tomorrow" exhibit
at New York World's Fair; 1969
- dropped as corporate symbol;
March 10, 1993 - reintroduced;
1997 - licensing
agreement made Elsie and Borden Cheese part of Dairy Farmers of
America.
September 12, 1937
- L'appellation d'origine contrôl Beaujolais created (Beaujolais
AOC); French certification under auspices Agriculture Institut
National des Appellations d'Origine (INAO), branch of French
Ministry of Agriculture, created July 30, 1935, to manage
administration of process for wines; rules stated Beaujolais
only officially sold after December 15 in year of harvest;
November 13, 1951 - rules relaxed, Union
Interprofessionnelle des Vins du Beaujolais (UIVB) formally set
November 15 as release date for Beaujolais Nouveau; 1985
- date changed to third Thursday in November to take best
advantage of marketing over following weekend.
September 28,
1937 - Joseph Bernard Friedman, of San
Francisco, CA, received a patent for "Drinking Tube" ("...soda
straw or similar drinking tube with a flexible section so
positioned ao that the tube may be bent during use without
substantially reducing the diameter of the straw"); 'bendy' soda
straw.
January
25, 1938 - New England Products, Inc. registered
"V8" trademark first used July 17, 1937 (combination of eight
vegetable juices).
July 24, 1938
- Nestlé company introduced Nescafé in Switzerland;
world's first commercial freeze-dried instant coffee (assisted
Brazilian government in solving coffee surplus, dwindling coffee
exports problem); dehydrated concentrated coffee; July 2,
1940 - Nestle's Milk Products, Inc. registered Nescafe
trademark first used October 11, 1939 (coffees, coffee extracts,
decaffeinated coffees, and decaffeinated coffee extracts, with
or without the admixture of other food ingredients).
December 31, 1938
- The "drunkometer," first breath test for car drivers, invented
by Dr Rolla N. Harger of Indiana University School of Medicine,
officially introduced in Indianapolis; first successful machine
for testing human blood alcohol content by breath analysis.
1941 - Loft Inc.
merged with Pepsi-Cola subsidiary, re-named Pepsi-Cola Company,
went public; 1950 -
Alfred N. Steele, former Coca-Cola
vice-president of sales,
became president; changed logo, changed to swirl-designed
bottle;
1959 - Donald M. Kendall, head of Pepsi-Cola
International, persuaded U.S. Vice-President Richard Nixon to
stop by the Pepsi booth at the Moscow Trade Fair with Nikita
Khrushchev, Soviet Premier; 1963 - Kendall named
President; advertised on massive, unprecedented scale;
introduced new brands of soft drinks; led industry in packaging
innovations; expanded overseas; diversified product line via
acquisitions.
November 29,
1942 - Coffee rationed in United States during
World War II (despite record coffee production in Latin American
countries) due to growing demand from both military and civilian
sources, demands placed on shipping (needed for other purposes);
July 1943 - coffee
released from rationing list (sugar rationed until June 1947).
1945 - Ruth Campbell Bigelow founded R.C. Bigelow,
Inc. to produce quality teas in Fairfield, CT; one of nation's
leading producers of Green Tea, Decaf Tea, Herbal Tea, Flavored
Tea, specialty teas; flagship Constant Comment Tea (sample tea
shared with family, friends, acquaintances caused 'constant
comments'); June 22, 1954 - registered "Constant
Comment" trademark first used in 1944 (tea); 2007
- sales of $110 million, 330 employees; third generation
management.
 Ruth Campbell Bigelow
- Bigelow Tea
(http://www.bigelowtea.com/media/36184/ruth_290x193.jpg)
Ruth Campbell Bigelow
- Bigelow Tea
(http://www.bigelowtea.com/media/36184/ruth_290x193.jpg)
December 1945
- Marvin Sands (21) formed Canandaigua Industries Company (8
employees) to sell bulk wine in barrels to bottlers in East;
first year - sold approximately 200,000 gallons of wine, gross
sales of $150,000; 1972 - renamed Canandaigua Wine
Company, Inc.; 1973 - went public; grew by
acquisition; 1990 - acquired Italian Swiss Colony
dessert wines; 1991 - acquires all assets, certain
liabilities of Guild Wineries (nation's seventh largest wine
producer); sales of approximately $200 million; 1994
- acquired Mission Bell Winery from Heublein (Almaden, Inglenook
wine brands and grape juice concentrate business); 1995
- acquired certain assets of United Distillers Glenmore (Mr.
Boston, Canadian LTD, Skol, Old Thompson, Kentucky Tavern,
Glenmore, di Amore, Fleischmann's, Chi Chi's, Schenley);
1997 - Canandaigua Brands, Inc. formed as parent
company; September 2002 - name changed to
Constellation Brands, Inc.; April 2003 - acquired
BRL Hardy Ltd. Pacific Wine Partners; became world's largest
producer, marketer of wine; sales in excess of 80 million cases
annually; 2004 - $6,000 investment 25 years ago
now valued at $1 million; December 2004 - acquired
The Robert Mondavi Corp. for $1.03 billion; 2006 -
became Fortune 500 company.
1946 -
Barney and Ally Hartman, operated Hartman Beverage bottling
plant in Knoxville, TN, created Mountain Dew (slang for
"moonshine"), lemon-lime drink used as mixer with whiskey);
August 11, 1953 -
Hartman Beverage Company (Knoxville, TN) registered "Mountain
Dew" trademark first used October 10, 1948 (non-alcoholic
maltless beverages sold as soft drinks, and syrups for making
same);
1954 - Tri-City Beverage in Johnson
City, TN became first Mountain Dew franchisee; November
30, 1957 - brand sold to Tip Corporation;
September 2, 1964 - Pepsi acquired Tip Corporation,
including rights to Mountain Dew.
November 9,
1948 - Louis G. MacDowell, of Lakeland, FL,
Edwin L. Moore and Cedric D. Atkins, of Winter Haven FL,
received a patent for a "Method of Preparing Full-Flavored Fruit
Juice Concentrates" ("...concentrated fruit juice containing a
substantial portion of the original aroma, flavor, and
palatability...by adding a portion of fresh, single-strength
juice to a relatively strong concentrate...and thereby obtaining
a concentrate of medium strength"); assigned to the United
States of America as represented by the Secretary of
Agriculture; frozen concentrate orange juice.
February 22,
1949 - T.H. Estanrooks Co., Ltd. registered "Red
Rose" trademark first used August 20, 1895 (tea).
June 26, 1951
- James B. Beam Distilling Co. registered "Jim Beam" trademark
first used May 21, 1928 (whiskey).
August 11, 1953 -
Hartman Beverage Company (Knoxville, TN) registered "Mountain
Dew" trademark first used October 10, 1948 (non-alcoholic
maltless beverages sold as soft drinks, and syrups for making
same).
November 30, 1950
- Concentrated milk first sold in U.S. in Wilmington, DE.
November 13, 1951
-
Vintner
Georges DuBoeuf introduced Beaujolais Nouveau (made
from Gamay Noir à Jus Blanc grape in Beaujolais region of
France, authorized for immediate sale after fermentation);
L'appellation d'origine contrôl Beaujolais created (Beaujolais
AOC) relaxed rules for release of primeur wines (previously
December 1).
November 10, 1952
- Jack Koeppler, then-owner of Buena Vista (San Francisco),
challenged international travel writer Stanton Delaplane to
re-create highly touted "Irish Coffee" served at Shannon Airport
(Ireland); serves up to 2,000 Irish Coffees a day; largest
single consumer of Irish whiskey in the U. S. (18,720
liter-sized bottles per year).
1957 - E.
& J. Gallo Winery introduced Thunderbird (lemon-flavored) wine -
higher alcohol content at cheaper price; (had watched black
customers mix concentrated lemon juice with white port);
January 7, 1958 - registered "Thunderbird" trademark
first used April 22, 1957 (wines).
April 2, 1958
- Antillean Brewery, maker of Amstel
beer, opened.
1959 - Ermal
Fraze of Dayton Reliable Tool and Manufacturing Co. invented
improved beverage can, with opener, a lever, attached;
1962 - Pittsburgh Brewing Co., maker of Iron City Beer,
ordered 100,000 cans, beer sales soared 400 percent in next six
months; 1965 - developed ring-pull version that
caused less bloodshed; over seventy-five percent of beer brewers
in the United States of America adopted Fraze's can;
October 31, 1967 - Omar L. Brown, Don B. Peters, of
Dayton, OH, assigned patent to Ermal Fraze of Dayton Reliable
Tool and Manufacturing Co. for a "Ring Shaped Tab for Tear
Strips of Containers" ("relates to a container having a portion
of its wall weakened to serve as a tear strip and, more
particularly, relates to the structure of the tab that is
attached to the tear strip to serve as a manual mean of severing
the strip"); "pop-top" (ring-pull) can assigned ; 1970s
- developed a now-mandatory non-removable ring, which reduced
litter.
February 9, 1960
- Adolph Coors,
grandson of Coors'
founder, chairman of Golden, CO brewery,
disappeared
while driving to work from his Morrison, Colorado, home;
kidnapped, held for ransom before shot to death; 1961
- Joe Corbett, former Fulbright scholar at University of Oregon,
was convicted (never testified at his trial, never made any
statement); 1980 - released.
May 8, 1961
- Office of Saline Water, U.S. Dept of the Interior opened first
practical seawater conversion plant in U.S. in Freeport, TX;
designed to produce about million gallons of water a day at cost
of about $1.25 per thousand gallons; large-scale evaporation
method used then replaced by reverse osmosis as scientific
advances have produced special polymers suitable for use as
filtering membranes.
1962
- First International Coffee Agreement (ICA) between
coffee-producing countries negotiated in New York at Conference
held under auspices of United Nations (in force for period of
five years, operated under successive Agreements negotiated in
1968, 1976, 1983, 1994, 2001, 2007); contained provisions for
application of quota system whereby supplies of coffee in excess
of consumer requirements withheld from market; production and
diversification policies initiated to limit supplies of coffee,
promotion activities instituted to increase consumption; kept
prices relatively stable throughout the years 1963 to 1972,
production and consumption became more evenly balanced;
1963 -
International Coffee Organization established in London;
1973 - quota
controls system suspended; 2007
- objective to strengthen global coffee sector, promote its
sustainable expansion in market-based environment for betterment
of all participants.
1963
- Fanta division of Coca-Cola introduced Tab, first diet soft
drink brand produced by company; second diet soft drink, after
Diet-Rite Cola; called Tab (helped people keep tabs on what they
consumed; initially sweetened with cyclamates [banned in 1969],
changed to saccharin; 1984
- formula revision blended saccharin with small amount of
aspartame.
1963 -
Earliest Department of Agriculture survey on home milk delivery:
milk delivered to 29.7% of consumers; 1975 - 6.9%
of total milk sales delivered to homes; 2005 -
0.4% of milk delivered.
October 1965 -
University of Florida football players, in game against LSU,
first used Gatorade sports drink, created by nephrologist J. Robert Cade,
director of University of Florida College of Medicine’s renal
and electrolyte division, to combat hydration in second half; 1967 - Stokely-Van Camp,
Inc. acquired marketing rights; April 30, 1968 -
Stokely-Van Camp, Inc. registered "Gatorade" trademark first
used March 1, 1967 (fruit flavored soft drink and powder for
making same); 1983 - Stokely acquired by Quaker
Oats; 2001 - Quaker acquired by Pepsico;
2007 - sports drink market size estimated at $19
billion.
 J. Robert Cade
- creator Gatorade
(http://www.uff.ufl.edu/FacultyEndowments/images/Profiles/Cade,Robert.jpg)
J. Robert Cade
- creator Gatorade
(http://www.uff.ufl.edu/FacultyEndowments/images/Profiles/Cade,Robert.jpg)
1965 - Donald
M. Kendall, President and Chief Executive Officer of Pepsi-Cola
and Herman W. Lay, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of
Frito-Lay, founded PepsiCo, Inc. through merger of two
companies; sales of $510 million, 19,000 employees; 1970
- sales pass $1 billion, 36,000 employees;
1977
- acquired Taco Bell; 1978 - acquired Pizza Hut;
1983 - Burger King began selling Pepsi products;
1986 - D. Wayne Calloway named chairman, CEO;
acquired Kentucky Fried Chicken (KFC); 1996 -
Roger A. Enrico, former head of the restaurants division, named
CEO; October 1997 - Tricon Global Restaurants,
Inc. formed (Taco Bell, Pizza Hut, KFC chains); August
1998 - acquired Tropicana Products, Inc. from Seagram
Company, Ltd. for $3.3 billion; 1999 - spun off
Pepsi Bottling Group, largest Pepsi bottler in world, in $2.3
billion IPO; focused exclusively on beverages, snack foods.
1966 - Robert G.
Mondavi founded Robert Mondavi Winery; first major winery built
in Napa Valley in post-Prohibition era;
December 22, 2004 - acquired by
Constellation Brands for nearly $1.303 billion.
1966 - Alfred Peet
opened Peet's Coffee & Tea Inc. on corner of Walnut and Vine in
in Berkeley, CA; originator of specialty coffee concept;
inspiration for Starbucks; 1984
- acquired by Jerry Baldwin, Gordon Bowker (co-founders of
Starbucks in 1971); 2007
- 150 stores.
1967 - Rheingold
Breweries (Brooklyn, NY) introduced Gablinger's Diet Beer (beer
without starch) developed by Joseph L. Owades, a biochemist;
acquired by Miller Brewing, renamed Miller Lite.
1969 - Schweppes
Ltd merged with Cadbury Group Ltd., created Cadbury Schweppes
plc.
1971 -
English teacher Jerry Baldwin, history teacher Zev Siegel, and
writer Gordon Bowker invested $1,350 each, borrowed another
$5,000 from a bank, opened Starbucks Coffee, Tea, and Spice in
Pikes Place Market in Seattle as retailer, not restaurant or bar
(supposedly named in honor of Starbuck, coffee-loving first mate
in Herman Melville's Moby Dick); sold whole-bean coffees, coffee
products; did not offer fresh-brewed coffee by cup, samples
sometimes available for tasting;
1981 - Howard Schultz, vice president and
general manager of U.S. operations for Hammarplast (Swedish
maker of stylish kitchen equipment, housewares) noticed that
Starbucks was placing larger orders than Macy's for certain type
of drip coffeemaker; September 1982
- Schultz hired as head of marketing, retail store management;
1984 - Baldwin,
Bowker acquired Peet's Coffee and Tea (5 stores in San
Francisco, CA); April 1984
- Starbuck's 6th store designed to sell beverages (300 square
feet in corner of new store), first one in downtown Seattle; 400
customers served on first day (250-customer average oat
Starbucks' best-performing stores);
June 1984 - 800 customers per day served
(most sales at espresso counter);
April 1986 - Schultz opened first Il Giornale
store (700 square feet); 300 customers served; October 1986 -
served more than 1,000 customers a day, speedy service was
competitive advantage; December
1986 - Schultz raised $1.65 million from about
30 investors (most from nine people, five of whom became
directors of new company); mid-1987
- sales at three stores equaled $1.5 million annually;
August 1987 -
acquired Starbucks (stores, roasting plant, name) for $3.8
million; Schultz (34) president and CEO.
 Jerry Baldwin
(right) - co-founder Starbucks
(http://www.peets.com/media/cms/JerryBaldwin_230x175.png)
Jerry Baldwin
(right) - co-founder Starbucks
(http://www.peets.com/media/cms/JerryBaldwin_230x175.png)

Gordon Bowker
- co-founder Starbucks
(http://proxied.changemakers.net/journal/
thatwaseasy/images/bowker.jpg)
1972
- Leonard Marsh, Hyman Golden and Arnold Greenberg owned
Unadulterated Food Corporation, sold carbonated apple soda
product in New York City; led to name "Snapple"; June 2,
1981 - registered "Snapple" trademark first used July
15, 1970 (fruit juices); 1992 - acquired by Thomas
H Lee and Company; 1994 - acquired by Quaker Oats;
1997 - acquired by Triarc Beverage Group;
2000 - acquired by Cadbury Schweppes.
May 24, 1976
- Steven Spurrier, British wine merchant, hosted "Judgment of
Paris" wine tasting: French wine experts (famous sommeliers,
restaurateurs, chateau owners) ranked California wines superior
to elite French vintages in a blind taste test; gave California
wines world-class stature.
January 1977
- House Republican Barber Conable (R-NY) introduced bill HR
2028; eventually become HR 1337/SR 3534;
October 14, 1978 - President Jimmy
Carter signed House Resolution 1337/Senate Amendment 3534
(proposed by Senator Cranston of California, Senator Schmitt of
New Mexico, Senator Bumpers of Arkansas, Senator Gravel of
Alaska); legalized home beer brewers and home winemakers;
allowed brewing up to 100 gallons per adult, up to 200 gallons
per household per year; 2007
- 2,000 breweries in United States, 1,400 of which classified as
"craft brewers" (independent breweries that produce fewer than
two million barrels of beer per year; source: National Brewer's
Association).
July 8, 1982 -
Coca-Cola introduced Diet Coke (Coca-Cola Light in non-English
speaking countries) at gala reception at Radio City Music Hall;
first new brand since 1886 to use the Coca-Cola trademark since
1886; contained around 1.3 Calories compared to 142 Calories for
regular can of Coca-Cola; 1983 - largest selling
low-calorie soft drink in U. S.; caffeine-free Diet Coke
introduced; 1986 - diet Cheery Coke launched;
2001 - Diet Coke with lemon introduced; Diet Vanilla
Coke introduced;
2004
- #1 selling sugar-free soda in world; fourth most-popular
carbonated soft drink in world; third-largest brand at the
company; sold in 149 countries; 9.8% market share in U. S.;
2005 - sweetened with "Splenda" (sucralose replaced
aspartame).
November 15, 1982
- Georges Duboeuf
released Beaujolais Nouveau in America ( made
from Gamay Noir à Jus Blanc grape
in Beaujolais region of France, authorized for immediate sale
after fermentation);
transformation from vine to bottle accomplished in matter of
weeks; fruity, juicy, light (not serious, complex).
November 9, 1983 -
Alfred Heineken, beer brewer from Amsterdam, was kidnapped, held
for a ransom of more than $10 million.
January 27, 1985
- Coke announced plans to sell soft drinks in Soviet Union
(Pepsico began distribution in U.S.S.R. twelve years earlier).
February 19, 1985 - Coca-Cola Company introduced
Cherry Coke.
April 23,
1985
-
Coca-Cola Co.
introduced New Coke, change in
secret formula for Coke, with slogan "The Best Just Got Better";
Negative public reaction
forced company to resume selling original version;
July
11, 1985 - announced it would bring back its
99-year-old formula - Classic Coke; bowed to pressure from irate
customers 79 days after introduction of New Coke; said it
would resume selling old-formula Coke; one of greatest marketing
blunders in consumer goods and business history;
January 30, 2009 -
announced it would remove "classic" from flagship brand (only
appeared on Coca-Cola bottles, cans in U. S.).
November 20, 1990
- Guinness & Co. acquired Spain's biggest brewer, La Cruz del
Campo (Cruzcampo) for $1 billion; largest foreign purchase of
Spanish property.
January 26, 1995
- Cadbury Schweppes P.L.C. acquired Dr. Pepper/Seven-Up Company
(third-biggest U.S. soft drink company) for $1.7 billion
(already owned A&W root beer, Canada Dry, and Crush and Sunkist
fruit colas) = 17% share of America's $49 billion soda market,
just behind Coca-Cola and Pepsico.
December 17, 1997
- Guinness plc merged with Grand Metropolitan plc; formed Diageo
plc (from the Latin dia [Day] and Greek geo
[World], meant to symbolize company's producing products
consumed every day throughout world); formed Britain's
7th-largest company, value of almost £24 billion.
December 22, 1997
- Coca-Cola acquired Orangina, the "sparkling" French beverage
formerly owned by Pernod Richard (ranked second to Coke in
overall market share in France), for $840 million; intended to
to expand roster of "non-cola" drinks."
September 14, 1998
- Companhia de Bebidas das Américas (American Beverage Company -
AmBev) incorporated as Aditus Participações S.A. in Sao Paulo,
Brazil; result of 1997 merger of
Companhia Cervejaria
Brahma, Companhia Antarctica Paulista Industria Brasileira de
Bebidas e Conexos; largest private company of consumer
goods in Brazil, Latin America’s largest brewer; fifth largest
brewer in world.
September 6, 2004
- Interbrew SA (formed by 1987 merger of Brasseries Artois,
second largest brewer in Belgium merged with Brasseries
Piedboeuf, largest brewer in Belgium) merged with Companhia de
Bebidas das Américas (American Beverage Company - AmBev),
formed by 1999 merger of
Companhia Cervejaria Brahma, Companhia Antarctica Paulista
Industria Brasileira de Bebidas e Conexos in Brazil) in
an $11.4 billion deal;
created InBrew, world's largest brewer, by volume (202
million hectoliters (hl) of beer, 3.5 million hl of soft drinks
in 2004); portfolio of more than 200 brands (Stella Artois®,
Brahma®, Beck's® , Lffe®); No. 1 or No. 2 in over 20 key beer
markets around world; more than 86,000 employees, operations in
over 30 countries, revenue of more than 13.3 billion € (2006).
May 16, 2005
- Supreme Court ruled in Swedenburg v. Kelly (Edward D. Kelly,
chairman of New York State Liquor Authority) that a New York law
preventing wine sales across state lines was unconstitutional;
case filed in Manhattan federal court by Juanita Swedenburg,
Virginia-based vintner, who was prevented from mailing cases of
wine to customers in New York state (wine could be mailed
intra-state); battle between Commerce clause to Constitution
(illegal for states to erect protective barriers against
interstate commerce) and 21st Amendment to Constitution
(repealed Prohibition in 1933, gave states power to regulate
alcohol).
March 8, 2006
- Beverage Digest, soda industry trade publication, reported
that number of cases of soda sold in United States in 2005 (10.2
billion cases) declined for first time in 20 years (down 0.7
percent); lost ground to bottled waters, sports drinks, energy
drinks.
May 3, 2006 -
Top three U.S. soft-drink companies (Coca-Cola, PepsiCo Inc.,
Cadbury Schweppes - together control more than 90 percent of
school sales) announced they would voluntarily remove sweetened
drinks (Coke, Pepsi, iced teas) from school cafeterias and
vending machines (35 million public school students) over a
three-year period in response to growing threat of lawsuits and
state legislation; elementary school students would be served:
bottled water, low-fat and nonfat milk, 100 percent fruit juice
(in 8 oz. of less servings, 10 oz. or less in middle school, 12
oz. or less in high school); high school students: low-calorie
juice drinks, diet sodas acceptable.
January 2007
- Reims Management School (RMS), Reims, France, appointed
international wine expert Dr. Stephen Charters as head of its
Champagne Chair; former senior lecturer in wine marketing and
wine studies at the Edith Cowan University (Perth, Australia);
funded (250 000 Euros/year) by CIVC (inter-professional council
for Champagne wineries), City of Reims, major champagne houses
(Moët & Chandon, Veuve Clicquot, Ruinart, Krug [all owned by
LVMH], Laurent Perrier, Nicolas Feuillatte, Pommery); only
chaired professor of champagne in world; wineries, or major
"Champagne houses", of Champagne region in France produce more
than 300 million bottles of Champagne annually, generate more
than 4 billion Euros/year (around 40% of production destined for
export outside of metropolitan France), employ more than 10,000
people directly employed.
October 9, 2007
- SABMiller (58% interest) and Molson Coors Brewing Company (42%
interest), 2nd and 3rd brewers in U.S., announced plans to merge
operations in U.S. and Puerto Rico; renamed MillerCoors (annual
sales of $6.6 billion, control of 29% American market vs. 49%
for Anheuser-Busch).
January 25, 2008
- British brewer Scottish & Newcastle
accepted $15.2 billion takeover
offer made by Carlsberg and Heineken.
March 31, 2008
- Pernod Ricard, French liquor company, announced it had agreed
to acquire Vin & Sprit, parent of Absolut vodka (sells 11
million cases/year, leading premium vodka brand), from Swedish
government for $8.87 billion, in conclusion of 4-month auction;
beat Fortune Brands (distributor of Absolut in US), Bacardi, EQT
(Swedish private equity firm).
(Absinthe),
Barnaby Conrad III (1988).
Absinthe: History in a Bottle. (San Francisco, CA,
Chronicle Books, 160 p.). Painter and Author Absinthe; Drinking
customs --History --19th century; Drinking customs --France
--History --19th century. Absinthe as social phenomenon, as
imaginative theme; 19th-century Europe's most popular,
addictive, drink (144-proof); notoriously addictive, drug of
choice for 19th-century poets, gaining bootleg popularity after
almost century of being banned (bitter green liqueur banned in
most of Europe, United States since 1913).
(Absolut Vodka), Carl Hamilton (1994).
Absolut: Biography of a Bottle. (New York, NY: Texere,
312 p.). Television host of the critically acclaimed show
Dilemma, a political commentator and a columnist for
Scandinavia's largest popular newspaper, Aftonbladet. Absolut
Vodka Company; Advertising -- Alcoholic beverages; Vodka
industry -- Sweden -- History.
 Lars
Olsson Smith - founder Absolut Vodka
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/62/L.O._Smith%2C_Nordisk_familjebok.png)
Lars
Olsson Smith - founder Absolut Vodka
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/62/L.O._Smith%2C_Nordisk_familjebok.png)
(Absolut Vodka), Richard W. Lewis (1996).
Absolut Book: The Absolut Vodka Advertising Story.
(Boston, MA: Journey Editions, 274 p.). Executive of TBWA
Chiat/Day, Absolut's advertising agency. Absolut Vodka Company;
Advertising--Alcoholic beverages; Vodka
industry--Sweden--History.
(Anheuser Busch), Roland Krebs in
collaboration with Percy J. Orthwein (1953).
Making Friends Is Our Business; 100 Years of Anheuser-Busch.
(St. Louis, MO, 449 p.). Anheuser-Busch, inc.
 Adolphus Busch
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/30/
Adolphus_busch2.jpg/220px-Adolphus_busch2.jpg)
Adolphus Busch
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/30/
Adolphus_busch2.jpg/220px-Adolphus_busch2.jpg)
 August A. Busch Jr.
(http://www.stlcommercemagazine.com/archives/december1999/images/cover3.jpg)
September 30, 1989 obituary - (http://www.nytimes.com/learning/general/onthisday/bday/0328.html)
August A. Busch Jr.
(http://www.stlcommercemagazine.com/archives/december1999/images/cover3.jpg)
September 30, 1989 obituary - (http://www.nytimes.com/learning/general/onthisday/bday/0328.html)
(Anheuser-Busch), Ronald J. Plavchan (1976).
A History of Anheuser-Busch, 1852-1933. (New York, NY:
Arno Press, 247 p.). Anheuser-Busch, Inc.
(Anheuser-Busch), Peter Hernon and Terry Ganey
(1991).
Under the Influence: The Unauthorized Story of the
Anheuser-Busch Dynasty. (New York, NY: Simon & Schuster,
461 p.). Busch family; Anheuser-Busch, inc.--History; Brewing
industry--United States--History.
(Anheuser-Busch), Julie MacIntosh (2010).
Dethroning the King: The Hostile Takeover of Anheuser-Busch, an
American Icon. (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 408 p.). U.S.
Mergers and Acquisitions Correspondent (Financial Times). Busch
family; Anheuser-Busch, inc.; Consolidation and merger of
corporations --United States. Takeover of one of most
well-known, beloved American brands by InBev, Belgian company
controlled by Brazilians; once lauded by beer industry (factory
workers, distributors), state of Missouri; Augie III despised, Augie IV laughingstock; how
InBev pulled it off: timing, missteps made by Busch family, AB
board.
(Arbuckle Bros.), Francis L. Fugate (1994).
Arbuckles: The Coffee That Won the West. (El Paso, TX:
Texas Western Press, 233 p.). Arbuckle Bros.--History; Coffee
industry--West (U.S.)--History.
(Assam Company Limited - established February
12, 1839), H. A. Antrobus (1957). A History of the Assam
Company, 1839-1953. (Edinburgh, Scotland: Priv. print. by T.
and A. Constable, 501 p.). Assam Company Limited. First tea
company in the world set up by a deed of the British Parliament.
(Bacardi Corporation), Peter Foster (1990).
Family Spirits: The Bacardi Saga. (Toronto, ON:
Macfarlane Walter & Ross, 305 p.). Bacardi family; Bacardí
Corporation (Puerto Rico)--History; Rum industry--Caribbean
Area--History; Distilling industries--Caribbean Area--History.
(Bacardi Corporation), Hernando Calvo Ospina;
translated by Stephen Wilkinson and Alasdair Holden; preface by
James Petras (2002).
Bacardi: The Hidden War. (Sterling Press: Pluto Press,
127 p.). Bacardí Corporation (Puerto Rico)--History; Bacardí
Corporation (Puerto Rico)--Political activity; Rum
industry--United States; Rum industry--United States--Political
activity.
(Bacardi Corporation), Tom Gjelten (2008).
Bacardi and the Long Fight for Cuba: The Biography of a Cause.
(New York, NY: Viking, 480 p.). National Public Radio
Correspondent. Bacardi Corporation (Puerto Rico) --History; Rum
industry --Cuba --History; Cuba --History --Intersection of
business, power, family, politics, community, exile.
Cuban origins of Bacardi clan
(patriots, bon vivants, entrepreneurs, intellectuals);
provided example of business, civic leadership in Cuba for
nearly century (now headquartered in Puerto Rico); no chapter in
Cuban history in which Bacardis have not played role.
(A. G. Barr plc), Robin Barr and Mark Jephcott
(2001). Robert Barr to A.G. Barr p.l.c. 1875 to 2001.
(Glasgow, Scotland: A.G. Barr p.l.c, 88 p.). Chairman of A.G.
Barr, plc; Brands Manager. Barr, Robert; A. G. Barr, plc; soft
drinks--history--Great Britain. History of business spanning
over 125 years.
(Bass Ratcliff & Gretton), Colin C. Owen
(1992). "The Greatest Brewery in the World": A History of
Bass, Ratcliff & Gretton. (Chesterfield, UK: Derbyshire
Record Society, 272 p.). Bass Brewers; Brewers -- England --
History.
(James B. Beam Distilling Company), F. Paul
Pacult (2003).
American Still Life: The Jim Beam Story and the Making of the
World's #1 Bourbon. (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 256 p.). Beam
family; James B. Beam Distilling Company; Whiskey industry
Kentucky History; Liquor industry executives Kentucky Biography;
Liquor industry executives Kentucky Genealogy; Kentucky
Genealogy.
(Beer), Peter Mathias (1959).
The Brewing Industry in England, 1700-1830 (Cambridge,
UK: Cambridge University Press, 595 p.).
(Beer), H. A. Mobckton (1966).
A History of English Ale and Beer. (London, UK: Bodley
Head, 238 p.). Brewing industry--Great Britain.
(Beer), Stanley W. Baron (1972).
Brewed in America; A History of Beer and Ale in the United
States. (New York, NY: Arno Press, 424 p. [orig. pub.
1962]). Brewing industry--United States--History.
(Beer), Ian Donnachie (1979).
A History of the Brewing Industry in Scotland.
(Edinburgh: Donald, 287 p.). Brewing
industry--Scotland--History.
(Beer), Terence R. Gourvish and
R.G. Wilson (1994).
The British Brewing Industry, 1830-1980. (New York, NY:
Cambridge University Press, 690 p.). Brewing industry--Great
Britain--History.
(Beer), Robert A. Musson (1997).
Brewing Beer in the Rubber City: A History of Akron’s Brewing
Industry from 1845 to 1997. (Akron, OH: R.A. Musson, 265
p.). Breweries--Ohio--Akron--History.
(Beer), Philip Van Munching
(1997).
Beer Blast: The inside Story of the Brewing Industry's Bizarre
Battles for Your Money (New York, NY: Times Business,
309 p.). Beer industry -- United States -- History -- 20th
century; Brewing industry -- United States -- History -- 20th
century; Advertising -- Beer -- United States -- History -- 20th
century; Competition -- United States -- History -- 20th
century.
(Beer), ed. R.G. Wilson and
T.R. Gourvish (1998).
The Dynamics of the International Brewing Industry Since 1800.
(New York, NY: Routledge, 294 p.). Brewing industry--History;
Beer industry--History.
(Beer), Timothy Harper (1999).
Moscow Madness: Crime, Corruption, and One Man's Pursuit of
Profit in the New Russia. (New York, NY: McGraw-Hill,
272 p.). Grajirena, Rick; Businessmen--United States--Biography;
Businessmen--Russia (Federation)--Biography; Business
ethics--Russia (Federation); Beer industry--Russia (Federation);
Russia (Federation)--Commerce.
(Beer), Glen C. Phillips (2000).
On Tap: The Odyssey of Beer and Brewing in Victorian
London-Middlesex. (Sarnia, ON: Cheshire Cat Press, 167
p.). Brewing industry--Ontario--London--History--19th century;
Brewing industry--Ontario--Middlesex--History--19th century;
Beer industry--Ontario--London--History--19th century.; Beer
industry--Ontario--Middlesex--History--19th century.
(Beer), Allen Winn Sneath
(2001).
Brewed in Canada: The Untold Story of Canada's 350-Year-Old
Brewing Industry. (Toronto, ON: Dundurn Press, 431 p.).
Co-Founder of Algonquin Brewing. Brewing
industry--Canada--History.
(Beer), Richard W. Unger
(2001).
A History of Brewing in Holland, 900-1900: Economy, Technology,
and the State. (Boston, MA: Brill, 428 p.).
Beer--Netherlands--History; Brewing.
(Beer), Glenn A. Knoblock and James T. Gunter (2004).
Brewing in New Hampshire. (Charleston, SC: Arcadia, 128
p.). Brewing industry--New Hampshire. History of New Hampshire's beer and ale brewing industry from
Colonial days (home, tavern based) to today's modern breweries.
(Beer), Max Nelson (2004).
The Barbarian's Beverage: A History of Beer in Ancient Europe.
(New York, NY: Routledge. Beer--Europe--History--To 1500;
Brewing industry--Europe--History--To 1500.
(Beer), Richard W. Unger
(2004).
Beer in the Middle Ages and the Renaissance.
(Philadelphia, PA: University of Pennsylvania Press, 319 p.).
Professor of History (University of British Columbia).
Beer--Europe--History--To 1500; Beer--Europe--History--To
1500--16th century; Brewing industry--Europe--History--To 1500;
Brewing industry--Europe--History--16th century.
(Beer), Robert A. Musson (2005).
Brewing in Cleveland. (Charleston, SC: Arcadia, 128 p.).
Brewing industry--Ohio--Cleveland--History--Pictorial works;
Beer industry--Ohio--Cleveland--History--Pictorial works;
Breweries--Ohio--Cleveland--History--Pictorial works; Cleveland
(Ohio)--History. Cyclical history of
beer-brewing industry in Cleveland: growth due to rapidly
increasing immigrant population of mostly Germans, Czechs, and
Irish; Prohibition; brewpubs and microbreweries.
(Beer), Victor J. Tremblay,
Carol Horton Tremblay (2005).
The U.S. Brewing Industry: Data and Economic Analysis.
(Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 379 p.). Professor and Associate
Professor of Economics (Oregon State University). Brewing
industry--United States--History--20th century.
(Beer), Maureen Ogle (2006).
Ambitious Brew: The Story of American Beer. (Orlando,
FL: Harcourt, 432 p.). Beer--History; Brewing--History' Brewing
industry--United States. History of beer from German immigrants of 1840's to microbrewers
of 1980's.
(Beer), Bob Skilnik (2006).
Beer: A History of Brewing in Chicago. (Fort Lee, NJ:
Barricade Books, 416 p.). Former Associate Editor for the
American Breweriana Journal. Beer
industry--Illinois--Chicago--History; Brewing
industry--Illinois--Chicago--History;
Beer--Illinois--Chicago--History.
History of Chicago against
backdrop of booming, ultimately doomed brewing industry.
(Beer), Doug Hoverson (2007).
Land of Amber Waters: The History of Brewing in Minnesota.
(Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press, 352 p.). St.
Thomas Academy (Mendota Heights, MN).
Brewing--Minnesota--History; Brewing
industry--Minnesota--History. 1849 - first brewery; nearly 300
breweries have opened, operated at one time or another in 125
cities, towns around state (small-town breweries that gave way
to larger companies with regional, national prominence; new wave
of breweries, brewpubs sustained by microbreweries, home
brewers, beer aficionados).
(Beer), Amy Mittelman (2007).
Brewing Battles: The History of American Beer. (New
York, NY: Algora Pub., 248 p.). Beer--United States--History;
Beer industry--United States--History; Beer--Taxation--United
States--History. American
brewing industry, its leading figures, from colonial beginnings
to present; struggle of German immigrant brewers; determination
of home, micro brewers to reassert craft; cultural meaning
from vantage point of brewers, their goals for market
domination; brewers' fight to create, control changing patterns
of consumption; how industry prevailed in sometimes unreceptive
environment; changes in economic clout of industry.
(Beer), Brian Yaeger (2008).
Red, White, and Brew: An American Beer Odyssey. (New
York, NY: St. Martin's Griffin, 257 p.). Beer industry --United
States; Brewers --United States; Breweries --United States; Beer
--United States. Roots of brewers who brought their craft with
them from their homeland (fourteen
breweries of various sizes); how the tradition is
faring today, where it may head in future.
(Beer),
Michael Pellegrino (2009).
Jersey Brew: The Story of Beer in New Jersey.
(Denville, NJ: Lake Neepaulin Pub., 160 p.). Lawyer.
Beer--history--New Jersey. Turbulent history of beer industry in
Garden State — from earliest breweries to those still brewing
craft beers to today; early settlers imbibed simply because
water wasn't safe to drink, because a lack of TV and Internet
left little else to do besides hang out at local pub; how New
Jersey became one of key players in nation's beer-production
industry (Newark's Gottfried Krueger Brewing Company was first
to sell beer in cans in 1935); illicit methods employed by
crafty mobsters to beat oppressive rules, restrictions of
Prohibition.
(Arthur Bell and Sons Ltd.), Jack House
(1976).
Pride of Perth: The Story of Arthur Bell & Sons Ltd, Scotch
Whisky Distillers. (London, UK: Hutchinson Benham, 135
p.). Bell (Arthur) and Sons, ltd.--History.
(Bollinger), Cyril Ray, Serena Sutcliffwe
(1994).
Bollinger, Tradition of a Champagne Family - Bollinger Today.
(London, UK: Heinemann, 220 [3rd ed.]). Bollinger (Firm);
Champagne (Wine).
(Booth's Distilleries Ltd.), Baron Patrick
Balfour Kinross (1959). The Kindred Spirit; A History of Gin
and of the House of Booth. (London, UK: Newman Neame, 93
p.). Booth's Distilleries ltd.; Gin.
(Borden), Clarence R. Wharton (1941). Gail
Borden, Pioneer. (San Antonio, TX: The Naylor Company, 229
p.). Borden, Gail, 1801-1874.
 Gail
Borden
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0b/Gail_Borden.jpg/220px-Gail_Borden.jpg)
Gail
Borden
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0b/Gail_Borden.jpg/220px-Gail_Borden.jpg)
(Borden), Nina Brown Baker (1955).
Texas Yankee; The Story of Gail Borden. (New York, NY:
Harcourt Brace, 129 p.). Borden, Gail, 1801-1874.
(M.J. Brandenstein), Ruth Bransten McDougall
(1964).
Under Mannie's Hat. (San Francisco, CA: Hesperian Press,
172 p.). Bransten, Manfred; Bransten family; M.J. Brandenstein
and Company; Coffee industry -- California -- San Francisco --
History.
--- (1978).
Coffee, Martinis, and San Francisco. (San Rafael, CA:
Presidio Press, 198 p.). Bransten, Manfred; M.J. Brandenstein
and Company -- History; Businessmen -- United States --
Biography; San Francisco (Calif.) -- History.
(BRL Hardy), Robert Mundle (1993).
Sir James Hardy: An Adventurous Life. (Double Bay, NSW:
M. Gee, 286 p.). Hardy, James, Sir, 1932- ; Adventure and
adventurers--Australia--Biography; Yacht
racing--Australia--History; Vintners--Australia--Biography;
Businesspeople--Australia--Biography; Civic
leaders--Australia--Biography.
(Brooklyn Brewery), Steve Hindy and Tom Potter
(2005).
Beer School: Bottling Success at the Brooklyn Brewery.
(Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 304 p.). President and cofounder of the
Brooklyn Brewery. Brooklyn Brewery--History; Brewing
industry--New York (State)--New York--History; Beer
industry--New York (State)--New York--History; Brooklyn (New
York, N.Y.)--History.
Entrepreneurial basics and success, new ideas and insight on
marketing, hiring, partnering, managing.
(Brown-Forman Corporation), Peter Krass
(2004).
Blood and Whiskey: The Life and Times of Jack Daniel .
(Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 275 p.). Daniel, Jack, 1846-1911; Whiskey
Tennessee Lynchburg History; Distillers Tennessee Lynchburg
Biography.

Jasper Newton "Jack" Daniel -
Brown Forman
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/92/Jackdaniel.jpg/200px-Jackdaniel.jpg)
(Buena Vista), Brian McGinty (1998).
Strong Wine: The Life and Legend of Agoston Haraszthy.
(Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, Great-Great-Grandson).
579 p. Haraszthy, Agoston, 1812-1869;
Vintners--California--Biography;
Viticulturists--California--Biography. Built first stone wineries in
California, introduced more than 300 varieties of European
grapes, planted more than thousand acres of wine vineyards;
first Hungarian to settle permanently in United States, author
of second Hungarian-language book about United States, founder
of one of earliest towns in Wisconsin; assessment of
contributions to American immigration, agricultural history.
(Calera Wine Company), Marq de Villiers
(1994).
The Heartbreak Grape: A California Winemaker’s Search for the
Perfect Pinot Noir. (San Francisco, CA:
HarperCollinsWest, 197 p.). Veteran Canadian Journalist. Calera
Wine Company; Pinot noir (Wine)--California; Wine and wine
making--California).
(Carlsberg), Kristof Glamann; translated by
Geoffrey French (1991).
Jacobsen of Carlsberg: Brewer and Philanthropist.
(Copenhagen, Denmark: Gyldenda, 283 p.). Jacobsen, J. C. (Jacob
Christian), 1811-1887; Carlsberg bryggerierne--History;
Brewers--Denmark--Biography; Businesspeople--Denmark--Biography;
Beer--Denmark--History.
 Jacob Christian Jacobsen
- Carlsberg (http://www.carlsbergpolska.pl/SiteCollectionImages/Grupa%20Carlsberg/grupa_historia1.jpg)
Jacob Christian Jacobsen
- Carlsberg (http://www.carlsbergpolska.pl/SiteCollectionImages/Grupa%20Carlsberg/grupa_historia1.jpg)
(Carlsberg), Kristof Glamann; translated by
Geoffrey French (1996).
Beer and Marble: Carl Jacobsen of New Carlsberg.
(Copenhagen, Denmark: Gyldendal, 352 p.). Jacobsen, Carl
Christian Hilmann, 1842-1914 --Art patronage; Ny Carlsberg
glypotek--History; Art--Collectors and
collecting--Denmark--Biography.
(Carnation Company), James Marshall (1970).
Elbridge A. Stuart, Founder of Carnation Company. (Los
Angeles, CA: Carnation Co., 257 p.). Stuart, Elbridge Amos,
1856-1944; Carnation Company.
 Elbridge Amos
Stuart - Carnation
(http://www.historylink.org/ db_images/wlt150.JPG)
Elbridge Amos
Stuart - Carnation
(http://www.historylink.org/ db_images/wlt150.JPG)
(Cascade Brewery Co.), Mike Bingham (1992).
Cascade: A Taste of History. (Hobart, Tasmania, AU: Cascade
Brewery Co., 216 p.). Cascade Brewery Co.;
Breweries--Australia--Hobart (Tas.).
(CFS Continental), Jim Bowman (1986).
More Than a Coffee Company: The Story of CFS Continental.
(Chicago, IL: Chicago Review Press, 207 p.). Coffee Industry,
CFS Continental.
(Champagne Taittinger), Claude Taittinger
(1996).
Champagne par Taittinger. (Paris, FR: Stock, 156 p.).
Champagne Taittinger (Firm); Champagne (Wine).
(Chateau Margaux), Nicholas Faith (2005).
Chateau Margaux. (Paris, FR: Flammarion, 158 p.).
Chateau Margaux (Firm); Wine and wine making--France--Margaux.
(Coca-Cola), Charles H. Candler (1950). Asa
Griggs Candler. (Atlanta, GA: Emory University, 502 p.).
Candler, Asa Griggs, 1851-1929; Coca-Cola Company, Wilmington,
Del.; Emory University.
 Dr. John Stith "Doc" Pemberton
- creator of Coca-Cola
(http://memory.loc.gov/ammem/ccmphtml/ccimages/pember1.jpg)
Dr. John Stith "Doc" Pemberton
- creator of Coca-Cola
(http://memory.loc.gov/ammem/ccmphtml/ccimages/pember1.jpg)
 Asa Griggs Candler
(worked for Pemberton, owned the business by
1891)
(http://www.georgiaencyclopedia.org/media_content/m-804.jpg)
Asa Griggs Candler
(worked for Pemberton, owned the business by
1891)
(http://www.georgiaencyclopedia.org/media_content/m-804.jpg)

Robert W. Woodruff
- took over management of Coca-Cola in 1923
(until 1981)
(http://www.georgiaencyclopedia.org/media_content/m-7135_thumb.jpg)
(Coca-Cola), E.J. Kahn (1960).
The Big Drink; the Story of Coca-Cola (New York, NY:
Random House, 174 p.). Coca-Cola Company.
(Coca-Cola), Pat Watters (1978).
Coca-Cola: An Illustrated History. (Garden City, NY:
Doubleday, 288 p.). Coca-Cola Company--History; Atlanta
(Ga.)--History.
(Coca-Cola), J.C. Louis and Harvey Z. Yazijian (1980).
The Cola Wars. (New York, NY: Everest House, 386 p.).
Coca-Cola Company; PepsiCo, inc.
(Coca-Cola), Charles Elliott (1982).
"Mr. Anonymous," Robert W. Woodruff of Coca-Cola
(Atlanta, GA: Cherokee Pub. Co., 310 p.). Woodruff, Robert
Winship; Coca-Cola Company -- History; Soft drink industry --
United States -- History; Businessmen -- United States --
Biography.
(Coca-Cola), Anne H. Hoy (1986). Coca-Cola:
The First Hundred Years. (Atlanta, GA: Coca-Cola Co., 159
p.). Coca-Cola Company--History; Coca-Cola Company--Pictorial
works; Soft drink industry--United States--History; Advertising
photography.
(Coca-Cola), Thomas Oliver (1986).
The Real Coke, The Real Story. (New York, NY: Random
House, 195 p.). Coca-Cola Company; Coca-Cola Company--History;
Soft drink industry--United States; Soft drink industry--United
States--History.
(Coca-Cola), Sanders Rowland with Bob Terrell
(1986).
Papa Coke: Sixty-Five Years Selling Coca-Cola.
(Asheville, NC: Bright Mountain Books, 224 p.). Rowland,
Sanders, 1906- ; Coca-Cola Company; Sales personnel--United
States--Biography.
(Coca-Cola), Flora Steinbach Palazzini (1989).
Coca-Cola Superstar. (New York, NY: Barron's, 142 p.).
Coca-Cola Company--History; Soft drink industry--History.
(Coca-Cola), Elizabeth Candler Graham and
Ralph Roberts (1992).
The Real Ones: Four Generations of the First Family of Coca-Cola.
(Fort Lee, NJ: Barricade Books, 344 p.). Candler, Asa Griggs,
1851-1929 --Family; Coca-Cola Company--History; Candler family.
(Coca-Cola), Mark Pendergrast (1993).
For God, Country and Coca-Cola: The Unauthorized History of the
Great American Soft Drink and the Company That Makes It
(New York, NY: Scribner's, 556 p.). Coca-Cola Company--History;
Soft drink industry--United States--History.
(Coca-Cola), Frederick Allen (1994).
Secret Formula: How Brilliant Marketing and Relentless
Salesmanship Made Coca-Cola the Best-Known Product in the World.
(New York, NY: HarperBusiness, 500 p.). Coca-Cola
Company--History; Soft drinks--Marketing.
(Coca-Cola), David Greising (1998).
I'd Like the World to Buy a Coke: The Life and Leadership of
Roberto Goizueta. (New York, NY: Wiley, 334 p.).
Goizueta, Roberto, 1931-1997; Coca-Cola Company; Chief executive
officers--United States--Biography; Soft drink industry--United
States.
(Coca-Cola), Mike Cheatham (1999).
"Your Friendly Neighbor": The Story of Georgia's Coca-Cola
Bottling Families. (Macon, GA: Mercer University Press,
187 p.). Coca-Cola Company--History; Soft drink
industry--Georgia--History; Soft drink industry--United
States--History.
(Coca-Cola), Kathryn W. Kemp (2002).
God's Capitalist: Asa Candler of Coca-Cola. (Macon, GA:
Mercer, 312 p.). Candler, Asa Griggs, 1851-1929; Capitalists and
financiers--Georgia--Atlanta--Biography; Capitalism--Religious
aspects.
(Coca-Cola), Constance L. Hays (2004).
The Real Thing: Truth and Power at the Coca-Cola Company.
(New York, NY: Random House, 398 p.). Former Food and Beverage
Industry Reporter (New York Times). Coca-Cola Company--History;
Soft drink industry--United States--History.
(Coca-Cola), Donald R. Keough (2008).
The Ten Commandments for Business Failure. (New
York, NY: Portfolio, 208 p.). Former President, COO at
Coca-Cola; chairman of Allen & Company. Business
failures. Responsible for New Coke fiasco; commandments: Quit
Taking Risks; Be Inflexible; Assume Infallibility; Put
All Your Faith in Experts; Send Mixed Messages; Be
Afraid of the Future.
(Coca-Cola), Mark Thomas (2008).
Belching Out the Devil: Global Adventures with Coca-Cola.
(London, UK: Ebury Press, 384 p.). Comedian (activist,
campaigning brand of comedy). Coca-Cola Company -- History.
Stories, people Coca-Cola's iconic
advertising campaigns don't mention.
(Coca-Cola), Michael Blanding (2010).
The Coke Machine: The Dirty Truth Behind the World's Favorite
Soft Drink. (New York, NY: Avery, 384 p.).
Contributing Editor, Boston magazine. Coca-Cola Company
--History; Soft drink industry; Bottled water industry;
International business enterprises. How Coke became number one
brand in world, how far it will go to stay there; secret formula
for greed: 1) history of winning at any cost ; 2) bottlers
accused of conspiring with paramilitaries to threaten, kidnap,
murder union leaders in bottling plants in Colombia; 3) how Coke
has harmed children's health, contributed to obesity epidemic
through exclusive soda contracts in schools; 3) horrific
environmental impact of Coke bottling plants in India and Mexico);
costs of growth andf expansion: ethics, health, public
resources, sometimes even human life.
(Coca-Cola), Norman L. Dean
(2010).
The Man Behind The Bottle: The Origin and History of the
Classic Contour Coca-Cola Bottle As Told By The Son Of
Its Creator. (Bloomington, IN: Xlibris
Corporation, 162 p.). Second and Only Surviving son of
Earl R. Dean. Coca-Cola Company; product design --
history; packaging design -- history.
Earl R. Dean, mold
shop supervisor of Root Glass Company of Terre Haute, IN, designed classic contour Coca-Cola
bottle prototype (bottle design with bulging middle,
parallel vertical grooves, tapered ends); bottling
equipment would not operate with bottle’s large center
bulge (unstable on conveyor belts); re-designed bottle,
equalized middle, bottom diameters; 1916 - won
design competition, among 11 entries, at Coca-Cola bottlers convention
in Atlanta, GA.
(Coca-Cola), Foreword by Muhtar Kent
(2011).
Coca-Cola. (New York, NY: Assouline 208 p.).
Coca-Cola Company --History. For 125 years, Coca-Cola
has connected with more people in more places than any
other product world has ever known; illustrated history
world's most iconic beverage (brand's photographs,
advertisements, designs, memories from film, social
history, pop culture - decade by decade).
(Coca-Cola Bottling), Spright Dowell (1983).
Columbus Roberts: Christian Steward Extraordinary.
(Macon, GA: Mercer University Press, 171 p. [orig. pub. 1951]).
Roberts, Columbus, 1870-1950;
Businesspeople--Georgia--Biography;
Philanthropists--Georgia--Biography;
Baptists--Georgia--Biography; Georgia--Biography.
(Coffee), William H. Ukers (1935).
All About Coffee. (New York, NY: The Tea and Coffee
Trade Journal Company, 818 p. [2nd ed.]). Editor, The Tea and
Coffee Trade Journal. Coffee; Coffee industry; Drinking customs.
(Coffee), Andres Uribe Compuzano (1954).
Brown Gold: The Amazing Story of Coffee. (New York, NY:
Random House, 237 p.). Coffee.
(Coffee), Ralph S. Hattox (1985).
Coffee and Coffeehouses: The Origins of a Social Beverage in the
Medieval Near East. (Seattle, WA: University of
Washington Press, 178 p.). Elliott Professor of History
(Hampden-Sydney College). Coffee --Middle East --History;
Coffeehouses --Middle East --History; Social history --Medieval,
500-1500; Coffee --History; Coffee-houses --History.
Social
history of coffee house in Muslim society.
(Coffee), Claude Saks (1996).
Strong Brew: One Man's Prelude to Change.
(Charlottesville, VA: Heartsfire Books, 276 p.). Saks, Claude,
1937- ; Businessmen--United States--Biography; Coffee
industry--United States.
(Coffee), Jeffrey M. Paige (1997).
Coffee and Power: Revolution and the Rise of Democracy in
Central America. (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University
Press, 432 p.). Coffee industry--Costa Rica--History--20th
century; Coffee industry--El Salvador--History--20th century;
Coffee industry--Nicaragua--History--20th century; Elite (Social
sciences)--Costa Rica--History--20th century; Elite (Social
sciences)--El Salvador--History--20th century; Elite (Social
sciences)--Nicaragua--History--20th century; Costa
Rica--Politics and government--20th century; El
Salvador--Politics and government--20th century;
Nicaragua--Politics and government--To 1960; Nicaragua--Politics
and government--1960-.
(Coffee), Heinrich Eduard Jacob; translated by
Eden and Cedar Paul (1998).
Coffee: The Epic of a Commodity. (Short Hills, NJ:
Burford Books, 296 p. [orig. pub. 1935]). Coffee; Drinking
customs.
(Coffee), Gregory Dicum snd Nina Luttinger
(1999).
The Coffee Book: Anatomy of an Industry from Crop to the Last
Drop. (New York, NY: The New Press, 196 p.). Coffee
industry; Coffee.
(Coffee), Mark Pendergrast (1999).
Uncommon Grounds: The History of Coffee and How It Transformed
the World.
(New York, NY: Basic Books, 520 p.). Investigative Journalist.
Coffee--History; Coffee industry--History.
(Coffee), Bennett Alan Weinberg, Bonnie K.
Bealer (2001).
The World of Caffeine: The Science and Culture of the World’s
Most Popular Drug. (New York, NY: Routledge, 394 p.).
Caffeine. History, social
effects of principal beverages that contain caffeine (coffee,
tea); explore coffee's Arabian origins, tea's roots in Asia,
chocolate's background in Americas; discuss Japan,
England, U.S., where caffeinated beverages are popular; address
chemistry, biology of caffeine and effects, positive and
negative, on organs, on mental function.
(Coffee), edited by William Gervase
Clarence-Smith, Steven Topik (2003).
The Global Coffee Economy in Africa, Asia and Latin America,
1500-1989.
(New York, NY: Cambridge University Press, p.). Coffee
industry--Africa--History; Coffee industry--Asia--History;
Coffee industry--Latin America--History.
(Coffee), Gerald Kinro (2003).
A Cup of Aloha: The Kona Coffee Epic. (Honolulu, HI:
University of Hawai'i Press, 149 p.). Pesticide Specialist with
the Hawai'i State Department of Agriculture. Coffee industry
Hawaii Kona (Hawaii Island) History.
(Coffee), Markman Ellis (2004).
The Coffee-House: A Cultural History. (London, UK:
Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 304 p.). Teaches 18th-Century Literature
and Culture (Queen Mary, University of London).
Coffeehouses--History; Coffeehouses--Social aspects;
Coffeehouses--England--London--History; London (England)--Social
life and customs--17th century; London (England)--Social life
and customs--18th century; London (England)--History--17th
century; London (England)--History--18th century.
1652 - first coffee-house opened
in London; centre of urban life for 100 years, distinctive
social culture (treated all customers as equals); 18th
century - key role in explosion of political, financial,
scientific, literary change; 19th century - declined (tea);
1950s - dramatic revival (espresso machines, coffee bar');
1990s - chains.
(Coffee), Antony Wild (2005).
Coffee: A Dark History. (New York, NY: Norton, 323 p.).
Credited with Having Introduced Specialty Coffees into the UK.
Coffee; Coffee--History.
(Coffee), Dean Cycon (2007).
Javatrekker: Dispatches from the World of Fair Trade Coffee.
(White River Junction, VT: Chelsea Green Pub., 300 p.). Owner,
Dean's Beans, all-organic, all-fair-trade, all-kosher coffee
roaster in Orange, MA. Cycon, Dean, 1953- --Travel; Coffee
industry; Coffee growers; Coffee; International trade.
Tour of ten countries,
face-to-face with 1) real people who make our morning coffee
ritual possible and 2) major issues of 21st century:
globalization, immigration, women's rights, pollution,
indigenous rights, self-determination; promise, hope of
sustainable business principles, products derived from
cooperation, fair pricing, profit sharing.
(Coffee), Ed. Markman Ellis (2007).
Eighteenth-Century Coffee-House Culture. (London, UK:
Pickering and Chatto, 1,840 p.). Teaches 18th-Century Literature
and Culture (Queen Mary, University of London).
Coffeehouses--History; Coffeehouses--Social aspects;
Coffeehouses--England--London--History; London (England)--Social
life and customs--17th century; London (England)--Social life
and customs--18th century; London (England)--History--17th
century; London (England)--History--18th century.
Where men went to read
newspapers, smoke tobacco, conduct business, see friends, drink
murky brown liquid (coffee); 19th century - end of "the great
age of the British coffee-house", tea-drinking grew; sociability
and economics.
(Coffee), Deborah Sick (2007).
Farmers of the Golden Bean: Costa Rican Households and the
Global Coffee Economy. (DeKalb, IL: Northern Illinois
University Press, 196 p.). Coffee growers --Costa Rica; Coffee
industry --Costa Rica; Family farms --Costa Rica; Competition,
Unfair --Costa Rica.
(Coffee), Meike Wollni (2007).
Coping with the Coffee Crisis: An Analysis of the Production and
Marketing Performance of Coffee Farmers in Costa Rica.
(New York: Peter Lang: New York, 173 p.). Coffee industry--Costa
Rica; Coffee--Production control--Costa Rica.
(Coffee), Mauricio A. Font. (2010).
Coffee and Transformation in São Paulo, Brazil.
(Lanham, MD: Lexington Books, 377 p.). Professor of Sociology at
The Graduate Center and Queens College (City University of New
York). Coffee industry -- Brazil -- São Paulo (State) --
History; Coffee growers -- Brazil -- São Paulo (State) --
History; Industrialization -- Brazil -- São Paulo (State) --
History; São Paulo (Brazil : State) -- Politics and government;
Elite (Social sciences) -- Brazil -- São Paulo (State) --
History; Immigrants -- Brazil -- São Paulo (State) -- History.
Political, economic implications of São Paulo’s great
transformation, segmentation as leader of Brazilian
modernization, development, industrialization since latter part
of 19th century(links to internal conflict, Brazilian Revolution
of 1930, regionalism).
(Cognac), Kyle Jarrard (2005).
Cognac: The Seductive Saga of the World's Most Coveted Spirit.
(Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 244 p.). Brandy.
(Coors), Robert J. Burges (1993).
Silver Bullets: A Soldier's Story of How Coors Bombed in the
Beer Wars. (New York, NY: St. Martin's Press, 256 p.).
Adolph Coors Company; Brewing industry--United States.
 Adolph Coors (http://s3.amazonaws.com/findagrave/photos/2001/222/coorsadolphbio.jpg)
Adolph Coors (http://s3.amazonaws.com/findagrave/photos/2001/222/coorsadolphbio.jpg)
(Coors), Russ Banham. (1998).
Coors: A Rocky Mountain Legend. (Lyme, CT: Greenwich
Pub. Group, 127 p.). Coors Brewing Company--History; Beer
industry--United States--History; Brewing industry--United
States--History.
(Coors), Dan Baum (2000).
Citizen Coors: An American Dynasty. (New York, NY:
Morrow, 367 p.). Coors family; Coors Brewing Company--History;
Beer industry--United States--History; Brewing industry--United
States--History.
(Cott Corporation), Gerry Pencer (1999).
The Ride of My Life: A Memoir. (Toronto, ON: Key Porter
Books, 247 p.). CEO of the World’s Largest Private Label Soft
Drink Maker. Pencer, Gerry, 1945-1998; Cott
Corporation--History; Businessmen--Canada--Biography; Soft drink
industry--Canada--History.
(Crown Distilleries), Frederic Gordon O'Neill
(1949).
Ernest Reuben Lilienthal and His Family. (Stanford, CA:
Stanford University Press, 176 p.). Lilienthal, Ernest Rubin;
Haas Brothers. Wholesale
liquor business entrepreneur.
(Culligan International), Don Hintz (1986).
The People of Culligan: 50 Years of Water Conditioning
Leadership, 1936-1986. (Northbrook, IL: Culligan
International Co., 687 p.). Culligan International
Company--History; Water purification equipment industry--United
States--History. Founded
1936; 2004 - acquired by buyout firm Clayton, Dubilier & Rice
for $610 million.
(Danisco), Jan Cortzen; translated by Jane
Stewart (1997).
Merchants and Mergers The Story of Danisco. (Copenhagen,
København: Børsen, 372 p.). Danisco--History; Liquor
industry--Denmark--History.
(De Kuyper), K. E. Sluyterman and H. H.
Vleesenbeek (1995). Three Centuries of De Kuyper: A History
of Geneva and Liqueurs, 1695-1995. (Schiedam, Netherlands:
De Kuyper. De Kuyper Royal Distillers; distilling
industries--Netherlands. Story of a deeply conservative,
family-owned firm.
(Distillers Co.), Ronald B. Weir (1995).
The History of the Distillers Company, 1877-1939:
Diversification and Growth in Whisky and Chemicals. (New
York, NY: Oxford University Press, 417 p.). Distillers Company
Limited--History; Whiskey industry--Scotland--History;
Distilling industries--Scotland--History; Chemical
industry--Scotland--History.
(Dogfish Head Craft Brewery), Sam Calagione
(2005).
Brewing Up a Business: Adventures in Entrepreneurship from the
Founder of Dogfish Head Craft Brewery. (Hoboken, NJ:
Wiley, 256 p.). Founder. Dogfish Head Craft Brewery;
Microbreweries--Delaware; Entrepreneurship--Delaware; Small
business--Delaware.
(Domaine Chandon), Jamie Laughridge (1983).
Rising Star : Domaine Chandon, A Decade of Sparkle. (New
York, NY: Hopkinson & Blake, 95 p.). Domaine Chandon (Firm);
Sparkling wines--California.
(Dr Pepper/Seven-Up Companies), Jeffrey L.
Rodengen (1995).
The Legend of Dr Pepper/Seven-Up. (Ft. Lauderdale, FL:
Write Stuff Syndicate, 144 p.). --History; Soft drink
industry--United States--History; Beverage industry--United
States--History.
(Dr Pepper/Seven-Up Companies), Karen Wright
(2006).
The Road to Dr Pepper, Texas: The Story of Dublin Dr Pepper.
(Abilene, TX: State House Press/McMurry University, 172 p.).
Founder, Former Publisher of The Dublin Citizen, and Former
Director of Old Doc's Soda Shop and Dr Pepper Museum in Dublin.
Dr. Pepper Co.--History; Soft drink
industry--Texas--Dublin--History. Success of Dublin Bottling Works.
(Les Vins Georges DuBoeuf) , Rudolph
Chelminski (2007).
I’ll Drink to That: Beaujolais and the French Peasant Who Made
It the World’s Most Popular Wine. (New York, NY: Gotham
Books, 320 p.). Dubœuf, Georges; Beaujolais
(Wine)--France--History; Vintners--France--Beaujolais; Wine and
wine making--France--Beaujolais--History; Beaujolais
(France)--History. Cinderella tale behind success of Beaujolais Nouveau: story of
wine, history of region, tale of peasant wine grower who became
richest, most famous individual wine dealer in France.
 Georges DuBoeuf - Beaujolais
(http://www.winespectator.com/contentimage/wso/Feature/Dubeouf-200w.jpg)
Georges DuBoeuf - Beaujolais
(http://www.winespectator.com/contentimage/wso/Feature/Dubeouf-200w.jpg)
(Duncan Brothers & Co.), The Company (1959).
The Duncan Group: Being a Short History of Duncan Brothers &
Co. Ltd., Calcutta, and Walter Duncan & Goodricke Ltd., London,
1859-1959. (London, UK: Walter Duncan and Goodricke, 184
p.). Duncan Brothers & Co.--History; Walter Duncan & Goodricke
Ltd.--History; Tea trade--India--History; Tea trade--Great
Britain--History.
(Farmville Lithia Water Co.), Robert G.
Flippen (1994). "Drink and Be Healed": A History of Farmville
Lithia Water. (Farmville, VA: R.G. Flippen, 135 p.).
Farmville Lithia Water Co.--History; Mineral water
industry--Virginia--Farmville--History; Mineral
waters--Virginia--Farmville--History; Farmville (Va.)--History.
(Ferrarelle), Daniela Brignone (2001).
Ferrarelle: A Sparkling Italian Story. (Milano, IT: Silvana,
69 p.). Ferrarelle (Firm)--History; Mineral water
industry--Italy--History; Bottled water
industry--Italy--History.
(Ferrari-Carano Winery ), Mike Weiss (2005).
A Very Good Year: The Journey of a California Wine from Vine to
Table. (New York, NY: Gotham Books, 288 p.). Reporter
(San Francisco Chronicle). Wine and wine making--California;
Viticulture--California.
(Fetzer Vineyards), Paul Dolan (2003).
True to Our Roots: Fermenting a Business Revolution.
(Princeton, NJ: Bloomberg Press, 240 p.). President and CEO
(Fetzer Vineyards). Fetzer Vineyards--Management; Wine
industry--United States--Management;
Vineyards--California--Mendocino County--Management; Organic
farming--California--Mendocino County.
(Fetzer Vineyards), Kathleen Fetzer with Sarah
Suggs (2005).
Kathleen's Vineyard: The Fetzer Family Matriarch Shares Her
Story. (Fort Bragg, CA: Cypress House, 240 p.). Fetzer,
Kathleen, 1921- ; Fetzer family;
Vintners--California--Biography; Wine and wine
making--California--History.
(Finsbury Distillery), David Wainwright
(1990).
Stone's Ginger Wine: Fortunes of a Family Firm 1740-1990.
(London, UK: Quiller, 124 p.). Finsbury Distillery; Alcoholic
drinks Production History London (England).
(J. A. Folger & Co.), Ruth Waldo Newhall
(1961).
The Folger Way: Coffee Pioneering Since 1850. (San
Francisco, CA: J.A. Folger & Co, 72 p.). J.A. Folger & Co.;
Coffee--History; Coffee--industry.

James A. Folger - Folger's Coffee
(http://www.nha.org/images/hn/hn-mooney-coffee.jpg)
(Fuller Smith and Turner), Andrew Langley
(1996).
London Pride: 150 Years of Fuller, Smith and Turner.
(Good Books, Melksham, 64 p.). Fuller, Smith and Turner Plc;
Breweries --Great Britain--history; Beer --Great Britain.
(Gales Brewery), Barry Stapleton and James H.
Thomas (2000).
Gales: A Study in Brewing, Business, and Family History.
(Burlington, VT: Ashgate, 192 p.). Gales family; Boyer family;
Gales Brewery--History; Brewing industry--Great
Britain--History; Industrialists--Great Britain--Biography.
(Gallo Wine), Ellen Hawkes (1993).
Blood and Wine: The Unauthorized Story of the Gallo Wine Empire.
(New York, NY: Simon & Schuster, 464 p.). Gallo family; Vintners
-- California -- Biography; Wine and wine making -- California
-- History.
(Gallo Wine), Ernest and Julio Gallo; with
Bruce B. Henderson (1994).
Ernest and Julio: Our Story. (New York, NY: Times Books,
358 p.). Gallo, Ernest; Gallo, Julio;
Vintners--California--Biography; Wine and wine
making--California--History.
(Gatorade), Darren Rovell (2005).
The First in Thirst: How Gatorade Turned the Science of Sweat
into a Cultural Phenomenon. (New York, NY: American
Management Association, 256 p.). ESPN.com Reporter. Gatorade
(Firm); Beverage industry--United States.
(A. Gettelman Brewing Company), Nancy Moore
Gettelman (1995).
The A. Gettelman Brewing Company: One-Hundred and Seven Years of
a Family Brewery in Milwaukee. (Milwaukee, WI:
Procrustes Press, 171 p.). Gettelman, Adam, 1847-1925; A.
Gettelman Brewing Company--History; Brewing
industry--Wisconsin--Milwaukee--History; Businesspeople--United
States--Biography.
(W & A Gilbey), Nicholas Faith (1983).
Victorian Vineyard: Chateau Loudenne and the Gilbeys.
(London, UK: Constable in association with Christie's Wine
Publications, 160 p.). Former Editor of the Sunday Times of
London. Wine Industry, Liquor Industry, W & A Gilbey. History of
W & A Gilbey.
(W. & A. Gilbey), Jane Kidd (1997).
Gilbeys, Wine and Horses. (Cambrudge, UK: Lutterworth,
206 p.). Gilbey (Family); W & A Gilbey (Firm)--History;
Businessmen--Great Britain--Biography; Alcoholic beverage
industry--Great Britain--Biography; Wine industry--Great
Britain--History; Horse racing--Great Britain--History.
(Glenlivet), F. Paul Pacult (2005).
A Double Scotch: How Chivas Regal and The Glenlivet Became
Global Icons. (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 290 p.). Founding
Editor and Publisher of F. Paul Pacult's Spirit Journal – The
Quarterly Independent Guide to Distilled Spirits, Beers, and
Wines (now in its 15th year of publication). Glenlivet
Distillery--History; Chivas Brothers Limited--History; Seagram
Company; Whiskey industry--Scotland--History.
(William Grant & Sons), Francis
Collinson (1979).
The Life & Times of William Grant. (Dufftown,
Banffshire: W. Grant & Sons, 102 p.). Grant, William, 1839-1923;
William Grant & Sons Ltd.; Whiskey--Scotland.
(William Grant & Sons), Grant Gordon and Nigel
Nicholson (2008).
Family Wars: Classic Conflicts in the Family and How To Deal
with Them. (Philadelphia, PA: Kogan Page, 288 p.).
William Grant & Sons (fifth generation); London Business School.
Family-owned business enterprises--Management; Family-owned
business enterprises--Succession; Family-owned business
enterprises. Independent family distiller for 5 generations.
Ups, downs of some of
biggest family-run companies in world (Ford, Gucci, McCain,
Guinness, Gallo, Redstone); origins, extent, resolution of some
of most famous family feuds in recent history; how family
in-fighting has threatened their downfall; way families do
business, how family in-fighting can threaten to blow business
apart.
(Greene King Plc), R.G. Wilson (1983).
Greene King: A Business and Family History. (London, UK:
Bodley Head, 337 p.). Greene King (Firm) -- History; Suffolk
Bury St Edmunds Brewing industries.
(Greenwood Ridge Winery), Richard Paul Hinkle
(2000).
Alligator Dreams: The Story of Greenwood Ridge Vineyards.
(Santa Rosa, CA: Silverback Books, 119 p.). Green, Allan Wright,
1949- ; Greenwood Ridge Winery--History; Wine and wine
making--California--Mendocino County--History--20th century.
(Guinness), Frederic Mullally (1981).
The Silver Salver: The Story of the Guinness Family.
(New York, NY: Granada, 255 p.). Guinness family.
 Arthur Guinness
(http://www.guinness.com/en-row/agf/img/agportrait.jpg)
Arthur Guinness
(http://www.guinness.com/en-row/agf/img/agportrait.jpg)
 Edward Cecil Guinness, First Earl of Iveagh
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/bb/1stEarlOfIveagh.jpg/200px-1stEarlOfIveagh.jpg)
Edward Cecil Guinness, First Earl of Iveagh
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/bb/1stEarlOfIveagh.jpg/200px-1stEarlOfIveagh.jpg)
(Guinness), Brian Sibley (1985).
The Book of Guinness Advertising. (Enfield, Middlesex
(UK): Guinness Books, 221 p.). Guinness (Firm)--History;
Advertising--Brewing industry--Ireland--History;
Advertising--Ireland--History; Commercial art--Ireland--History.
(Guinness), Jonathan Guinness (1997).
Requiem for a Family Business (London, UK: Macmillan,
390 p.). Guinness family; Guinness (Firm)--History; Brewing
industry--Great Britain--History.
(Guinness), Derek Wilson (1998).
Dark and Light: The Story of the Guinness Family
(London, UK: Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 319 p.). Guinness family;
Brewers--Ireland--Biography; Brewing--Ireland--History.
(Guinness), S.R. Dennison and Oliver MacDonagh
(1998).
Guinness 1886-1939: From Incorporation to the Second World War
(Cork, IR: Cork University Press, 282 p.). Guinness
(Firm)--History; Brewing industry--Great Britain--History.
(Guinness), Al Byrne (1999).
Guinness Times: My Days in the World's Most Famous Brewery
(Dublin, IR: Town House, 236 p.). Byrne, Al; Guinness
(Firm)--History; Brewing industry--Ireland--History.
(Guinness), Mark Griffiths (2004).
Guinness is Guinness: The Colorful Story of a Black and White
Brand. (London, UK: Cyan Books, 192 p.). Guinness
family; Guinness (Firm)--History; Brewing industry--Great
Britain--History. Author wanders through the drink’s storied
history, focuses heavily on communications and advertising
campaigns over the past century; long-term view demonstrates
Guinness’ survival through 250 years of brewing. This book
celebrates the brand’s remarkable success.
(Guinness), Bill Yenne (2007).
Guinness: The 250-Year Quest for the Perfect Pint.
(Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 250 p.). Guinness family; Guinness
(Firm)--History; Brewing industry--Ireland--History. 250-year
history of family; technology, craftsmanship of brewery:
Arthur Guinness, entrepreneur patriarch;
Arthur (son) developed recipe for black stout; third generation,
Edward Cecil Guinness, First Earl of Iveagh, built family business into
largest brewery in world (became richest man in Ireland).
(Guinness), Patrick Guinness (2008).
Arthur's Round: The Life of Brewing Legend Arthur Guinness.
(London, UK: Peter Owen Ltd., 288 p.). Guinness (Firm)--History;
Guinness, Arthur; Brewing History--Ireland.
Founding father of one of
Ireland's most powerful dynasties: his background, account of
brewing process, descriptions of economic and political
backgrounds in rapidly developing Ireland; family's origins in
Ulster, Gaelic, Protestant-Irish tenant-farmers from humble
backgrounds on both sides.
(Guinness), Stephen Mansfield (2009).
The Search for God and Guinness: A Biography of the Beer That
Changed the World. (Nashville, TN: Thomas Nelson, 273
p.). Beer industry -- Ireland -- History; Brewing industry --
Ireland -- History; Guinness family; Guinness (Firm) -- History.
How
Guinness family and company used wealth to relieve social ills;
created one of world’s great brands;
generational drama, business adventure, industrial and social
reforms, deep-felt faith, beer; brewed beer that
provided healthier alternative to poisonous waters, liquors of times.
(Hamm Brewing Company), John T. Flanagan
(1989).
Theodore Hamm in Minnesota: His Family and Brewery. (St.
Paul, MN: Pogo Press, 127 p.). Hamm, Theodore, 1825-1903; Hamm
family; Theo. Hamm Brewing Company--History; Brewing
industry--Minnesota--Saint Paul--History;
Brewers--Minnesota--Saint Paul--Biography;
Businesspeople--United States--Biography.
 Theodore Hamm - Hamm Brewing
(http://collections.mnhs.org/visualresources/VRDbimages/pf104/pf104627.jpg)
Theodore Hamm - Hamm Brewing
(http://collections.mnhs.org/visualresources/VRDbimages/pf104/pf104627.jpg)
(Hargrave Vineyard), Louisa Thomas Hargrave
(2003).
The Vineyard:The Pleasures and Perils of Creating an American
Family Winery. (New York, NY: Viking, 254 p.). Hargrave,
Louisa Thomas; Viticulturists--New York--Long Island--Biography;
Vintners--New York--Long Island--Biography.
(G. Heileman Brewing), Paul D. Koeller & David
H. DeLano (2004).
Brewed With Style: The Story of the House of Heileman.
(La Crosse, WI: University of Wisconsin-La Crosse Foundation,
266 p.). Son of a Heileman Brewery Worker of more than 40 years;
Employed by Heileman for 23 years as Corporate Credit Manager as
well as Resident Historian. G. Heileman Brewing Company --
History; Breweries--Wisconsin -- History.
(Heineken), Barbara Smit (1996).
Heineken: Een Leven in de Brouwerij. (Nijmegen,
Netherlands: SUN, 320 p.). Heineken, Alfred Henry, 1923- ;
Heineken's Bierbrouwerij Maatschappij; Brewing
industry--Netherlands--History.
 Gerard Adriaan Heineken
(http://historiek.net/images/stories/personen/gerard-adriaan-heineken.jpg)
Gerard Adriaan Heineken
(http://historiek.net/images/stories/personen/gerard-adriaan-heineken.jpg)
(Heineken), M.G.P.A. and W.H.G. Maas
Jacobs (2001).
The Magic of Heineken. (Amsterdam, Netherlands:
Heineken NV, 300 p.). Heineken, Alfred Henry, 1923- ;
Heineken's Bierbrouwerij Maatschappij; Brewing
industry--Netherlands--History. History of company; over
200 illustrations of Heineken advertisements, magazine
ads, advertising logos, slogans.
(High Tor Vineyards), Everett Crosby
(1973).
The Vintage Years; The Story of High Tor Vineyards.
(New York, NY: Harper & Row, 227 p.). Crosby, Everett;
High Tor Vineyards. 1950 - Author
bought High Tor site to prove he could
produce quality grapes, wines just 20 miles north of George Washington Bridge (land of High Tor granted
to Van Orden family by King George III; grapes had been
growing on property since 18th century); marketed as Rockland White, Rockland Red, Rockland Rose; trials, successes in planting dream
vineyard on craggy mountain, winning
connoisseur acceptance of French hybrid wines; acquired
by New York restaurateur; 1981 - acquired by New York
economist Christopher Wells; revived vineyards,
eventually sold it; most famous small winegrowing estate
in eastern America from 1950-1989.
(Hills Bros. Coffee), T. Carroll Wilson
(1967). A Background Story of Hills Bros. Coffee, Inc., as
Presented by T. Carroll Wilson, Philadelphia District Sales
Meeting, September 9, 1966. (San Francisco, CA: James H.
Barry Co., 80 p.). Hills Bros. Coffee, Inc.
(Hull Brewery Company), Written, Researched
and Compiled by Robert Barnard for the Local History Archives
Unit (1990).
Barley, Mash and Yeast: A History of the Hull Brewery Company,
1782-1985. (Beverley, UK: Hutton, 60 p.). Hull Brewery
Company; Brewing History; Humberside (England).
(innocent ltd), Dan Germain and Richard Reed
(2009).
A Book About Innocent: Our Story and Some Things We've Learned.
(London, UK: Michael Joseph, 192 p.). innocent ltd; smoothies;
Beverage industry--Great Britain--History. 1999 - three
Cambridge University friends established London-based beverage
(smoothie) company; sold 24 bottles first day; 2009 - sell more
than 2 million bottles/week; lessons - ideas, making drinks,
running a business, getting started, nature and fruit, company
life, working with friends, stuff we've got right, stuff we got
wrong, doing right thing; started from scratch; listening carefully to
more clever people; March 2009 - sold minority
stake to Coca-Cola for $15 million.
(Italian Swiss Colony), Jack W. Florence
(1999).
Legacy of a Village: The Italian Swiss Colony Winery and the
People of Asti, California. (Chandler, AZ: Raymond Court
Press, 320 p.). Wine and wine making; Italian Swiss Colony;
Asti, California.
(Krug), John Arlott (1976).
Krug, House of Champagne. (London, UK: Davis-Poynter,
224 p.). Krug (Firm)--History; Champagne (Wine)--History.
(Krug), Henri et Remi Krug (1979). L’Art du
Champagne. (Paris, FR: R. Laffont, 233 p.). Krug (Firm);
Champagne (Wine).
(John Labatt Limited), Paul Brent (2004).
Lager Heads: Labatt and Molson Face Off for Canada's Beer Money.
(Toronto, ON: HarperCollins, 243 p.). John Labatt Limited --
History; Molson Companies -- History; Brewing industry -- Canada
-- History.
 John Kinder Labatt
(top right), John
Labatt II (top
left) -
Labatt's Beer
(http://www.lib.uwo.ca/files/business/images/labatt2.jpg)
John Kinder Labatt
(top right), John
Labatt II (top
left) -
Labatt's Beer
(http://www.lib.uwo.ca/files/business/images/labatt2.jpg)
(Jos. Laurer Brewery Co.), George J. Laurer
(2006). The Laurer Brewers and the Jos. Laurer Brewery Co.
1892. (Morrisville, NC: Lulu.com, 64 p.). Jos. Laurer
Brewery Co.; Breweries--New York State. 1892 - established brewery in
Binghamton, NY.
(Lipton Tea), Captain John J. Hickey (1932).
The Life and Times of the Late Sir Thomas J. Lipton from the
Cradle to the Grave, International Sportsman and Dean of the
Yachting World. (New York, NY: The Hickey publishing
company, 259 p.). Lipton, Thomas Johnstone, Sir, bart.,
1850-1931.
 Sir
Thomas J. Lipton - Lipton Tea
(http://ec3.images-amazon.com/images/G/01/ciu/d2/98/cf22b2c008a0b82fbf83a010._AA240_.L.jpg) Sir
Thomas J. Lipton - Lipton Tea
(http://ec3.images-amazon.com/images/G/01/ciu/d2/98/cf22b2c008a0b82fbf83a010._AA240_.L.jpg)
(Lipton Tea), Alec Waugh (1950).
The Lipton Story, A Centennial Biography. (Garden City,
NY: Doubleday, 277 p.). Lipton, Thomas Johnstone, Sir, bart.,
1850-1931.
(Locke's Distillery), Andrew Bielenberg
(1993).
Locke's Distillery: A History. (Dublin, IR: Lilliput
Press, 122 p.). Locke's Distillery--History; Whiskey
industry--Ireland--History.
(Mann Crossman & Paulin Ltd.), Hurford Janes
(1958). Albion Brewery, 1808-1958: The Story of Mann,
Crossman & Paulin Ltd. (London, UK: Harley Pub. Co,, 115
p.). Mann, Crossman & Paulin Ltd.
(Marston's), Khadija Buckland (1999).
A Brewer of Pedigree: A Celebration of Marston's, Its People and
Beers, in Words and Pictures. (London, UK: M.W.F.
Hurdle, 118 p.). Marston's (Firm) -- History.
(Martini), Barnaby Conrad III (1995).
The Martini: An Illustrated History of an American
Classic. (San Francisco, CA, Chronicle Books,
132 p. .). Painter and Author. Martinis --History.
Originally mixed in 19th century, became American
icon in 20th century; how deeply permeated every
aspect of American culture, from literature and film to
politics, high society - chilled, crystal glass; the
purest gin; a touch of dry vermouth--vigorously shaken,
not stirred--and a plump, green olive.
(Paul Masson), Robert Lawrence Balzer (1970).
This Uncommon Heritage; The Paul Masson Story. (Los
Angeles, CA: Ward Ritchie Press, 118 p.). Masson, Paul,
1859-1940; Paul Masson (Firm).
 Paul
Masson
(http://www.chainedor.com/ images/OLDpaulmasson.jpg)
Paul
Masson
(http://www.chainedor.com/ images/OLDpaulmasson.jpg)
(Meerlust), Phillida Brooke Simons;
photography by Alain Proust (2003).
Meerlust: 300 Years of Hospitality. (Vlaeberg, South
Africa: Fernwood Press, 176 p.). Myburgh family; Meerlust (South
Africa) --History. History of the house to
present day.
(Merrydown Wine Plc), Graeme Wright (1988).
Merrydown: Forty Vintage Years. (Heathfield, UK:
Merrydown Wine plc, 127 p.). Merrydown Wine Public Limited
Company history; East Sussex Heathfield Wines industries.
(Miller Brewing Company), Tim John (2005).
The Miller Beer Barons: The Frederick J. Miller Family and Its
Brewery.
(Oregon, WI: Badger Books Inc., 250 p.). Miller, Frederick J.
(Frederick Johnas), 1824-1888; Miller, Frederick J. (Frederick
Johnas), 1824-1888 --Family; Miller Brewing Company--History;
Brewers--Wisconsin--Milwaukee--Biography;
Breweries--Wisconsin--Milwaukee--History; Beer
industry--Wisconsin--Milwaukee--History. Family
that built a beer empire.
 Frederick John Miller
- Miller Beer
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e4/Frederick_miller.jpg/150px-Frederick_miller.jpg)
Frederick John Miller
- Miller Beer
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e4/Frederick_miller.jpg/150px-Frederick_miller.jpg)
(Moët & Chandon), Michel Refait (1998).
Moët & Chandon: De Claude Moët à Bernard Arnault.
(Prez-sur-Marne, FR: Dominique Guéniot, 221 p.). Moët & Chandon
(Firm)--History; Moët-Hennessy--History; Louis Vuitton
Moët-Hennessy (Firm)--History.
 Claude Moet
(http://placorama.free.fr/images/M/moet152.jpg)
Claude Moet
(http://placorama.free.fr/images/M/moet152.jpg)
(Moët & Chandon), Claire Desbois-Thibault
(2003). L'Extraordinaire Aventure du Champagne: Moët &
Chandon, Une Afaire de Famille, 1792-1914. (Paris, FR:
Presses universitaires de France, 390 p.). Moët & Chandon
(Firm)--History; Champaigne--History; Champagne Wine -
Industrial History - Family History - 18th-20th Century.
(Molson), Merrill Denison (1955).
The Barley and the Stream; The Molson Story; A Footnote to
Canadian History. (Toronto, ON: McClelland and Stewart,
398 p.). Molson's Brewery, ltd.

John
Molson
(http://www.mcgill.ca/files/donorreport05-07/john_molson.jpg)
(Molson), Shirley E. Woods (1983).
The Molson Saga, 1763-1983. (Garden City, NY: Doubleday,
370 p.). Molson family; Businesspeople--Canada--Biography.
(Molson), Douglas Hunter (2001).
Molson: The Birth of a Business Empire. (Toronto, ON:
Viking, 486 p.). Molson, John, 1763-1836; Molson, John,
1763-1836; Molson Companies--History; Compagnies
Molson--Histoire; Businesspeople--Canada--Biography; Gens
d'affaires--Canada--Biographies.
(Molson), Karen Molson (2001).
The Molsons: Their Lives & Times, 1780-2000. (Buffalo,
NY: Firefly Books, 416 p.). Molson family; Molson's
Brewery--History; Brewing industry--Canada--History; Beer
industry--Canada--History.
(Mondavi), Cyril Ray (1984).
Robert Mondavi of the Napa Valley. (New York, NY: Warner
Books, 171 p.). Mondavi, Robert, 1913- ;
Vintners--California--Biography; Wine and wine
making--California--Napa Valley--History.
 Robert
Mondavi
(http://www.news.ucdavis.edu/photos_images/news_images/05-2008/robertmondavi.jpg)
Robert
Mondavi
(http://www.news.ucdavis.edu/photos_images/news_images/05-2008/robertmondavi.jpg)
(Mondavi), Robert Mondavi with Paul Chutkow
(1998).
Harvests of Joy: My Passion for Excellence. (New York,
NY: Harcourt Brace, 364 p.). California Vintner. Robert Mondavi,
Wine Industry, Napa Valley.
(Mondavi), Olivier Torres (2006).
The Wine Wars: The Mondavi Affair, Globalisation and "Terroir".
(New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan, 192 p.). Assistant Professor
at the University of Montpellier (ERFI-GREG), Associate
Researcher at EM Lyon, France. Mondavi, Robert, 1913- ; Robert
Mondavi Winery; Wine industry--France--Languedoc-Roussillon;
Globalization--Social aspects--France; Globalization--Political
aspects--France. Anti-globalization rebellion (ecologists, communists,
neo-rurals, wild boar hunters) halted Mondavi venture in small,
world-renowned wine-producing village in south of France.
(Mondavi), Julia Flynn Siler (2007).
The House of Mondavi: The Rise and Fall of an American Wine
Dynasty. (New York, NY: Gotham Books, 464 p.). Reporter
(Wall Street Journal). Mondavi family; Robert Mondavi
Winery--History; Vintners--United States--Biography;
Family-owned business enterprises--United States--Case studies;
Wine industry--United States--Case studies.
Four generations of talented,
visionary family - genius, sibling rivalry, betrayal; blood
feuds as spectacular as business triumphs. Cesare Mondavi's
sons, Robert and Peter, came to blows; Robert’s sons, Michael
and Timothy, battled with each other for control of company, led
to board coup, sale of company.
(Moosehead), Harvey Sawler (2008).
Last Canadian Beer: The Moosehead Story. (Halifax, Nova
Scotia: Nimbus Pub Ltd, 178 p.). Moosehead Breweries; ;Oland
family; brewing--Canada--history. Last of independent Canadian beer companies; Oland family's long tenure running one of Canada's most
popular breweries in face of increasing pressure from
international brew giants. Who are the they?; What has made them successful?; How will they
continue to keep Moosehead as independently owned family
business?
(Mountain Dew), Dick Bridgforth (2007).
Mountain Dew: The History. (North Charleston, SC:
Booksurge, 315 p.). Mountain Dew (Trademark)--History; Soft
drinks--United States--History; Soft drink industry--United
States--History.
(National Fruit Flavor Company Inc. - formed
in 1917), Mathew Paul Bonnifield; epilogue by Virgil Browne
(1976).
Oklahoma Innovator: The Life of Virgil Browne. (Norman,
OK: Published for the Oklahoma Heritage Association by the
University of Oklahoma Press, 240 p.). Browne, Virgil, 1877- ;
Soft drink industry--United States--History; Oklahoma City
(Okla.)--History. Company made Orange Squeeze (carbonated soft
drink).
(Nederburg), Phillida Brooke Simons (1992).
Nederburg: The First Two Hundred Years. (Cape Town, SA:
Struik Publishers, 231 p.). Nederburg (Winery); Stellenbosch
Farmers' Winery; Wine and wine making--South Africa--Cape
Town--History.
(H. R. Nicholson Company), Harry R. Nicholson,
Jr. (1996).
The House of Quality: The History of the H.R. Nicholson
Company, 1906-1996. (Baltimore, MD: Gateway Press, 120
p.). H.R. Nicholson Company--History; Soft drink
industry--United States--History; Carbonated beverage
industry--United States--History; Fruit juice industry--United
states--History; Cola drinks--United States--History.
(Niebaum-Coppola), Steve Kolpan
(1999).
A Sense of Place: An Intimate Portrait of the Niebaum-Coppola
Winery and the Napa Valley. (New York, NY: Routledge,
234 p.). Professor of Wine Studies and Gastronomy at Culinary
Institute of America. Wine and wine making--California--Napa
Valley; Wineries--California--Napa Valley.
(Nikka Whiskey Distilling Co. Ltd.), Olive
Checkland (2001).
Japanese Whisky, Scotch Blend. (Dalkeith, Scotland:
Scottish Cultural Press, 160 p.). Taketsuru, Masataka; Whiskey
industry--Japan; Nikka Whiskey Distilling Co. Ltd.
("Old Bushmills" Distillery), Alf McCreary
(1983).
Spirit of the Age: The Story of "Old Bushmills".
(Bushmills, Antrim, No. Ireland: "Old Bushmills" Distillery Co.
; [Belfast] : Distributed by Blackstaff Press, 232 p.). "Old
Bushmills" Distillery Company--History; Whiskey
industry--Northern Ireland--Bushmills--History.
(Pabst), Thomas C. Cochran (1975).
The Pabst Brewing Company: The History of an American Business.
(Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, 451 p. [Reprint 1948 ed.]).
Pabst Brewing Company, Milwaukee, Wis.
 Captain Frederick Pabst (http://images.wisconsinhistory.org/700002010001/0201000330-m.jpg)
Captain Frederick Pabst (http://images.wisconsinhistory.org/700002010001/0201000330-m.jpg)
(Pacific Western Brewing Co.), Jan-Udo Wenzel
(1993).
Ginter. (Prince George, BC: Caitlin Press, 196 p.).
Ginter, Ben; Businesspeople--Canada--Biography; Real estate
developers--British Columbia--Biography; Construction
industry--British Columbia--History--20th century; Brewing
industry--British Columbia--History--20th century; Prince George
(B.C.)--Biography.
(Panther Creek), Linda Kaplan (2005).
My First Crush: Misadventures in Wine Country.
(Guilford, CT: Lyon's Press, 224 p.). Wine and wine
making--Oregon--McMinnville--Miscellanea.
(Peet's), Andree Abecassis (1992). Peet's
Coffee & Tea: A History in Honor of Its Twenty-Fifth Birthday.
(Berkeley, CA: Peet's Coffee & Tea, 48 p.). Peet's Coffee & Tea,
Peet, Alfred; Coffee industry--United States.
(Pepsi), Milward W. Martin (1962).
Twelve Full Ounces. (New York, NY: Holt, Rinehart and
Winston, 136 p.). Pepsi-Cola Company.
 Roger A. Enrico -
Pepsico (http://www.pepsico.com/Annual-Reports/1996/images/1996/enrico.gif)
Roger A. Enrico -
Pepsico (http://www.pepsico.com/Annual-Reports/1996/images/1996/enrico.gif)
(Pepsi), Walter Mack with Peter Buckley
(1982).
No Time Lost. (New York, NY: Atheneum, 211 p.). Mack,
Walter; Pepsi-Cola Company--History; Businessmen--United
States--Biography.
(Pepsi), Roger Enrico and Jesse Kornbluth
(1986).
The Other Guy Blinked: How Pepsi Won the Cola Wars. (New
York, NY: Bantam, 280 p.). CEO, Pepsi. Pepsi-Cola Company;
Coca-Cola Company; Soft drink industry--United States.
(Pepsi), Rajendar Dara (1991). The Real
Pepsi, The Real Story. (New Delhi, India: R. Dara, 178 p.).
Pepsi Cola Company; Soft drink industry--India; International
business enterprises--India--Case studies.
(Pepsi), Bob Stoddard (1999).
Pepsi: 100 Years. (Los Angeles, CA: General Publishing
Corp. PepsiCo, inc.--History; Soft drink industry--United
States--History.
(Pepsi), Stephanie Capparell (2007).
The Real Pepsi Challenge: The Inspirational Story of Breaking
the Color Barrier in American Business. (New York, NY:
Free Press, 368 p.). Editor for the Wall Street Journal's
Marketplace Page. PepsiCo, inc.--Employees--Recruiting--History;
African American executives--United States--History; Cola
drinks--United States--Marketing--History; African American
consumers--United States--History. Group of African-American
businessmen -- twelve at its peak -- changed face of American
business by being among the first black Americans to work at
professional jobs in Corporate America, to target black
consumers as distinct market.
(Pernod Ricard), Paul Ricard (1983).
La Passion de Créer. (Paris, FR: A.Michel, 267 p.).
Ricard, Paul, 1909- ; Ricard (Firm)--History;
Businesspeople--France--Biography.
(Pernod Ricard), Marie-France Pochna (1996).
Paul Ricard: l'Homme Qui Se Ressemble. (Paris, FR:
P.A.U., 188 p.). Ricard, Paul, 1909- ; Ricard (Firm)--History;
Businesspeople--France--Biography; Pastis
industry--France--History.
(Pernod Ricard), Marie-Claude Delahaye (2008).
Pernod: Créateur de L'Absinthe.
(Auvers-sur-Oise FR: Musée de l'absinthe, 109 p.). Absinthe --
History; Pernod Ricard (Firm) -- History; Industrial history;
French alcoholic beverage.
(Pet Milk Company), Martin L. Bell (1962).
A Portrait of Progress, A Business History of Pet Milk Company
from 1885 to 1960. (St. Louis, MO: The Company, 199 p.).
Pet Milk Company.
(Pete's Brewing), Pete Slosberg (1998).
Beer for Pete's Sake: The Wicked Adventures of a Brewing
Maverick. (Boulder, CO: Siris Books, 258 p.). Slosberg,
Pete; Pete's Brewing Company; Brewers--United States--Biography.
(Poland Spring), David L. Richards (2005).
Poland Spring: A Tale of the Gilded Age, 1860-1900.
(Durham, NH: University of New Hampshire Press, 336 p.).
Assistant Director, Margaret Chase Smith Library (Northwood
University). Ricker family; Hiram Ricker & Sons;
Springs--Maine--Poland Spring--History; Resorts--Maine--Poland
Spring--History; Businessmen--Maine--Poland Spring--Biography;
Poland Spring (Me.)--History; Poland Spring (Me.)--Social life
and customs; Poland Spring (Me.)--Economic conditions; Poland
Spring (Me.)--Biography.
 Hiram Ricker - Poland Spring
(http://baharris.org/ historicpolandspring/Rickers/Hrickert.gif)
Hiram Ricker - Poland Spring
(http://baharris.org/ historicpolandspring/Rickers/Hrickert.gif)
(Redhook Ale Brewery), Peter Krebs (1998).
Redhook: Beer Pioneer. (New York, NY: Four Walls Eight
Windows, 208 p.). Redhook Ale Brewery--History;
Microbreweries--Washington (State)--Seattle.
(Republic of Tea), Mel Ziegler, Bill
Rosenzweig, Patricia Ziegler (1992).
The Republic of Tea: Letters to a Young Zentrepeneur.
(New York, NY: Doubleday, 314 p.). Republic of Tea (Firm); Tea
trade--Management--Case studies; Retail trade--Management--Case
studies; New business enterprises--Management--Case studies.
(John Reid & Co. ltd.), Hilary F. Reid (1969).
A Century in Commerce; The Story of John Reid & Co. Ltd.,
1869-1969. (Aukland, NZ: J. Reid & Co., Ltd., 86 p.).
John Reid & Co.--History; Wine and wine making--New
Zealand--Auckland.
(Roddy Manufacturing Company), Pat Roddy, Jr.
(1983).
75 Years of Refreshment. (Knoxville, TN: J.P. Roddy, 202
p.). Roddy Manufacturing Company--History; Coca-Cola
Company--History; Bottle industry--Tennessee--History; Soft
drink industry--Tennessee--History.
(Rum),Hugh Barty-King, Anton
Massel (1983).
Rum, Yesterday and Today. (London, UK: Heinemann, 264
p.). Rum.
(Rum), John J. McCusker (1989).
Rum and the American Revolution: The Rum Trade and the Balance
of Payments of the Thirteen Continental Colonies (New
York, NY: Garland Pub., 2 vols. (1,367 p.)). Rum industry--North
America--History--18th century; Balance of payments--Great
Britain--Colonies--History--18th century; United
States--History--Revolution, 1775-1783--Causes; United
States--History--Revolution, 1775-1783--Economic aspects.
(Rum), Frederick H. Smith (2005).
Caribbean Rum: A Social and Economic History.
(Gainesville, FL: University Press of Florida, 340 p.).
Anthropologist (College of William and Mary). Rum--Caribbean
Area--History; Rum--Social aspects--Caribbean Area;
Rum--Economic aspects--Caribbean Area. Rum's transformation: 1) small
colonial activity to 2) major export throughout Atlantic World
to 3) multi-billion dollar industry controlled by multinational
corporations.
(Rum), Wayne Curtis (2006).
And a Bottle of Rum: A History of the New World in Ten Cocktails.
(New York, NY: Crown Publishers, 304 p.). Contributing Editor to
Preservation magazine. Rum--North America--History;
Rum--Caribbean Area--History; North America--History; Caribbean
Area--History. Homely
spirit once distilled from the industrial waste of the exploding
sugar trade has managed to infiltrate every stratum of New World
society.
(Saint Louis Brewery), Tom Schlafly (2006).
A New Religion in Mecca: Memoir of a Renegade Brewery in St.
Louis. (St. Louis, MO: Virginia Pub. Co., 102 p.).
Founder of Schlafly Brewery in 1991 - city's first micro-beer in
the shadow. Saint Louis Brewery--History;
Microbreweries--Missouri--St. Louis--History; Beer
industry--Missouri--St. Louis; Brewing industry--Missouri--St.
Louis. 15th anniversary of
The Schlafly Tap Room, Schlafly Beer; 1991 - started city's
first micro-beer in shadow of Anheuser-Busch; took abandoned
warehouse in midtown St. Louis, turned it into one of nation's
most successful micro-brewers.
(Schweppes), Douglas A. Simmons (1983).
Schweppes, The First 200 Years. (London, UK: Springwood
Books, 160 p.). Schweppes (Firm)--History; Soft drink
industry--Great Britain--History.
 Johann Jacob Schweppe
(http://www.ginologist.com/Wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2009/03/j-j-schweppes.jpg)
Johann Jacob Schweppe
(http://www.ginologist.com/Wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2009/03/j-j-schweppes.jpg)
(Scottish and Newcastle), Berry Ritchie
(1999).
Good Company: The Story of Scottish and Newcastle.
(London, UK: James & James, 172 p.). Scottish and Newcastle;
Breweries--Great Britain--history.
(Seagram's), Peter C. Newman (1979).
King of the Castle: The Making of a Dynasty: Seagram's and the
Bronfman Empire. (New York, NY: Atheneum, 304 p.).
Distillers Corporation-Seagrams Ltd.--History; Capitalists and
financiers--Canada--History.
 Joseph E. Seagram -
Seagram's
(http://www.waterlooregionmuseum.com/media/4220/seagram-joseph-emm.jpg)
Joseph E. Seagram -
Seagram's
(http://www.waterlooregionmuseum.com/media/4220/seagram-joseph-emm.jpg)
 Samuel Bronfman
(http://particle.physics.ucdavis.edu/
Graphics/Canada/samuel_bronfman.jpg)
Samuel Bronfman
(http://particle.physics.ucdavis.edu/
Graphics/Canada/samuel_bronfman.jpg)
(Seagram's), Michael R. Marrus (1991).
Samuel Bronfman: The Life and Times of Seagram's Mr. Sam.
(Hanover, NH: University Press of New England, 551 p.).
Bronfman, Samuel, 1891-1971; Businessmen--Canada--Biography;
Whiskey industry--Canada--History.
(Seagram's), Edgar M. Bronfman (1998).
Good Spirits: The Making of a Businessman. (New York,
NY: Putnam, 248 p.). Bronfman, Edgar M., 1929- ; Seagram
Company--History; Executives--Canada--Biography; Liquor
industry--Canada--History; Conglomerate
corporations--Canada--History.
(Seagram's), Leo Kolber, L. Ian MacDonald
(2003).
Leo a Life: The Life and Times of a Man of Influence.
(Montreal, QU: McGill-Queen's University Press, 320 p.).
Chairman, Cemp Investments (Bronfman Family Trust), Cadiallac
Fairview Corporation.
(Seagram's), Nicholas Faith (2006).
The Bronfmans: The Rise & Fall of the Bronfmans of Seagram.
(New York, NY: Thomas Dunne Books, 352 p.). Former Senior Editor
(The Economist, London Sunday Times). Bronfman family; Seagram
Company; Distilling industries--Canada;
Businesspeople--Canada--Biography. Post-prohibition history of the
liquor industry.
(Schweppes), Douglas A. Simmons (1983).
Schweppes, The First 200 Years. (London, UK: Springwood
Books, 160 p.). Schweppes (Firm)--History; Soft drink
industry--Great Britain--History.
(Second Cup), Frank O'Dea and John Lawrence
Reynolds (2007).
When All You Have Is Hope. (Toronto, ON: Viking Canada,
256 p.). Founder, Second Cup. O'Dea, Frank; Second Cup; Coffee
industry--History; Coffee industry--Canada; Coffee--Social
aspects; Coffee shops--Social aspects. Rags-to-riches story of Frank
O'Dea, from destitute panhandler on streets of Toronto to
founder of Second Cup coffee chain, Canada's largest specialty
coffee retailer; message: HOPE, VISION, ACTION.
(Shiner Beer), Mike Renfro (2008).
Shine On: 100 Years of Shiner Beer Book. (Houston, TX:
Bright Sky Press, 192 p.). Shiner Beer; Breweries
--Texas--history. History of oldest independent brewery in
Texas; development, from improbable beginning of German and
Czech immigrants who founded brewery, to successes, struggles of
growing business, many times brand was good as dead; story of
beating the odds, tribute to independent, well-made beer.
(Philippe Simard & fils), Carl Beaulieu
(2004). Philippe Simard & Fils, Une Tradition Corporative.
(Chicoutimi, QC: Editions du patrimoine, 246 p.). Simard family;
Simard, Philippe, 1894-1982; Philippe Simard & fils--History;
Businessmen--Québec (Province)--Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean
Region--Biography; Business enterprises--Québec
(Province)--Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean Region--History;
Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean Region (Québec)--Biography.
(Smirnov), V.P. Smirnov; [redaktory-sostaviteli,
Aleksandr Nikishin i Kira Smirnova] (2004). Russkii Kharakter.
(Moskva, Russia: "Vagrius", 381 P.). Smirnov, V. P. (Vladimir
Petrovich); Smirnov, P. A. (Petr Arsen'evich); Smirnov (Firm);
Distillers--Russia--Biography; Vodka industry--Russia--History.
(Smirnov), Linda Himelstein (2009).
The King of Vodka: The Story of Pyotr Smirnov and the Upheaval
of an Empire. (New York, NY: Collins, 416 p.). Former
Silicon Valley bureau chief (BusinessWeek). Smirnov, P. A. (Petr
Arsenevich); Smirnov (Firm); Distillers --Russia --Biography;
Vodka industry --Russia --History. Humble serf who rose from
backrooms, side streets of 19th century Moscow, to create one of
most celebrated business empires world has ever known; bizarre coincidences prevented legacy
from oblivion.
(Soda), Lawrence Dietz (1973).
Soda Pop; The History, Advertising, Art, and Memorabilia of Soft
Drinks in America. (New York, NY: Simon & Schuster, 184
p.). Advertising specialties--Catalogs; Advertising--Carbonated
beverages.
(Soda), John R. Paul and Paul W. Parmalee
(1973).
Soft Drink Bottling: A History with Special Reference to
Illinois. (Springfield, IL: Illinois State Museum
Society, 121 p.). Bottling--Illinois--History; Soft drink
industry--Illinois--History; Industries--Illinois--History.
(Soda), Michael Karl Witzel and Gyvel
Young-Witzel (1998).
Soda Pop!: From Miracle Medicine to Pop Culture.
(Stillwater, MN: Town Square Books, 144 p.). Carbonated
beverages. Explosive growth of soda pop
around world, from miracle medicine to prominent role in
refreshment industry, daily staple and international commodity.
(Sokol Blosser Winery), Susan Sokol Blosser
(2006).
At Home in the Vineyard: Cultivating a Winery, an Industry, and
a Life. (Berkeley, CA: University of California Press,
236 p.). President of Sokol Blosser Winery, Oregon Wine Pioneer.
Blosser, Susan Sokol; Vintners--Oregon--Biography; Wine and wine
making--Oregon; Wine industry--Oregon.
How she fell in
love with vineyard, learned how to run it, ultimately achieved
vision of producing Pinot Noirs to rival those of Burgundy.
(Source Perrier), Nicolas Marty (2005).
Perrier, c’Est Nous!: Histoire de la Source Perrier et de Son
Personnel. (Paris, FR: Editions de l’Atelier, 245 p.).
Source Perrier (Firm)--History; Bottled water
industry--France--History; Source Perrier
(Firm)--Employees--History;. History of Perrier and its
workers from 1903 to 1990; interaction of French business and
labor in twentieth-century Languedoc.
(Starbucks), Howard Schultz and Dori Jones
Yang (1997).
Pour Your Heart into It: How Starbucks Built a Company One Cup
at a Time. (New York, NY: Hyperion, 351 p.). Starbucks
Coffee Company; Coffee industry--United States.
 Howard Schultz -
Starbucks
(http://www.businessweek.com/the_thread/brandnewday/archives/hschultz.jpg)
Howard Schultz -
Starbucks
(http://www.businessweek.com/the_thread/brandnewday/archives/hschultz.jpg)
(Starbucks), John Simmons. (2004).
My Sister's a Barista: How They Made Starbucks a Home from Home.
(London: Cyan, 188 p.). Director of Training and Brand Language
(The Writer). Starbucks Coffee Company; Brand name products --
Case studies.
(Starbucks), John Moore (2006).
Tribal Knowledge: Business Wisdom Brewed from the Grounds of
Starbucks Corporate Culture. (Chicago, IL: Kaplan Pub.,
264 p.). Former Retail Marketing Manager for Starbucks Coffee,
Former Director of National Marketing for Whole Foods Market.
Starbucks Coffee Company; Coffee industry--United States;
Coffee--United States--Marketing; Corporate culture--United
States; Organizational effectiveness--United States.
How Starbucks focused passionately
on details of customer experience.
(Starbucks), Dr. Joseph A. Michelli
(2006).
The Starbucks Experience: 5 Principles for Turning Ordinary into
Extraordinary. (New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 208 p.).
Founder of Lessons for Success. Starbucks Coffee Company;
Success in business--Handbooks, manuals, etc.
5 key leadership principles: 1) Make It Your Own; 2) Everything
Matters; 3) Surprise and Delight; 4) Embrace Resistance; 5)
Leave Your Mark.
(Starbucks), Karen Blumenthal (2007).
Grande Expectations: A Year in the Life of Starbucks’ Stock.
(New York, NY: Crown Business, 320 p.). Former Reporter (Wall
Street Journal). Starbucks Coffee Company; Stocks--United
States; Corporations--Valuation--United States.
Year of rapid store openings,
fancy new drinks, clever promotions; how players propel its
shares up and down; market's quirks, inner workings.
(Starbucks), Taylor Clark (2007).
Starbucked: A Double Tall Tale of Caffeine, Commerce, and
Culture. (New York, NY: Little, Brown, 304 p.). Staff
Writer for the Portland, Oregon, alt-weekly Willamette Week.
Starbucks Coffee Company; Coffee industry--History;
Coffee--Social aspects; Coffee shops--Social aspects; Corporate
culture--Case studies; International business
enterprises--United States--Case studies. How coffeehouse movement changed
everyday life, from evolving neighborhoods, workplaces to
shopping, socializing, self-medicating.
July 4, 2008 -
 (http://graphics8.nytimes.com/images/2008/07/04/business/starbuckslarge.jpg)
(http://graphics8.nytimes.com/images/2008/07/04/business/starbuckslarge.jpg)
(Starbucks), Kim Fellner (2008).
Wrestling with Starbucks: Conscience, Capital, Cappuccino.
(New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 283 p.). Starbucks
Coffee Company; Coffee industry --United States; Coffee --United
States --Marketing; Corporate culture --United States.
Corporation filled with contradictions:
employee-friendly processes, anti-union practices;
internationalist vision, longing for global dominance; community
individuality, cultural hegemony; profitable enough to please
Wall Street, principled enough to please social justice
advocates; forces that affect Starbucks's worth and worthiness;
compelling, unexpected look at Starbucks, global economy,
economic convictions, values.
(Starbucks), Bryant
Simon (2009).
Everything But the Coffee: Learning about America from Starbucks.
(Berkeley, CA, University of California Press.320 p.). Professor
of History and the Director of American Studies (Temple
University).Coffee United States; Coffeehouses United States;
Starbucks Coffee Company. How Starbucks' explosive success, rapid deflation
exemplify American culture; deeply felt American need for
predictability and class standing, community and authenticity; Starbucks' appeal lies in easily consumed identity
(not product itself).
(Starbucks), Howard Schultz and Joanne
Gordon (2011).
Onward: How Starbucks Fought for Its Life Without Losing Its
Soul. (Emmaus, PA: Rodale, 368 p.). Chairman,
President, and CEO of Starbucks; Former Writer and Contributing
Editor (Forbes). Schultz, Howard; Starbucks Coffee Company;
Coffee industry --United States; Coffee --United States
--Marketing; Organizational change --United States; Leadership
--United States.
2008 - Schultz, president and chairman of
Starbucks, returned as CEO 8 years after stepping down from
daily managing of company; how Starbucks again achieved
profitability, sustainability without sacrificing humanity; how
company struggled, recreated itself; maturing of brand and
businessman.
(Steward & Patteson), Terence R. Gourvish
(1987).
Norfolk Beers from English Barley: A History of Steward &
Patteson, 1793-1963. (Norwich, UK: University of East
Anglia, 206 p.). Steward & Patteson--History; Brewing
industry--Great Britain--History.
(Sun-drop Bottling Company), Edward L. Rankin, Jr.
(2004). A Century of Sodas,
1904-2004: The Story of Uncle Tommy and Margaret.
(Concord, NC: Concord Printing Co., 100 p.). King,
Margaret Towell, 1923-; Honeycutt, John Thomas,
1882-1964; Sun-drop Bottling Company --History;
Carbonated beverage industry --North Carolina --History;
Bottling --North Carolina --History.
(Sutter Home Winery), Kate Heyhoe and Stanley
Hock (2004).
Harvesting the Dream: The Rags-to-Riches Tale of the Sutter Home
Winery. (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 235 p.). Sutter Home
Winery--History; Wine and wine making--California--Napa
Valley--History; Wineries--California--Napa Valley--History.
(Taittinger), Claude Taittinger (1996).
Champagne par Taittinger. (Paris, FR: Stock, 156 p.).
Tattinger--history; Champagne (Wine).
(Tea Trade), J. M. Scott. (1965).
The Great Tea Venture. (New York, NY: Dutton, 203 p.).
Tea trade--History.
(Tea Trade), David R. MacGregor (1986).
The China Bird: The History of Captain Killick, and the Firm He
Founded, Killick Martin & Company. (London, UK: Conway
Maritime, 224 p, [2nd rev. ed.]). Killick, James, 1816-1889;
Killick Martin & Company.
(Tea Trade), Jason Goodwin (1991).
A Time for Tea: Travels Through China and India in Search of Tea.
(New York, NY: Knopf, 287 p.). Tea trade--History; Tea
trade--England--London--History; Tea trade--China--History; Tea
trade--India--History.
(Tea Trade), Paul J. Smith (1991).
Taxing Heaven's Storehouse: Horses, Bureaucrats, and the
Destruction of the Sichuan Tea Industry, 1074-1224.
(Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 489 p.). Tea
trade--China--Sichuan Sheng--History; Horse
industry--China--Sichuan Sheng--History;
Tea--Taxation--China--History; Cavalry horses--China--History;
China--History--Song dynasty, 960-1279.
(Tea Trade), Gangadhar Banerjee (1996).
Tea Plantation Industry, Between 1850 and 1992: Structural
Changes. (Guwahati, Assam: Lawyer's Book Stall, 540
p.). Tea trade --India --History.
(Tea Trade), Roy Moxham (2003).
Tea: Addiction, Exploitation, and Empire. (New York, NY:
Carroll & Graf, 271 p.). Tea trade--Great Britain--History.
(Tea Trade), Alan Macfarlane and Iris
Macfarlane (2004).
The Empire of Tea: the Remarkable History of the Plant That Took
Over the World. (New York, NY: Overlook Press, 308 p.).
Tea--History; Tea--Social aspects; Tea trade--History.
Tragic, liberating effects of
Camelia plant in history of civilization.
(Tea Trade), Beatrice Hohenegger (2006).
Liquid Jade: The Story of Tea from East to West. (New
York, NY: St. Martin’s Press, 320 p.). Guest Curator of a
Traveling Museum Exhibition on the History and Culture of Tea.
Tea--History; Tea--Social aspects; Tea trade--History.
Social, cultural aspects of tea -
western greed, eastern bliss.
(Tea Trade), G.D. Banerjee, Srijeet Banerjee
(2007).
Darjeeling Tea: The Golden Brew. (Lucknow, India:
International Book Distributing Co., 561 p.). Tea trade -- India
-- Darjeeling (District).
(Tea Trade), Gangadhar Banerjee, Srijeet
Banerji (2008). Tea Industry: A Road Map Ahead. (Delhi,
India: Abhijeet Publications, 564 p.). Deputy General Manager
cum Officer-in-Charge in NABARD Nagaland Regional Office;
freelance writer; Tea trade -- India; Tea -- India.
Overview of tea industry, botany of tea,
traces history of tea leaf, development tea industry during 1950
to 2007, dynamics of auction system in India and abroad, product
diversification.
(Tea Trade), Debabrata Mitra (2009).
Globalization and Industrial Relations in
Tea Plantations: A Study on Dooars Region of West Bengal.
(Delhi, India: Abhijeet Publications, 164 p.). Head, Department
of Management (University of North Bengal). Tea plantation
workers -- India -- Dooars; Industrial relations -- India --
Dooars; Globalization -- Economic aspects -- India -- Dooars.
(Tea Trade), Sarah Rose (2009).
For All the Tea in China: Espionage, Empire and the Secret
Formula of the World's Favourite Drink. (London, UK:
Hutchinson, 288 p.). Tea trade -- India.
True story of pirates, rebels, subterfuge, industrial espionage; how
Robert Fortune, Scottish gardener, botanist, plant hunter - spy, triumphed
over exotic, corrupt Empire; 1848 - hired by East
India Company to
steal closely guarded secrets of Chinese tea to enable East
Company to establish its own plantations in Himalayas of British
India; made clandestine trip to China; risked his life for
science, adventure, place among great plant explorers.
 Robert Fortune
- Tea Trade
(http://www.plantexplorers.com/explorers/images/Fortune02.giff)
Robert Fortune
- Tea Trade
(http://www.plantexplorers.com/explorers/images/Fortune02.giff)
(Tea Trade), Jason Lim (2010).
Linking an Asian Transregional Commerce in Tea: Overseas Chinese
Merchants in the Fujian-Singapore Trade, 1920-1960.
(Boston, MA: Brill, 252 p.). Postdoctoral Fellow in the
Department of History (National University of Singapore). Tea
trade -- China -- Fujian Sheng -- History -- 20th century; Tea
trade -- Singapore -- History -- 20th century.
State of tea
production in Fujian (vs. Sino-British trade, impact of
capitalism, modern technology on tea production in India and
Ceylon); overseas Chinese tea merchants, fluctuations of trade
during period of political instability in China; Sino-Japanese
War; decolonisation in Singapore; period of collectivisation in
China, Cold War.
(Tequila), Ana Guadalupe Valenzuela-Zapata and
Gary Paul Nabhan (2004).
Tequila: A Natural and Cultural History. (Tucson, AZ:
University of Arizona Press, 113 p.). Tequila
agave--Mexico--Jalisco; Tequila industry--Mexico.
(Tiger Beer), Jacky Tai (2008). Tiger Beer:
Distinctly Asian: Unmistakably World Class. (Tarrytown, NY:
Marshall Cavendish Corp., 173 p.). Former Branding Program
Manager with International Enterprise Singapore. Tiger
Beer--history; Beer industry -- Singapore -- History.
Humble beginnings in 1932 to
extraordinary growth, worldwide recognition; entered established
market on global scale.
(Tropicana Products Inc.), Sanna Barlow Rossi
(1986).
Anthony T. Rossi, Christian and Entrepreneur: The Story of the
Founder of Tropicana. (Downers Grove, IL: InterVersity
Press, 200 p.). Rossi, Anthony T.; Tropicana Products, Inc.;
Baptists--United States--Biography; Businesspeople--United
States--Biography.
(R. Twining and Company limited), Stephen H.
Twining (1956). The House of Twining, 1706-1956; Being a
Short History of the Firm of R. Twining and Co. Ltd., Tea and
Coffee Merchants. (London, UK: R. Twining, 115 p.). Twining
(R.) and Company limited. [from old catalog].
(TyPhoo), Ken Williams (1990).
The Story of TyPhoo and the Birmingham Tea Industry.
(Shropshire, UK: Quiller, 132 p.). TyPhoo.
(Vernor's), Lawrence L. Rouch (2003).
The Vernor's Story: From Gnomes to Now. (Ann Arbor, MI:
University of Michigan Press, 147 p.). President
(Studio3/Innovations). Vernor's (Firm) History; Soft drink
industry United States History.
(Vernor's), Keith
Wunderlich (2008).
Vernor’s Ginger Ale.
(Charleston, SC Arcadia Pub., 128 p.). Founder of
Vernor's Ginger Ale Collector's Club. Vernor’s (Firm)
--History --Pictorial works; Soft drink industry
--United States --History --Pictorial works. 1866 -
opened pharmacy in Detroit; small
back-room product to highly successful brand; from
pharmacy to factory, from entrepreneur to franchised
corporation.
(Veuve Clicquot Ponsardin), Tilar J. Mazzeo
(2008).
The Widow Clicquot: The Story of a Champagne Empire and the
Woman Who Ruled It. (New York, NY: HarperCollins, 288
p.). Assistant Professor of English (Colby College).
Clicquot-Ponsardin, Barbe-Nicole, 1777-1866; Vintners --France
--Champagne --Biography; Champagne (Wine) --History.
Barbe-Nicole
Clicquot Ponsardin, young widow who built Veuve Clicquot brand
and champagne empire, showed world how to live with style,
emerged a legend; became one of world's first great
businesswomen, one of richest women of her time.
 Barbe-Nicole Clicquot-Ponsardin
- Veuve Clicquot Ponsardin
(http://www.champagneardenne.pref.gouv.fr/var/sgar/storage/images/media/images/
portrait_de_la_veuve_clicquot_ponsardin/6317-1-fre-FR/portrait_de_la_veuve_clicquot_ponsardin_medium.jpg)
Barbe-Nicole Clicquot-Ponsardin
- Veuve Clicquot Ponsardin
(http://www.champagneardenne.pref.gouv.fr/var/sgar/storage/images/media/images/
portrait_de_la_veuve_clicquot_ponsardin/6317-1-fre-FR/portrait_de_la_veuve_clicquot_ponsardin_medium.jpg)
(Victoria Wine), Asa Briggs (1985).
Wine for Sale: Victoria Wine and the Liquor Trade, 1860-1984
(Chicago, Il: University of Chicago Press, 199 p.). Victoria
Wine (Firm)--History; Wine industry--Great Britain--History.
(Vodka), David Christian (1990).
Living Water: Vodka and Russian Society on the Eve of
Emancipation. (New York, NY: Oxford University Press,
447 p.). Vodka industry--Russia--History--19th century;
Vodka--Social aspects--Russia; Drinking of alcoholic
beverages--Russia--History--19th century; Russia--Social
conditions--1801-1917. Social, economic,
political role of vodka in 19th-century Russia; "Green Serpent"
first appeared in 16th-century Muscovy; became essential
ingredient in all working class celebrations (personal,
religious, commercial); 19th century - generated one third of
government revenue; importance of vodka trade to all aspects of
Russian life.
(Vodka), William Pokhlebkin ; translated by
Renfrey Clarke (1992).
A History of Vodka. (New York, NY: Verso, 222 p.).
Vodka--History; Vodka industry--Russia (Federation)--History.
Vodka means water in Russian.
(Watney Mann ltd.), H. Hurford Janes (1963).
The Red Barrel; A History of Watney Mann. (London, UK:
J. Murray, 226 P.). Watney Mann ltd.
(Welch's Grape Juice), William Chazanof
(1977).
Welch's Grape Juice: From Corporation to Co-operative.
(Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 407 p.). Welch Grape
Juice Company, inc.--History.
 Dr. Thomas Bramwell Welch
(http://www.welchs.com/images/allaboutwelchs/1869-100edit.gif)
Dr. Thomas Bramwell Welch
(http://www.welchs.com/images/allaboutwelchs/1869-100edit.gif)
(Whiskey), Ross Wilson (1970).
Scotch: The Formative Years. (London, UK: Constable, 502
p.). Whiskey industry--Scotland.
(Whiskey), Henry G. Crowgey
(1971).
Kentucky Bourbon; The Early Years of Whiskeymaking.
(Lexington, KY: University Press of Kentucky, 171 p.).
Whiskey--Kentucky--History; Distilling
industries--Kentucky--History.
(Whiskey), Michael Brander
(1975).
The Original Scotch: A History of Scotch Whisky From the
Earliest Days. (New York, NY: C. N. Potter, 149 p.).
Whiskey--Scotland--History.
(Whiskey), Ronald B. Weir
(1975). The History of the Malt Distillers' Association of
Scotland. (Elgin, Scotland: The Association, 177 p.). Malt
Distillers' Association of Scotland--History; Whiskey
industry--Scotland--History.
(Whiskey), Allen Andrews
(1977).
The Whisky Barons. (London, UK: Jupiter, 148 p.).
Whiskey industry--Great Britain--History; Distilling
industries--Great Britain--History.
(Whiskey), Margaret A. Kennedy
(1997).
The Whiskey Trade of the Northwestern Plains: A
Multidisciplinary Study. (New York, NY: P. Lang, 181
p.). Whiskey industry--Great Plains--History; Bison
industry--Great Plains--History; Fur trade--Great
Plains--History; Indians of North America--Alcohol use--Great
Plains--History; Indians of North America--Commerce--Great
Plains--History.
Final boom phase of
Indian trade economy on North America's northwestern plains
(1865 to 1875).
(Whiskey), Michael S. Moss, John R. Hume (2002).
The Making of Scotch Whisky. (Edinburgh, Scotland:
Canongate, 368 p. [rev. ed.]). Whiskey -- Scotland -- History;
Whiskey industry -- Scotland -- History.
(Whiskey), Iain Banks (2003).
Raw Spirit: In Search of the Perfect Dram. (London, UK:
Century, 368 p.). Banks, Iain, 1954- --Travel --Scotland;
Whiskey --Scotland --History; Whiskey industry --Scotland
--History; Distilleries --Scotland --History; Highlands
(Scotland) --Description and travel.
(Whiskey), F. Paul Pacult
(2005).
A Double Scotch: How Chivas Regal and The Glenlivet Became
Global Icons. (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 290 p.). Founding
Editor and Publisher of F. Paul Pacult's Spirit Journal – The
Quarterly Independent Guide to Distilled Spirits, Beers, and
Wines (now in its 15th year of publication). Glenlivet
Distillery--History; Chivas Brothers Limited--History; Seagram
Company; Whiskey industry--Scotland--History.
(Whiskey), Stuart Delves (2006).
Scotch Whisky: The Story of Scotland's Greatest Export.
(London, UK: Cyan Communications, 192 p.). Whiskey industry;
Whiskey -- Scotch; Whiskey industry -- Scotland.
Ways that marketing, advertising
served to establish dominance in whisky market, how drink
achieved exclusive role in beverage industry.
(Whitbread), The Company (1964).
The Story of Whitbread's. (Dunstable, UK: Whitbread, 54
p. [3rd ed.; orig. pub. 1947]). Whitbread.
(Whitbread), Berry Ritchie (1992).
An Uncommon Brewer: The Story of Whitbread, 1742-1992.
(London, UK: James & James, 144 p.). Whitbread, Samuel;
Whitbread Breweries; Beer industry -- Great Britain -- History.
(Whiteway's of Whimple), E. V. M. Whiteway
(1990).
Whiteway's Cyder: A Company History. (Newton Abbot, UK:
David & Charles, 160 p.). ; Alcoholic drinks Production History
England.
(Wine), Vincent P. Carosso
(1951).
The California Wine Industry, 1830-1895: A Study of the
Formative Years. (Berkeley, CA: University of California
Press, 241 p.). Wine and wine making--California.
(Wine), Hugh Barty-King (1977).
A Tradition of English Wine: The Story of Two Thousand Years of
English Wine made from English Grapes. (Oxford, UK:
Illustrated Press, 250 p.). Wine and wine
making--England--History.
(Wine), Nicholas Faith (1978).
The Winemasters of Bordeaux: The Inside Story of the World's
Greatest Wines. (New York, NY: Harper & Row, 328 p.).
Former Business Editor of The Sunday Times of London. Wine,
Winemaking.
(Wine), Leo A. Loubère (1978).
The Red and the White: A History of Wine in France and Italy in
the Nineteenth Century. (Albany, NY: State University of
New York Press, 401 p.). Wine industry--France--History; Wine
industry--Italy--History.
(Wine), Thomas Pinney (1989).
A History of Wine in America: From the Beginnings to Prohibition.
(Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 553 p.). William
M. Keck Distinguished Service Professor and Chairman of the
Department of English (Pomona College). Wine and wine
making--United States--History. America's
alluring promise of wine - baffled, begun, realized.
(Wine), James Conaway (1990).
Napa. (Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin, 529 p.). Wine
industry--California--Napa Valley--History; Napa Valley
(Calif.)--History.
(Wine) Leo A. Loubère (1990).
The Wine Revolution in France: The Twentieth Century.
(Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 288 p.). Wine
industry--France; Wine industry--Technological
innovations--France; Viticulture--France;
Viticulture--Technological innovations--France.
(Wine), Simon Loftus (1994).
Puligny-Montrachet: Journal of a Village in Burgundy.
(New York, NY: Holt, 308 p.). Wine and wine
making--France--Puligny-Montrachet; Puligny-Montrachet
(France)--History.
(Wine), Thomas Brennan (1997).
Burgundy to Champagne: The Wine Trade in Early Modern France.
(Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, 350 p.).
Associate Professor in the Department of History (U.S. Naval
Academy). Wine industry--France--History.
(Wine), Lewis Perdue (1999).
The Wrath of Grapes: The Coming Wine Industry Shakeout and How
To Take Advantage of It. (New York, NY: Spike, 253 p.).
Wine industry--United States; Wine as an investment--United
States.
(Wine), William F. Heintz (1999).
California's Napa Valley: One Hundred Sixty Years of Wine Making.
(San Francisco, CA: Scottwall Associates, 500 p.). Leading Wine
Historian in Northern California. Wine and wine
making--California; Napa Valley (Calif.) --History.
Comprehensive history of wine industry in Napa Valley: earliest settlers; pylloxera infestation; gradual
development of fine quality wines; Prohibition, Depression; great boom in California wines after
World War II; great names.
(Wine), Stephen Brook (2001).
Bordeaux: People, Power, and Politics. (London, UK: M.
Beazley, 224 p.). Wine and wine
making--France--Bordeaux--History--20th century; Wine
industry--France--Bordeaux--History--20th century.
(Wine), James Conaway (2002).
The Far Side of Eden: New Money, Old Land, and the Battle for
Napa Valley. (Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin, 365 p.).
Wine industry--California--Napa Valley--History; Napa Valley
(Calif.)--History; Napa Valley (Calif.)--Social conditions; Napa
Valley (Calif.)--Economic conditions.
(Wine), Donald Kladstrup, Petie Kladstrup
(2002).
Wine and War: The French, the Nazis, and the Battle for France's
Greatest Treasure. (New York, NY: Broadway, 304 p.).
Network Television News Correspondent; Freelance Writer. World
War, 1939-1945 --Underground movements --France; Wine and wine
making --France --History --20th century; World War, 1939-1945
--France; France --History --German occupation, 1940-1945.
1940 - France fell to Nazis; almost immediately German
army began campaign of pillaging French wine (represented
a living for nearly 20% of France's population);
winemakers mobilized to oppose their occupiers; undertook ingenious, daring measures to save cherished
crops, bottles; how men and
women risked their lives for cause that meant saving heart, soul
of France as much as protecting its economy; central role wine
has long played in France’s military campaigns; based on three
years of research, interviews with survivors.
(Wine), Alan Deutschman (2003).
A Tale of Two Valleys: Wine, Wealth and the Battle for the Good
Life in Napa and Sonoma. (New York, NY: Broadway Books,
p.). Wine industry--Social aspects--California--Sonoma Valley;
Wine industry--Social aspects--California--Napa Valley;
Wealth--Social aspects--California--Sonoma Valley;
Wealth--Social aspects--California--Napa Valley; Social
conflict--California--Sonoma Valley; Social
conflict--California--Napa Valley; Sonoma Valley
(Calif.)--Social life and customs; Napa Valley (Calif.)--Social
life and customs; Sonoma Valley (Calif.)--Rural conditions; Napa
Valley (Calif.)--Rural conditions.
(Wine), Kolleen M. Guy (2003).
When Champagne Became French: Wine and the Making of a National
Identity. (Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University
Press, 245 p.). Assistant Professor of History (University of
Texas at San Antonio). Champagne (Wine)--History.
 (http://graphics8.nytimes.com/images/2008/06/14/business/0614-biz-web-CHAMPAGNEmap.gif) (http://graphics8.nytimes.com/images/2008/06/14/business/0614-biz-web-CHAMPAGNEmap.gif)
(Wine), Charles L. Sullivan; foreword by Paul
Draper (2003).
Zinfandel: A History of a Grape and Its Wine. (Berkeley,
CA: University of California Press, 224 p.).
Grapes--California--History; Viticulture--California--History;
Wine and wine making--California--History.
Definitive history of Zinfandel -
from Austria to East Coast of U.S. in 1820s, to Gold Rush
California, through early days of state's wine industry; ups and
downs of grape's popularity, two great mysteries: myth of Agoston Haraszthy's role in importing Zinfandel, heated
controversy over relationship between California Zinfandel and
Italian Primitivo.
(Wine), William Echikson
(2004).
Noble Rot: A Bordeaux Wine Revolution. (New York, NY:
Norton, 288 p.). Brussels Bureau Chief (Dow Jones Newswires).
Wine industry--France; Wine and wine making--France.
(Wine), Victor W. Geraci
(2004).
Salud!: The Rise of Santa Barbara's Wine Industry.
(Reno, NV: University of Nevada Press, 250 p.). Associate
Director - Food and Wine Historian, University of California,
Berkeley - Regional Oral History Office. Wine and wine making
--California --Santa Barbara County --History; Wine industry
--California --Santa Barbara County --History. 1965 -
Soil and
climatic studies indicated that Santa Ynez and Santa Maria
valleys of Santa Barbara County, California, offered suitable
conditions for growing grapes; 2004 - California is one of
world's major wine producers, Santa Barbara County contributes
significantly to volume, renowned quality of this wine
production.
(Wine), Christopher Campbell
(2005).
The Botanist and the Vintner: How Wine Was Saved for the World.
(Chapel Hill, NC: Algonquin Books of Chapel Hill, 360 p.).
Grapes--Diseases and pests--France--History--19th century;
Viticulture--France--History--19th century.
(Wine), Don and Petie Kladstrup (2005).
Champagne: How the World's Most Glamorous Wine Triumphed Over
War and Hard Times. (New York, NY: William Morrow, 304
p.). Former Foreign Correspondent for ABC and CBS News; Former
Protocol Officer for the U.S. Ambassador to UNESCO. Champagne
(Wine)--History. How this
sparkling wine became a symbol of glamour, good times,
celebration.
(Wine), Thomas Pinney (2005).
A History of Wine in America: From Prohibition to the Present.
(Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 532 p.). William
M. Keck Distinguished Service Professor Emeritus and Former
Chairman of the Department of English (Pomona College). Wine and
wine making--United States--History; Wine industry--United
States--History. Definitive account of winemaking in the United States.
(Wine), George M. Taber (2005).
Judgment of Paris: California vs. France and the Historic 1976
Paris Tasting That Revolutionized Wine. (New York, NY:
Scribner, 336 p.). Paris Correspondent (Time Magazine). Wine
tasting--France--Paris--History--20th century; Wine
industry--France--History--20th century; Wine
industry--California--History--20th century; Wine and wine
making--France--History--20th century; Wine and wine
making--California--History--20th century. True story of the legendary Paris
Tasting of 1976 - revolutionary impact on the world of wine.
(Wine), Dan Ginsburg (2006).
The Art and Business of Champagne. (Jefferson, NC:
McFarland, 242 p.). President and Majority Owner of Champagne de
Meric, the only American-owned winery in Champagne. Champagne
(Wine); Sparkling wines; Wine and wine making; Wine industry.
Inside look—from the vineyard to the marketplace—at the world of
champagne.
(Wine), Hugh Johnson (2006).
A Life Uncorked. (Berkeley, CA: University of California
Press, 384 p.). Johnson, Hugh, 1939- ; Wine writers--Biography;
Food writers--Biography; Horticultural writers--Biography.
Tasting, cellaring,
choosing, understanding, comparing, buying wine; its
personal pleasures, lures, and mysteries.
(Wine), Ann B. Matasar (2006).
Women of Wine: The Rise of Women in the Global Wine Industry.
(Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 265 p.).
Professor of Business Emerita at the Walter E. Heller College of
Business Administration (Roosevelt University). Women in the
wine industry. Women's
increasingly influential role in the wine industry,
traditionally a very male-dominated domain.
(Wine), Steve Heimoff; foreword by H. William
Harlan (2007).
New Classic Winemakers of California: Conversations with Steve
Heimoff.
(Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 300 p.). West
Coast editor for Wine Enthusiast.
Vintners--California--Biography; Wine and wine
making--California--History. Survey of multibillion-dollar
business with global reputation, oral history of contemporary
California winemaking; personalities, intellects, philosophies,
passions of individual winemakers, opinions on recent
high-alcohol vintages, globalization, "cult" wine phenomenon.
(Wine), Photographs by George Rose;
Essay by Rod Smith (2007).
The Art of Terroir: A Portrait of California Vineyards.
(San Francisco, CA: Chronicle Books, 112 p.).
Photojournalist; Writer. Vineyards--California,
Northern--Pictorial works; Vineyards in art; Landscape
photography--California, Northern; California,
Northern--Pictorial works. Phenomenon of mystical
melding of light, water, soil, air, human touch that
creates a wine unique to its origin - through
photographs showcasing seasonal beauty of Northern
California wine country.
(Wine), George M. Taber (2007).
To Cork or Not To Cork: Tradition, Romance, Science, and
the Battle for the Wine Bottle. (New York, NY:
Scribner, 278 p.). Cork industry; Wine and wine making.
History of wine corks (vs.
plastic, glass, screwcap, some other type of closure) to
seal a bottle of wine; pivotal moments in
production, storage, consumption of wine; portrait of
intriguing controversy.
(Wine), Richard Mendelson (2008).
From Demon to Darling: A Legal History of Wine in
America. (Berkeley, CA: University of California
Press, 320 p.). Wine Law Specialist at Dickenson,
Peatman & Fogarty in Napa, CA, and Lecturer at the
University of California at Berkeley School of Law,
Directs Program on Wine Law and Policy. Wine and wine
making --Law and legislation --United States --History.
American wine law from colonial
times to
present; how current laws shape wine industry (pricing and taxation, licensing,
appellations, health claims and warnings, labeling, domestic and international commerce);
how lives, livelihoods affected by rise,
fall of social movements.
(Wine), Benjamin Wallace (2008).
The Billionaire’s Vinegar: The Mystery of the World’s
Most Expensive Bottle of Wine. (New York, NY:
Crown Publishers, 336 p.). Wine and wine
making--Miscellanea. Most elaborate con since
Hitler diaries; 1787 bottle of Château Lafite Bordeaux,
supposedly owned by Thomas Jefferson, sold for $156,000
at Christie’s of London auction in 1985 to member of
Forbes family; rumors about bottle arose; history of
wine, vivid accounts of subterranean European
laboratories where old vintages are dated, of
Jefferson’s colorful, wine-soaked days in France.
(Wine), Vivienne Sosnowski (2009).
When the Rivers Ran Red: An Amazing Story of Courage and Triumph
in America's Wine Country. (New York, NY: Palgrave, 256
p.). Editorial Director of Examiner newspapers. Vintners
--California, Northern --History --20th century; Wine --Social
aspects --California, Northern --History --20th century;
Vintners --California, Northern --Biography; Prohibition
--California, Northern; Prohibition --United States; Violence
--California, Northern --History --20th century; California,
Northern --History --20th century; California, Northern --Social
conditions --20th century. How
California's Italian-American wine families struggled to keep
their business, industry alive during 14 years of Prohibition
(1919-1933); turned to struggle, subterfuge; Prohibition took
effect three months after one of greatest California grape
harvests of all time; violence, chaos descended on Northern
California; Federal agents spilled thousands of gallons of wine
in rivers and creeks, gun battles erupted on dark country roads,
local law enforcement officers, sympathetic to winemaking
neighbors, found ways to run circles around intruding
authorities; surviving Prohibition meant facing impossible
decisions for state's winemaking families: give up idyllic way
of life their families had known for generations or break aw to
enable their wine businesses, their livelihood to survive; how
ordinary people fought to protect beautiful and timeless culture
in hills and valleys of wine country.
(Wine), Lorri Hathaway and Sharon Kegerreis (2010).
The History of Michigan Wines: 150 Years of Winemaking Along the
Great Lakes. (Charleston, SC: History Press, 160 p.).
Wine and wine making --Michigan --History; Wine and wine making
--Great Lakes Region (North America) --History; Vineyards
--Michigan --History; Vintners --Michigan --Biography; Wineries
--Michigan --Directories. Joseph Sterling ignited Michigan's
first viable wine region in 1800s along Lake Erie; how Detroit
River was used for bootlegging during Prohibition; how raid on
red wine in Upper Peninsula generated national headlines, how
Michigan became first to repeal; Michigan - a leading wine
producer through 1960s; second most agriculturally diverse
state.
(Wine), MJ Daspit, Eric Weisinger (2011).
Rogue Valley Wine. (Charleston, SC: Arcadia
Publishing, 128 p.). Rogue Valley, OR -- history; Wine and wine
making --Oregon --History. 1850 - Peter Britt, of Jacksonville,
brought grapevine cuttings from California to create Valley View
Vineyard; 1890 - Southern Oregon State Board of Agriculture
forecast Rogue Valley to rival "the castled
Rhine, the classical vales of Italy and the sunny slopes of
France"; 1916 - Prohibition (law in Oregon four years
before rest of country), killed nascent industry; 1970s -
Americans discovered passion for wine, reestablished winegrowing
and winemaking in Southern Oregon's Rogue Valley; pear orchards
converted to vineyards, winemaking in boutique wineries began, thrived.
(Wine), Eric D. Lehman and Amy Nawrocki (2011).
A History of Connecticut Wine: Vineyard in Your Backyard.
(Charleston, SC: The History Press, 128 p.). University of
Bridgeport professors Wine and wine making --Connecticut
--History; Vineyards --Connecticut --History.
Industry’s history
- number of varieties thrive (pinot gris, chardonnay, cabernet
franc, cayuga white, st. croix); intricacies of region's local
blends, vintners, tasters.
(Wine), David Darlington (2011).
An Ideal Wine: One Generation's Pursuit of Perfection--and
Profit--in California. (New York, NY: Harper, 352
p.). Wine and wine making --California --History.
Wine rush of 1970s; sales of wine exceeded
beer, number of vineyards and wineries began in California;
parallel paths of two men: 1) Leo McCloskey founded Enologix to
help wineries produce successful commercial product (vineyards
send grapes to Enologix, uses chemical analysis to advise
customers on quality of grapes, quality of wines that such
grapes might produce; 2) Randall Grahm, winemaker.
(Wine), Mike Veseth (2011).
Wine Wars: The Curse of the Blue Nun, The Miracle of Two Buck
Chuck, and the Revenge of the Terroirists. (Lanham,
MD: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, 244 p.). Robert G.
Albertson Professor of International Political Economy
(University of Puget Sound). Wine industry; Globalization
--Economic aspects. How globalization,
market forces are changing way wine is made, sold, consumed,
perceived; globalization pushed back borders of wine world,
created complex, inter-connected market (Old World and New World
wines, producers compete head to head; power, taste at stake):
Who will call shots in wine market of future? Who will set
price? Whose palate will prevail? Whose idea of wine will reign
supreme?
(Wine Advocate), Elin McCoy (2005).
The Emperor of Wine: The Rise of Robert M. Parker, Jr.
and the Reign of American Taste. (New York, NY:
ECCO, 304 p.). Wine and Spirits Columnist (Bloomberg).
Parker, Robert M., 1947- ; Wine industry--United
States--Biography. King of wine criticism.
 Robert M. Parker - Wine Advocate
(http://graphics8.nytimes.com/images/2006/08/13/business/yourmoney/13rate.3.190.jpg)
Robert M. Parker - Wine Advocate
(http://graphics8.nytimes.com/images/2006/08/13/business/yourmoney/13rate.3.190.jpg)
(Yakima Brewing Company), Bert Grant,
with Robert Spector (1998).
The Ale Master: How I Pioneered America's Craft Brewing
Industry, Opened the First BrewPub, Bucked Trends, and
Enjoyed Every Minute of It. (Seattle, WA:
Sasquatch Books, 142 p.). Grant, Bert, 1928- ;
Brewers--United States--Biography.
(Yuengling), Mark A. Noon (2005).
Yuengling: A History of America's Oldest Brewery.
(Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Co., Inc., 221 p.).
Yuengling, D. G. (David Gottlieb), 1806-1877; Yuengling
(Firm);
Microbreweries--Pennsylvania--Pottsville--History;
Breweries--United States--History; Brewing
industry--United States--History.
(Yuengling), Robert A. Musson, M.D. (2010).
Brewing Beer Since 1829: A Pictorial Saga of the D. G. Yuengling
& Son Brewing Company of Pottsville, Pennsylvania.
(Medina, OH: Zepp Publications, 40 p.). Vein Surgeon. D. G.
Yeungling & Son Brewing Company; beer -- history.
More than 180
years of brewing by six generations of Yuengling family; how
company went from barely staying alive in 1970s (made 100,000
barrels of beer each year for limited clientele in mountains of
eastern Pennsylvania coal country) to making 2,000,000 barrels a
year today in three breweries, with customer base all along East
Coast, moving westward.
Judith M. Bennett (1996).
Ale, Beer and Brewsters in England: Women's Work in a Changing
World, 1300-1600. (New York, NY: Oxford University
Press, 260 p.). Professor of History (University of North
Carolina at Chapel Hill). Women brewers--England--History;
Women--England--History--Middle Ages, 500-1500.
1300 - women brewed, sold most of ale drunk in England; 1600 -
industry largely controlled by men; how, when, why brewing
ceased to be woman's trade, became trade of men; new light on
effects of early capitalism on status of women's work.
Francis H. Chapelle (2005).
Wellsprings: A Natural History of Bottled Spring Waters.
(New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 279 p.).
Hydrologist at the U.S. Geological Survey. Bottled water
--United States --History. Drinking water --United
States; Water-supply --United States.
History, science
of subsurface water; history of bottled water industry
in America from beginnings in Europe hundreds of years
ago to present; how geologic conditions vary throughout
country, affect kinds, quality of bottled
water; how bottled water industry uses natural
history, perceived health benefits of
spring waters, to market products.
Philip J. Cook (2007).
Paying the Tab: The Costs and Benefits of Alcohol Control.
(Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 278 p.). Professor
of Public Policy and Economics (Duke University).
Alcoholism--Government policy--United States; Alcoholism--United
States--Prevention; Alcoholic beverages--Taxation--United
States. First comprehensive analysis of alcohol abuse; history
of attempts to "legislate morality," overlooked lessons from
Prohibition, rise of Alcoholics Anonymous; higher alcohol excise
taxes, other supply restrictions are effective and underutilized
policy tools that can cut abuse, preserve pleasures of moderate
consumption.
Anne Cooper Funderburg (2002).
Sundae Best: A History of Soda Fountains. (Bowling
Green, OH: Bowling Green State University Popular Press, 232
p.). Soda fountains--United States--History.
William Grimes (1993).
Straight Up or on the Rocks: A Cultural History of American
Drink. (New York, NY: Simon & Schuster, 193 p.).
Reporter (New York Times). Cocktails; Alcoholic
beverages--United States--History.
Yuantao Guo (2006).
Global Big Business and the Chinese Brewing Industry.
(New York, NY: Routledge, 240 p.). Brewing industry--China;
International business enterprises; Big business.
Relationship between big
business, competition, state intervention in context of
developing economies, in relation to Chinese brewing industry.
Lorri Hathaway and Sharon Kegerreis (2010).
The History of Michigan Wines: 150 Years of Winemaking Along the
Great Lakes. (Charleston, SC: History Press, 160 p.).
Wine and wine making --Michigan --History; Wine and wine making
--Great Lakes Region (North America) --History; Vineyards
--Michigan --History; Vintners --Michigan --Biography; Wineries
--Michigan --Directories. Joseph Sterling ignited Michigan's
first viable wine region in 1800s along Lake Erie; how Detroit
River was used for bootlegging during Prohibition; how raid on
red wine in Upper Peninsula generated national headlines, how
Michigan became first to repeal; Michigan - a leading wine
producer through 1960s; second most agriculturally diverse
state.
Alan Jenkins; with a foreword by Cledwyn
Hughes (1970).
Drinka Pinta: The Story of Milk and the Industry That Serves It.
(London, UK: Heinemann, 242 p.). Milk trade--Great Britain.
Fiftieth anniversary of National Milk Publicity Council.
Philip A. Pfeiffer (1998).
Pensacola’s Soda Water Legacy, 1837-1998.
(Pensacola, FL: Pfeiffer Printing Co., 94 p.).
Carbonated beverages --Florida --Pensacola --History
--19th century; Carbonated beverages --Florida
--Pensacola --History --20th century.
Evelyne Resnick (2008).
Wine Brands: Success Strategies for New Markets, New Consumers
and New Trends. (New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan, 256
p.). Co-founder of ReSMO. Wine industry --Marketing; Wine and
wine making. New era for wine marketers:
peers trust peers; top-down messaging losing ground, bottom-up
buzz gaining power; e-marketing to reach niche markets, measure
consumption patterns of entire market (for first time), adjust
quickly to behaviors.John J. Riley (1958).
A History of the American Soft Drink Industry; Bottled
Carbonated Beverages, 1807-1957. (Washington,
DC: American Bottlers of Carbonated Beverages, 302 p.).
Carbonated beverages.
Elizabeth Royte (2008).
Bottlemania: How Water Went on Sale And Why We Bought It.
(New York, NY: Bloomsbury, 256 p.). Bottled water
industry--Social aspects; Bottled water--Social aspects.
Commercialization of drinking water; second to soda, on verge of
becoming most popular beverage in country; people, machines,
economies, cultural trends that bring it from nature to
supermarkets.
Teresa da Silva Lopes (2007).
Global
Brands: The Evolution of Multinationals in Alcoholic Beverages.
(New York, NY: Cambridge University Press, 272 p.). Senior
Lecturer in the School of Business and Management (Queen Mary,
University of London). Alcoholic beverage industry;
International business enterprises; Brand name products.
How
world's largest multinationals in alcoholic beverages achieved
global leadership; predominant corporate governance structures
for firms' marketing-based industries; why these firms form
alliances with direct competitors. beverages.
Tom Standage (2005).
A History of the World in Six Glasses. (Toronto, ON:
Doubleday Canada, 320 p.). Technology Correspondent (The
Economist). Beverages; World History.
Dave Thomas and Bob Marchant (1997). When
Milk Came in Bottles: A History of Toronto Dairies. (Port
Hope, ON: Cowtown Publishers, 254 p.). Dairy products
industry--Ontario--Toronto--History;
Dairying--Ontario--Toronto--History; Dairy
plants--Ontario--Toronto--History; Milk bottles--Collectors and
collecting--Ontario--Toronto.
Donald Yates (2003).
Ginger Beer & Root Beer Heritage 1790 to 1930.
(Homerville, OH: Donald Yates Publishers, 356 p.).
Carbononated beverages -- history; ginger beer -- history;
root beer -- history.
________________________________________________________
Business History Links
American Hop Museum
http://www.americanhopmuseum.org/
The museum chronicles the history of the American Hop industry
from its early days in the New England colonies to the rapid
expansion into California and ultimately the Pacific Northwest.
First colonists introduced hops, grew it on
Manhattan Island as early as 1607. Only hop museum dedicated to
showcasing the history of the obscure perennial vine bearing the
botanical name Humulus lupulus.
Beverage Digest
Http://Www.Beverage-Digest.Com
Newsletter and information
service provides comprehensive news
and data on the global non-alcoholic beverage industry.
California Wine
Industry Interviews, The Bancroft Library
http://bancroft.berkeley.edu/ROHO/wine.html
Oral histories on the California wine industry -
autobiographical interviews with persons who have contributed
significantly to the development of California and the West.
Cider Museum
http://www.cidermuseum.co.uk/
History of cider making - how the apples were milled and pressed
and how the resulting juice was fermented to produce cider. Set
in a former cider making factory, visitors can explore original
cider champagne cellars and view cidermaking equipment, a
cooper's workshop and a vat house. Listen to oral history
recordings and view 19th century watercolours of cider apples
and perry pears and appreciate the delicately engraved
collection of English lead crystal cider glasses dating from the
18th century onwards.
The Coffee Science Information Centre
http://www.cosic.org/
Celebrating the drink that Bach referred to as "lovelier than a
thousand kisses," the Web site of the Coffee Science Information
Centre has a variety of sections relating different material on
the work of the Centre and general information about this
occasionally maligned beverage. The prime goal of the Coffee
Science Information Centre is "to provide accurate, balanced and
consistent information to all audiences across Europe who have
an interest in coffee, caffeine and health." Specifically,
different sections of the site deal with coffee and health,
world coffee events, and a brief essay on coffee throughout
history. The site also contains links to different scientific
reports that refute certain commonly misconceptions about
coffee, including the idea that prolonged coffee ingestion will
lead to extreme dehydration. This site will be of great interest
to those with a strong affinity for coffee and also for those
interested in current scientific research on caffeine.
Coors Visitor Centre & The Museum of
Brewing
http://www.coorsvisitorcenter.co.uk/
Formerly the Bass Museum, the Coors Visitor Centre houses the
UK's premier museum dedicated to brewing "The Museum of
Brewing", offering a unique blend of living heritage - brings
together a unique collection of artefacts and memorabilia
tracing the fascinating history of the brewing industry. Visit
the Shire Horse Stables, explore the Museum Micro Brewery,
authentic Cooperage, vintage vehicle collection and working
stationary steam engine plus lots more. And there's plenty for
children to enjoy too, including Virtual Burton, a unique
interactive touch-screen exhibit which introduces a cast of
virtual characters from the town census year of 1881.
Dr. Pepper Museum and Free Enterprise
Institute
Http://Www.Drpeppermuseum.Com
The mission of the Dr Pepper Museum and Free Enterprise
Institute, a non-profit organization, is to educate and
entertain the general public through the collection,
preservation, interpretation, and exhibition of objects relevant
to the history of the soft drink industry, and through that
example, the free enterprise system.
The Great Brands &
Champagne Houses
http://www.maisons-champagne.com/traduction/ english/index_gb.php
Aware of the numerous risks in their activity and concerned to
advance together using their common knowledge, the Champagne
Houses have always encouraged a "team spirit". This is the
origin of the sharing out of the fruits of their activity
between shareowners, vine-growers, employees and local
communities, with the continual need to respect the customers
who insist that their pleasure remain affordable.
Growing Up in the
Wine Industry
http://marketplace.publicradio.org/shows/2006/11/16/
AM200611162.html
Transcript and audio of a 2006 radio interview with E.&J. Gallo
Winery president Joseph Gallo "about learning the family
business from Ernest and Julio, and passing it on." Also
includes a brief history of this California winery, which "has
earned a reputation for being a pioneer and tastemaker, from
being the first company to introduce screw-cap bottles in the
1940s to being one of the first wine producers to advertise."
From American Public Media.
History of Beer
http://www.beerhistory.com/
A concise timeline of beer history by Prof. Linda Raley, Texas
Tech University.
International Coffee Organization (ICO)
http://www.ico.org
Statistics on the coffee trade, covering prices, imports and
exports, and production. Also features reports on the
international coffee market, background information about coffee
plants and coffee-making methods, and information about the
economics of the coffee industry. The ICO is an
intergovernmental organization for coffee that was set up under
the auspices of the United Nations. Subjects: Coffee industry;
Coffee.
Museum of the American Cocktail
http://www.kingcocktail.com/motac.htm
Non-profit museum and tourist attraction that celebrates and
preserves a rich aspect of American culture; the
two-hundred-year-old American cocktail. Museum will discover,
collect, and preserve materials pertaining to the history of the
American Cocktail and its influence on the world's beverage
industry.
Museum of Beverage
Containers
Http://Www.Gono.Com/Vir-Mus/Museum.Htm
The world's largest collection of beverage containers and
advertising. Featuring Coke, Budweiser and 100's more.
National Brewery Centre
http://www.nationalbrewerycentre.co.uk/
Celebrates Burton upon Trent's proud brewing heritage and it's
influence on brewing techniques throughout the world; evolution
of brewing techniques, from ancient times to modern day. There
are hundreds of exhibits and rare artefacts on display, plus a
dazzling holographic-style show using the age-old 'Peppers
Ghost' illusion and a variety of multi-media presentations to
bring the story to life.
Root Family Museum
http://www.moas.org/Americana.html
Features one of the largest Coca-Cola memorabilia collections in
the world; every conceivable item relating to the bottling,
advertising and consumption of Coca-Cola in their collection,
the Root family has amassed one of the most historically
important anthologies of the American soft drink on which their
family fortune was founded. Through a selection of glass bottles
representing the changing trends in bottling over the decades,
this exhibit chronicles the transition of Root Family Glass
Works into Associated Coca-Cola, the largest independent
Coca-Cola bottler in the nation.
Soda Museum
http://www.sodamuseum.bigstep.com/homepage.html
Collection of historical information about soda and soda
collecting.
Sonoma County Wine Library
http://www.sonoma.lib.ca.us/wine/index.html
Special service and collection of the Sonoma County Library, the
collection comprises 5,000 books on wine and related subjects,
subscriptions and backfiles to over 80 wine-related periodicals.
Important Events
in the History of Tea
http://hjem.get2net.dk/bnielsen/teachronology.html
Temperance &
Prohibition
http://prohibition.osu.edu
Collection of essays, images, and other material on the history
of prohibition in the U.S., "a measure designed to reduce
drinking by eliminating the businesses that manufactured,
distributed, and sold alcoholic beverages." Covers the U.S.
brewing industry, the Woman's Crusade of 1873-74, the
Anti-Saloon League, the Prohibition Party, and related topics.
From The Ohio State University Department of History and the
Goldberg Program for Excellence in Teaching.
The Wine and Wine
Industry Collection
http://www.csupomona.edu/~library/LibraryInfo/special/
WineIndCol.html
A special collection at Cal Poly Pomona which documents and
honors the Southern California wine industry, including
wine-related organizations and events. Information is collected
on California wine, with emphasis on Southern California. Also
included is information on regional wineries, wine selling, wine
competitions, wine organizations, and wine events. Business
and organization archives, archival records relating to
festivals and events, documentation on the history of
viticulture and winemaking in Southern California, family
histories and reminiscences of local growers and vintners, and
archives of individual wineries are collected. Geographic areas
include Los Angeles, Orange, Riverside, San Bernardino, San
Diego, Santa Barbara, and Ventura Counties.
Wine Industry Oral History
http://libweb.sonoma.edu/regional/subject/wineoral.html
Sonoma State University Library's North Bay Regional Collection
provides access to a wide range of information about the North
Bay counties of Lake, Marin, Mendocino, Napa, Solano and Sonoma.
Wine Institute
http://www.wineinstitute.org/
Public policy advocacy association of California wineries. Wine
Institute brings together the resources of 715 wineries and
affiliated businesses to support legislative and regulatory
advocacy, international market development, media relations,
scientific research, and education programs that benefit the
entire California wine industry. The Mission of the Wine
Institute is to initiate and advocate state, federal and
international public policy to enhance the environment for the
responsible consumption and enjoyment of wine.

|

